Understanding The Link Between Federal Debt And Mortgage Rates
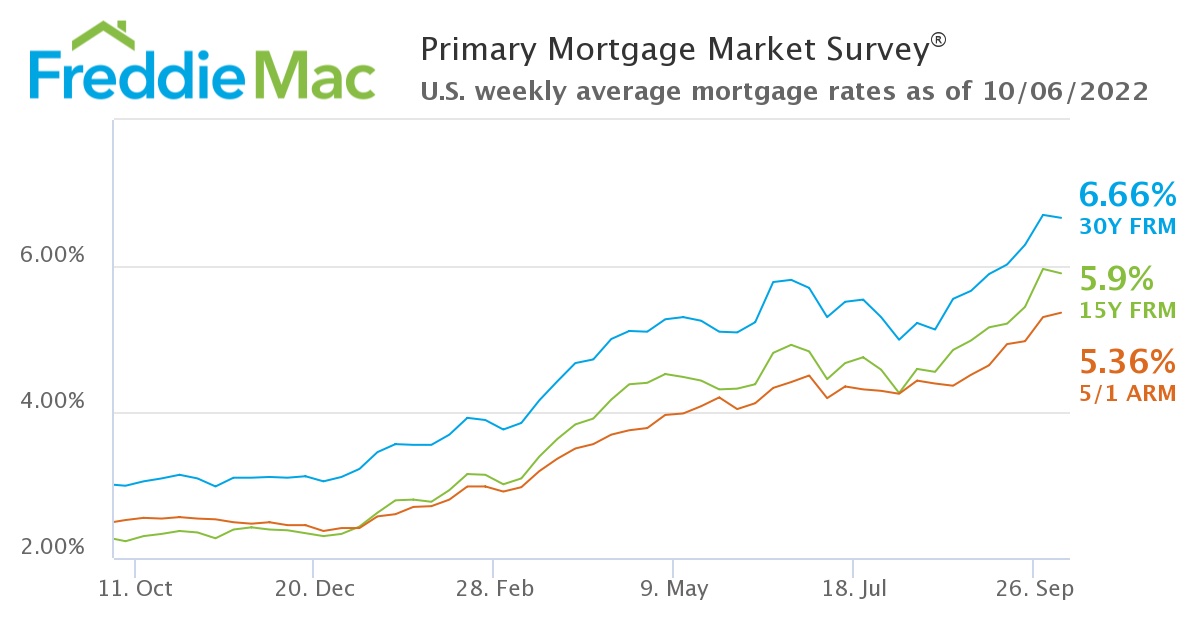
Table of Contents
How Federal Debt Influences Interest Rates
The level of federal debt significantly influences interest rates, including those for mortgages. This influence operates primarily through two key mechanisms: government borrowing and inflationary pressures.
The Role of Government Borrowing
The U.S. government frequently borrows money to finance its spending. This borrowing primarily occurs through the issuance of Treasury bonds and notes. These bonds are sold at auctions, with the interest rate determined by the interplay of supply and demand.
- Treasury Bonds and Auctions: When the government needs to borrow, it sells Treasury bonds. The more bonds it issues, the greater the supply of loanable funds. High demand for these bonds drives up prices, pushing down yields (interest rates). Conversely, increased supply of bonds relative to demand drives yields higher.
- Impact on Interest Rates: Increased government borrowing competes with private sector borrowing for available funds. This increased demand pushes up interest rates across the board, impacting not only Treasury yields but also mortgage rates, corporate bonds, and other loan products. The higher the federal debt, the greater the potential for increased borrowing and, consequently, higher interest rates.
Inflationary Pressures
High levels of federal debt can contribute to inflationary pressures. When the government borrows heavily, it often increases the money supply through increased government spending or directly by creating money.
- Increased Money Supply and Inflation: An increase in the money supply without a corresponding increase in the production of goods and services can lead to inflation – a general increase in the price level.
- Federal Reserve Response: The Federal Reserve (the Fed), the central bank of the United States, monitors inflation closely. To combat inflation spurred by high federal debt, the Fed typically raises interest rates. Higher interest rates make borrowing more expensive, cooling down the economy and reducing inflationary pressures. This, in turn, leads to higher mortgage rates.
The Federal Reserve's Response to Federal Debt
The Federal Reserve plays a crucial role in managing the economy's response to high federal debt and resulting inflation.
Monetary Policy and Interest Rates
The Fed uses monetary policy tools to influence interest rates. The most important of these is the federal funds rate – the target rate that banks charge each other for overnight loans.
- Influencing Mortgage Rates: While the Fed doesn't directly set mortgage rates, its actions heavily influence them. Changes in the federal funds rate ripple through the financial system, affecting the yields on Treasury bonds (particularly the 10-year Treasury yield, a key benchmark for mortgage rates).
- Balancing Act: The Fed faces a challenging balancing act. Raising interest rates to combat inflation can stifle economic growth and potentially lead to job losses. Lowering interest rates to stimulate growth can exacerbate inflation if the economy is already overheating.
Quantitative Easing and its Effects
In periods of economic crisis, the Fed may employ quantitative easing (QE). This involves purchasing large quantities of government bonds and mortgage-backed securities.
- Bond Purchases and Mortgage Rates: By purchasing these securities, the Fed injects liquidity into the financial system, driving down long-term interest rates, including mortgage rates.
- Short-Term and Long-Term Effects: While QE can provide short-term relief by lowering borrowing costs, its long-term effects are more complex and debated. It can contribute to inflation if not carefully managed.
Other Factors Affecting Mortgage Rates
While federal debt and the Fed's response are significant factors, other economic forces also influence mortgage rates.
Economic Growth and Consumer Confidence
The overall health of the economy significantly impacts mortgage rates independently of federal debt.
- GDP Growth, Unemployment, and Consumer Spending: Strong economic growth, low unemployment, and robust consumer spending typically lead to higher demand for loans, which can push mortgage rates upward.
- Strong Economy, Higher Rates: A booming economy can increase inflationary pressures, prompting the Fed to raise interest rates, thus affecting mortgage rates.
Global Economic Conditions
International economic factors influence U.S. mortgage rates.
- Global Interest Rates and Currency Fluctuations: Changes in global interest rates and currency fluctuations can affect investor confidence in U.S. assets, impacting demand for U.S. Treasury bonds and influencing mortgage rates.
- Geopolitical Events: Geopolitical instability can create uncertainty in the markets, influencing investor behavior and potentially driving up interest rates, including mortgage rates.
Conclusion
Federal debt plays a significant, albeit not exclusive, role in determining mortgage rates. The Federal Reserve's response to both debt levels and inflation significantly impacts the market, attempting to balance economic growth with inflation control. Other economic factors, including domestic economic health and global conditions, also contribute to the fluctuations in mortgage rates. Understanding the link between federal debt and mortgage rates is crucial for making sound financial decisions. Stay informed about both to navigate the mortgage market effectively. For further information on federal debt, visit the U.S. Treasury Department website, and for information on current mortgage rates, consult reputable financial news sources.

Featured Posts
-
 Michael Morales Ruthless Ko Victory Gilbert Burns Falls At Ufc Vegas 106
May 19, 2025
Michael Morales Ruthless Ko Victory Gilbert Burns Falls At Ufc Vegas 106
May 19, 2025 -
 Controversial Ufc 313 Prelims Victory Fighters Confession
May 19, 2025
Controversial Ufc 313 Prelims Victory Fighters Confession
May 19, 2025 -
 Legal Challenge Launched London Parks Future Uncertain Amidst Festival Plans
May 19, 2025
Legal Challenge Launched London Parks Future Uncertain Amidst Festival Plans
May 19, 2025 -
 Greg Sankey Backs Nine Game Sec Football Schedule What It Means For Texas Longhorns
May 19, 2025
Greg Sankey Backs Nine Game Sec Football Schedule What It Means For Texas Longhorns
May 19, 2025 -
 Analyzing Juan Sotos Performance Early Struggles For The Mets
May 19, 2025
Analyzing Juan Sotos Performance Early Struggles For The Mets
May 19, 2025
