Understanding Ontario's $14.6 Billion Deficit: Tariffs And Economic Challenges
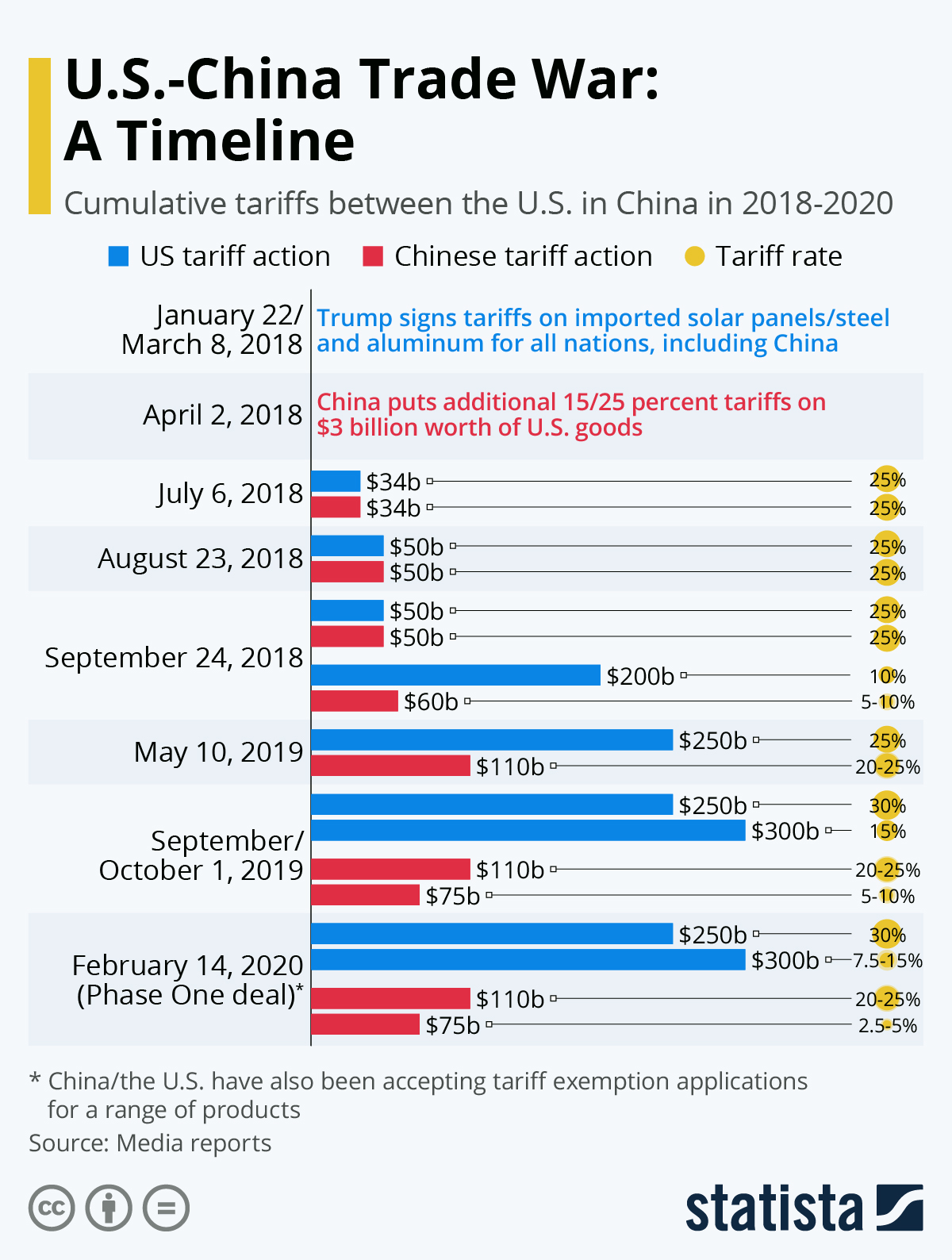
Table of Contents
The Role of Tariffs in Exacerbating Ontario's Fiscal Situation
The imposition of tariffs, both domestically and internationally, has significantly worsened Ontario's fiscal situation. These trade barriers have had a ripple effect throughout the provincial economy, impacting businesses and consumers alike.
Impact of Trade Wars and Retaliatory Tariffs on Ontario Businesses
Trade wars and retaliatory tariffs have dealt a heavy blow to several key Ontario industries.
- Automotive Manufacturing: The automotive sector, a cornerstone of Ontario's economy, has been particularly hard hit by tariffs imposed during recent trade disputes. Increased costs for imported parts and reduced export demand have led to plant closures and job losses.
- Agriculture: Ontario's agricultural producers have also faced significant challenges due to tariffs on exports, leading to reduced market access and lower prices for their products.
- Steel and Aluminum: Tariffs on steel and aluminum have increased input costs for various manufacturing sectors, impacting their competitiveness and profitability.
These tariffs increased production costs, reduced export opportunities, and ultimately contributed to a decline in manufacturing jobs and overall economic output within the province. The impact of these Ontario tariffs is measurable in lost revenue and increased unemployment. Data from [insert source – e.g., Statistics Canada] could illustrate the precise scale of this negative impact. Understanding the consequences of retaliatory tariffs and their impact on the export decline is crucial for formulating effective economic policies.
Increased Costs for Consumers Due to Tariffs
Tariffs don't just affect businesses; they directly impact consumers through higher prices.
- Everyday Goods: The increased cost of imported goods, from clothing and electronics to food and building materials, directly impacts consumer prices.
- Inflation: These tariff-induced price increases contribute to overall inflation, eroding the purchasing power of Ontarians and dampening consumer spending.
The impact of tariffs on consumers is a reduction in disposable income and a decrease in overall economic activity. The rising cost of living, fueled in part by tariffs, further exacerbates the financial pressures on families and individuals across Ontario.
Beyond Tariffs: Other Economic Challenges Contributing to the Deficit
While tariffs play a significant role, other economic factors contribute to Ontario's substantial deficit.
The Impact of the Global Economic Slowdown on Ontario's Revenue
The global economic slowdown has had a direct impact on Ontario's tax revenues.
- Decreased Tax Revenue: Reduced corporate profits and lower personal incomes due to the economic downturn have resulted in a significant decline in provincial tax revenue.
- Interconnected Economy: Ontario's economy is deeply intertwined with the global economy, making it vulnerable to international economic fluctuations.
The impact of this global recession and the resulting economic slowdown on tax revenue decline underscores the need for robust economic diversification strategies. The interconnectedness of the Ontario economy with global markets highlights the inherent risks associated with external economic shocks.
Increased Government Spending and Program Costs
Rising government spending in key areas has also contributed to the deficit.
- Healthcare: The aging population and increasing demand for healthcare services have led to escalating healthcare costs.
- Education: Investments in education, while crucial for long-term economic growth, represent a significant portion of government spending.
- Social Programs: Social safety net programs, such as welfare and disability support, are essential but also costly.
These increased expenditures in government spending, healthcare costs, education funding, and social programs are crucial for social well-being but demand careful fiscal management to avoid exacerbating the deficit.
Demographic Shifts and Aging Population
Ontario's aging population presents significant fiscal challenges.
- Healthcare Burden: An aging population places an increasing strain on the healthcare system, requiring greater investment in long-term care and other health services.
- Pension Costs: Rising pension obligations for an aging workforce add to the financial burden on the government.
Understanding demographic trends, including the aging population and its impact on the healthcare burden and pension costs, is critical for developing sustainable long-term fiscal strategies.
Potential Solutions and Strategies for Addressing the Deficit
Addressing Ontario's deficit requires a multifaceted approach that combines fiscal responsibility with strategic investments in economic growth.
Government Spending Review and Efficiency Improvements
A comprehensive review of government spending and implementation of efficiency improvements are crucial.
- Cost-Cutting Measures: Identifying areas for streamlining operations and eliminating redundancies can release significant funds.
- Debt Reduction: Implementing strategies to reduce government debt is essential for long-term fiscal sustainability.
The pursuit of fiscal responsibility and government efficiency through effective cost-cutting measures is fundamental to tackling the province's debt.
Economic Diversification and Job Creation Initiatives
Investing in economic diversification and job creation initiatives is paramount for long-term fiscal health.
- Innovation: Investing in research and development, fostering innovation, and supporting emerging industries can stimulate economic growth.
- Infrastructure Investment: Modernizing infrastructure is vital for attracting investment and creating jobs.
- Education: Investing in education and skills development ensures a skilled workforce capable of adapting to the changing economic landscape.
Strategies for economic diversification and job creation, focused on innovation and infrastructure investment, are key to generating economic growth and expanding the tax base.
Understanding and Addressing Ontario's $14.6 Billion Deficit
Ontario's $14.6 billion deficit is a complex issue stemming from a confluence of factors, including tariffs, a global economic slowdown, increased government spending, and demographic shifts. Understanding these interconnected challenges is crucial for developing effective solutions. Key takeaways emphasize the need for responsible fiscal management, investment in economic growth, and addressing the long-term impacts of an aging population. Addressing this significant deficit requires a sustained commitment to fiscal responsibility, economic diversification, and strategic investment in Ontario's future. Stay informed about government initiatives and continue the conversation to help shape a brighter economic future for Ontario.

Featured Posts
-
 Fanatics Your Source For Boston Celtics Gear During Their Back To Back Finals Run
May 17, 2025
Fanatics Your Source For Boston Celtics Gear During Their Back To Back Finals Run
May 17, 2025 -
 Fortnite Refund Indicates Upcoming Cosmetic System Changes
May 17, 2025
Fortnite Refund Indicates Upcoming Cosmetic System Changes
May 17, 2025 -
 Seattle Mariners Vs Cincinnati Reds Game Prediction And Best Odds
May 17, 2025
Seattle Mariners Vs Cincinnati Reds Game Prediction And Best Odds
May 17, 2025 -
 Nba Crew Chief Acknowledges Missed Call Cost Pistons Game Against Knicks
May 17, 2025
Nba Crew Chief Acknowledges Missed Call Cost Pistons Game Against Knicks
May 17, 2025 -
 The Geopolitics Of Rare Earths A Looming Cold War
May 17, 2025
The Geopolitics Of Rare Earths A Looming Cold War
May 17, 2025
