Understanding High Stock Market Valuations: Insights From BofA
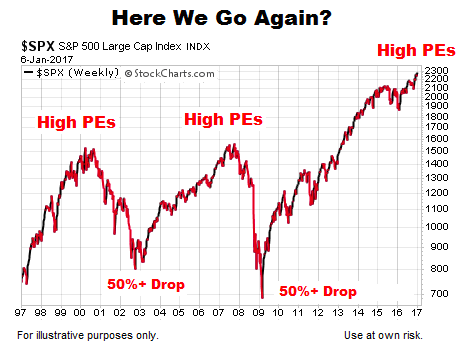
Table of Contents
BofA's Current Market Outlook and Valuation Metrics
BofA's overall sentiment on current market valuations often shifts, so checking their most recent reports is crucial. While it's impossible to definitively state their current stance without access to their most up-to-date research, they frequently utilize a range of metrics to assess market health and potential risks.
-
Key valuation metrics used by BofA: BofA analysts typically consider a range of valuation metrics, including the Price-to-Earnings ratio (P/E), the cyclically adjusted price-to-earnings ratio (Shiller PE), and Tobin's Q. These metrics help gauge whether the market is overvalued or undervalued relative to historical averages and earnings potential.
-
BofA's assessment of these metrics relative to historical averages: BofA's analysis often compares current valuation metrics to their historical averages. High deviations from historical norms might signal potential overvaluation, increasing the risk of a correction. Conversely, low valuations could suggest undervaluation and potential upside. (Note: Specific data points would need to be obtained from current BofA reports.)
-
Specific sectors BofA flags as overvalued or undervalued: BofA's research frequently highlights specific sectors that are perceived as overvalued or undervalued based on their valuation metrics and future growth prospects. For example, they might point to high growth tech stocks as potentially overvalued in a period of rising interest rates or suggest that certain value sectors are undervalued based on their earnings potential.
-
Relevant data points and charts from BofA reports: (This section would ideally include charts and graphs from publicly available BofA reports illustrating their valuation assessments. Due to the dynamic nature of market data, this cannot be included here.)
Factors Contributing to High Stock Market Valuations
Several factors contribute to periods of high stock market valuations. BofA's analysis likely considers the interplay of these elements:
-
Impact of low interest rates on valuations: Low interest rates generally fuel higher stock valuations. When interest rates are low, the opportunity cost of investing in stocks is reduced, making them more attractive compared to bonds or other fixed-income instruments. This increases demand and pushes prices higher.
-
Role of quantitative easing and its effect on market liquidity: Quantitative easing (QE) policies, where central banks inject liquidity into the financial system, can inflate asset prices, including stocks. Increased liquidity makes it easier for investors to buy assets, driving up demand and valuations.
-
Contribution of strong corporate earnings growth: Periods of robust corporate earnings growth can support higher stock valuations. Strong earnings justify higher price-to-earnings ratios as investors are willing to pay more for companies generating substantial profits.
-
Influence of technological innovation and its effect on investor sentiment and future growth expectations: Breakthroughs in technology often generate excitement and optimistic future growth expectations, leading investors to bid up stock prices. The potential for disruptive technologies to reshape industries can create a positive feedback loop.
-
Other factors: Geopolitical events, inflation expectations, and overall investor sentiment play significant roles in influencing market valuations. BofA’s analysis would likely account for these dynamic factors.
Potential Risks Associated with High Valuations
While high valuations can signal future growth, they also present significant risks:
-
Vulnerability to interest rate hikes and inflation: Rising interest rates typically lead to lower stock valuations. Higher rates increase borrowing costs for companies, reduce corporate earnings, and make bonds more attractive relative to stocks. Inflation erodes purchasing power and can dampen future earnings growth.
-
Risk of a market correction or significant downturn: High valuations can make markets more vulnerable to corrections or even crashes. When investor confidence wanes, a sharp sell-off can occur, leading to significant price declines.
-
Potential for asset bubbles in specific sectors: Certain sectors might experience speculative bubbles, where prices are driven far beyond their fundamental value. This can lead to a sharp decline if the bubble bursts.
-
Implications for long-term investors versus short-term traders: High valuations might present challenges for long-term investors, who might face reduced returns or increased risk. Short-term traders, on the other hand, might attempt to profit from market volatility.
-
"Red flags" BofA might have identified: (This section would require access to current BofA research to identify specific "red flags" they might be highlighting in their analysis.)
BofA's Investment Strategies in a High Valuation Environment
Navigating a high-valuation environment requires careful consideration of risk and reward. BofA's suggested strategies likely involve:
-
Suggested portfolio diversification techniques: Diversification across asset classes (stocks, bonds, real estate, etc.) and sectors reduces the overall risk of a portfolio.
-
Sectors BofA might recommend for investment (and why): BofA might suggest investing in sectors they deem undervalued or possessing strong growth prospects despite the overall high market valuations.
-
Strategies for mitigating risk in a high-valuation market: Strategies might include reducing overall equity exposure, focusing on high-quality, dividend-paying stocks, or employing hedging strategies to protect against market declines.
-
Potential hedging strategies to protect against market declines: Hedging strategies, like options or inverse ETFs, can help mitigate losses during market downturns.
-
Importance of long-term investment planning: Maintaining a long-term investment horizon helps investors weather market fluctuations and potentially benefit from the long-term growth of the market.
Conclusion
Understanding high stock market valuations is crucial for informed investing. BofA's analyses offer valuable insights into the complex interplay of factors driving valuations, the potential risks involved, and strategies to mitigate those risks. They often highlight key valuation metrics, contributing factors like low interest rates and quantitative easing, and potential threats such as inflation and interest rate hikes. Remember that these are complex issues with no easy answers. By staying updated on BofA's analyses and other market insights, investors can make more strategic decisions regarding their portfolios. Continue your research on understanding high stock market valuations and consult with a financial advisor for personalized guidance.

Featured Posts
-
 Recent Obituaries Local Residents Who Passed Away
May 13, 2025
Recent Obituaries Local Residents Who Passed Away
May 13, 2025 -
 Soaring Bike Thefts In Amsterdam A New Record High For The Netherlands
May 13, 2025
Soaring Bike Thefts In Amsterdam A New Record High For The Netherlands
May 13, 2025 -
 Eva Longorias Hair Transformation Before And After Sun Kissed Highlights
May 13, 2025
Eva Longorias Hair Transformation Before And After Sun Kissed Highlights
May 13, 2025 -
 Russias Arctic Shadow Fleet Renewed Activity And Growing Concerns
May 13, 2025
Russias Arctic Shadow Fleet Renewed Activity And Growing Concerns
May 13, 2025 -
 Persipura Jayapura Dominasi Rans Fc 8 0 Di Playoff Liga 2 Kokoh Di Puncak Grup K
May 13, 2025
Persipura Jayapura Dominasi Rans Fc 8 0 Di Playoff Liga 2 Kokoh Di Puncak Grup K
May 13, 2025
