Understanding The Conclave: Electing The Head Of The Catholic Church
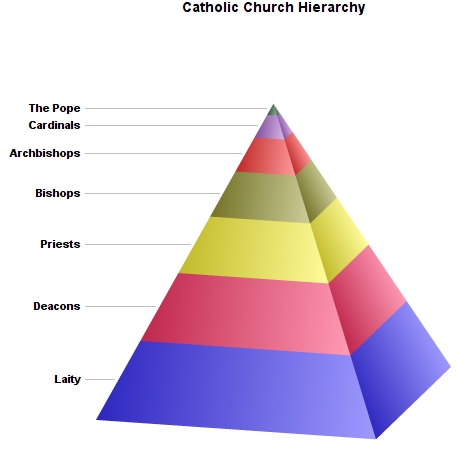
Table of Contents
The History and Evolution of the Conclave
The history of Papal elections is a fascinating journey, marked by both tumultuous periods and gradual refinements aimed at ensuring a fair and orderly selection of the Pope. Early Papal elections were often characterized by political maneuvering, bribery, and even violence. The lack of formal procedures frequently led to protracted and contentious processes.
- Early Papal elections: These were often chaotic, influenced heavily by powerful families and factions within the Church. The selection process lacked transparency, making it vulnerable to corruption.
- Introduction of formal procedures: Over time, the need for a more structured approach became apparent. Formal procedures were gradually introduced to enhance transparency and minimize the influence of external pressures. These early attempts, however, were not always completely successful.
- Key reforms in the 20th and 21st centuries: Significant reforms to the Papal conclave rules have occurred in recent centuries, particularly in the 20th and 21st centuries, aiming to streamline the process, enhance secrecy, and prevent undue influence. These reforms reflect the evolving needs of the Church in a globalized world.
- Significant historical conclaves: The conclave of 1268, which lasted nearly three years, stands out as a stark example of the challenges faced in earlier centuries. In contrast, the relatively swift 2005 Conclave, which elected Pope Benedict XVI, showcases the efficiency of the modernized process. Studying these historical Papal elections offers valuable context. Related keywords include: Papal election history, Papal election reform, history of the papacy.
The Participants in the Conclave: Cardinals and their Role
The Conclave is exclusively the domain of the cardinal electors. These individuals, chosen by the Pope, hold a unique position within the Catholic Church. Their eligibility to participate in the Conclave is a matter of meticulous consideration.
- Criteria for Cardinal Electors: Only cardinals under the age of 80 are eligible to participate in the Papal election process. This age limit ensures that the electors are physically and mentally capable of undertaking the demanding task.
- Role and responsibilities of the cardinals: During the Conclave, cardinals bear significant responsibility. They are entrusted with maintaining absolute secrecy, ensuring the orderly conduct of the proceedings, and engaging in prayerful deliberation to select the most suitable candidate.
- The significance of the College of Cardinals: The College of Cardinals is a body of high-ranking clergy appointed by the Pope. Its members are responsible for advising the Pope and electing his successor.
- Number of cardinal electors: The number of cardinal electors varies, depending on the number of cardinals under 80 at the time of the vacancy.
- Maintaining secrecy and order: The cardinals take an oath of secrecy, pledging to maintain the confidentiality of the deliberations. The Camerlengo plays a crucial role in this, managing the sede vacante period.
- The role of the Camerlengo during the sede vacante period: The Camerlengo, a high-ranking cardinal, acts as a caretaker of the Church during the sede vacante period, which is the time between the death of a Pope and the election of his successor. Related keywords include: Cardinal electors, College of Cardinals, Camerlengo, Sede Vacante.
The Conclave Process: From Beginning to End
The Conclave itself is a carefully orchestrated process, steeped in tradition yet adapted to ensure efficiency and fairness. From the moment the sede vacante is declared, a series of events unfold leading to the announcement of the new Pope.
- Beginning of the sede vacante: The death or resignation of the Pope marks the start of the sede vacante. Immediately, preparations for the Conclave begin.
- Preparation of the Sistine Chapel: The Sistine Chapel is meticulously prepared to host the Conclave. Security measures are heightened, and the chapel is furnished to accommodate the cardinals.
- The scrutiny (voting process): The core of the Conclave lies in the scrutiny, a series of secret ballots cast by the cardinals. Strict procedures are followed to maintain absolute secrecy.
- Importance of secrecy and rules surrounding communication: Communication with the outside world is strictly limited, ensuring the cardinals can deliberate without external influence.
- Mechanics of the voting process: Ballots are cast, counted, and then burned in a stove. The smoke that emerges signals the outcome of each ballot.
- The significance of the white smoke signal: White smoke signifies the election of a new Pope, while black smoke indicates that no candidate has achieved the required majority.
- The formal announcement of the newly elected Pope (Habemus Papam!): Once a candidate receives the necessary two-thirds majority, the announcement is made from the balcony of St. Peter's Basilica, with the iconic phrase "Habemus Papam!" Related keywords include: Sistine Chapel, scrutiny, papal election process, white smoke, Habemus Papam.
The Symbolism and Significance of the Conclave
Beyond its practical aspects, the Conclave is rich in symbolism, reflecting the spiritual and historical significance of the event.
- The spiritual significance of the election process: The Conclave is viewed as a deeply spiritual event, a time of prayer and discernment aimed at choosing a leader guided by the Holy Spirit.
- The symbolism of the white smoke and its worldwide impact: The white smoke, a simple visual signal, has become an internationally recognized symbol of hope and anticipation. It signifies the culmination of the Conclave and the start of a new era for the Catholic Church.
- The symbolism of the location (Sistine Chapel): The Sistine Chapel, famous for its artistic masterpieces, provides a powerful backdrop for this momentous occasion.
- The importance of the Conclave in upholding Church traditions: The Conclave is central to maintaining the continuity and authority of the Catholic Church, ensuring a smooth transition of leadership. Related keywords include: Papal symbolism, Catholic traditions, religious rituals, Church governance.
Conclusion
The Conclave, a process centuries in the making, is far more than a simple election; it's a pivotal moment in the life of the Catholic Church. Understanding its history, participants, procedures, and symbolism offers invaluable insight into the leadership transition within this global faith. From the tumultuous early Papal elections to the refined procedures of the modern Conclave, the process reflects the enduring efforts to ensure the selection of a Pope who can effectively guide the Church. To further your understanding of this fascinating process, delve deeper into the history of the Papal Conclave, research the complexities of the Election of the Pope, explore the intricacies of Catholic Church leadership, and investigate the rich history found in Conclave history by consulting resources such as the Vatican website and reputable theological publications.

Featured Posts
-
 Major Xrp Whale Accumulates 20 Million Tokens Market Analysis
May 07, 2025
Major Xrp Whale Accumulates 20 Million Tokens Market Analysis
May 07, 2025 -
 Who Wants To Be A Millionaire Celebrity Special Analyzing The Celebrity Contestants Strategies
May 07, 2025
Who Wants To Be A Millionaire Celebrity Special Analyzing The Celebrity Contestants Strategies
May 07, 2025 -
 Zendayas Half Sisters Shocking Cancer Claim A Plea For Help
May 07, 2025
Zendayas Half Sisters Shocking Cancer Claim A Plea For Help
May 07, 2025 -
 Zasluzhennoe Priznanie Krikunov O Meste Ovechkina V Zale Slavy Iihf
May 07, 2025
Zasluzhennoe Priznanie Krikunov O Meste Ovechkina V Zale Slavy Iihf
May 07, 2025 -
 The Design Of Hawkgirls Wings Isabela Merceds Organic Approach
May 07, 2025
The Design Of Hawkgirls Wings Isabela Merceds Organic Approach
May 07, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Glen Powells The Running Man Transformation Fitness And Character
May 08, 2025
Glen Powells The Running Man Transformation Fitness And Character
May 08, 2025 -
 The Thunder Vs The National Media A Heated Confrontation
May 08, 2025
The Thunder Vs The National Media A Heated Confrontation
May 08, 2025 -
 The Long Walk Trailer A Stephen King Approved Dark Thriller
May 08, 2025
The Long Walk Trailer A Stephen King Approved Dark Thriller
May 08, 2025 -
 First Trailer Hunger Games Directors New Dystopian Horror Film Based On Stephen King
May 08, 2025
First Trailer Hunger Games Directors New Dystopian Horror Film Based On Stephen King
May 08, 2025 -
 Dispute Erupts Between Okc Thunder And National Media
May 08, 2025
Dispute Erupts Between Okc Thunder And National Media
May 08, 2025
