Understanding The U.S. Measles Outbreak: Data And Locations
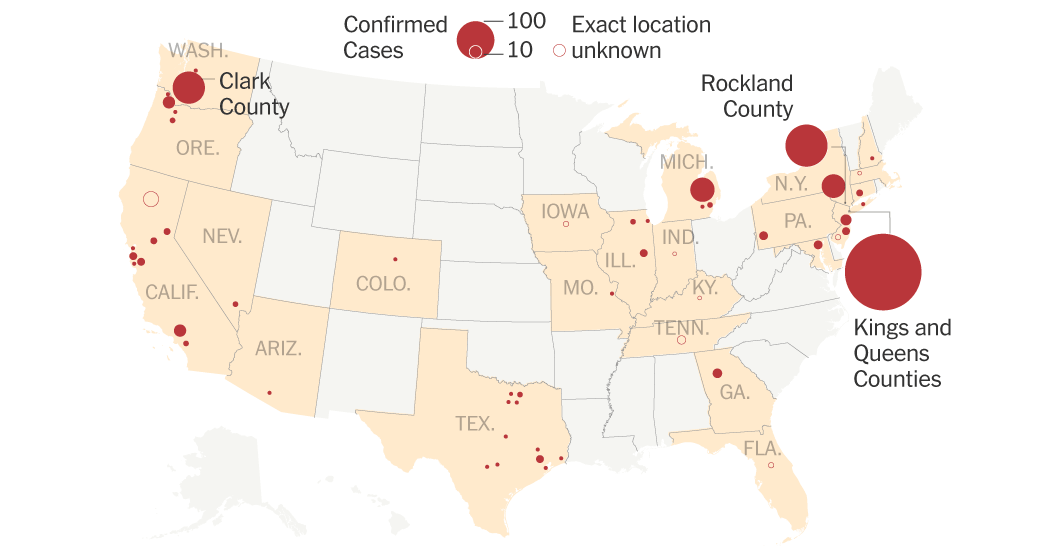
Table of Contents
Recent Measles Outbreak Data in the U.S.
The resurgence of measles in the U.S. is a serious public health concern. Analyzing U.S. measles outbreak data reveals a worrying trend. While measles was declared eliminated in the U.S. in 2000, outbreaks have periodically occurred due to low vaccination rates and international travel. Examining the measles cases and measles statistics from recent years provides critical insights into the nature of these outbreaks.
-
Total number of cases reported in [Insert most recent year with data]: [Insert Data - Source: CDC]. This represents a [Percentage Increase/Decrease] compared to [Previous Year] and a significant increase compared to the average number of cases reported annually in the previous decade. It's important to note that these numbers often lag, as reporting can take time.
-
Age demographics most affected by the outbreak: Outbreaks disproportionately affect unvaccinated children under the age of five, although outbreaks can affect any unvaccinated individual. Data shows [Insert data on age demographics if available – Source: CDC].
-
Geographic distribution of cases (state-level data if available): [Insert data on states with the highest number of cases. If possible, include a chart or graph visualizing this data. Source: CDC]. This uneven distribution underscores the importance of targeted public health interventions.
-
Trends in vaccination rates and their correlation with outbreak severity: A strong correlation exists between low vaccination rates and the severity of measles outbreaks. Areas with lower MMR (Measles, Mumps, and Rubella) vaccination rates tend to experience larger and more sustained outbreaks. [Insert data illustrating this correlation if available – Source: CDC].
-
Sources for data (CDC, WHO, etc.): The data presented here is primarily sourced from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) and the World Health Organization (WHO), which are reliable sources for accurate and up-to-date information on infectious disease outbreaks.
Geographic Locations Most Affected by the Measles Outbreak
Mapping the measles outbreak in the USA reveals a clear geographic pattern. While outbreaks can occur anywhere, certain states and regions are consistently more affected. Understanding these measles cases by state helps target prevention efforts.
-
States with the highest number of reported cases: [Insert list of states with the highest case counts, Source: CDC].
-
Specific counties or cities within those states experiencing significant outbreaks: [Insert specific locations within the high-case states, Source: CDC]. This level of geographic detail is crucial for effective public health response.
-
Factors contributing to higher infection rates in specific areas (e.g., low vaccination rates, population density): Several factors contribute to higher infection rates in specific areas. These include low MMR vaccination rates, high population density (facilitating easier transmission), and communities with lower access to healthcare.
-
Discussion of potential reasons behind geographic clustering: Geographic clustering of measles cases is often linked to unvaccinated populations, whether due to philosophical objections, lack of access to healthcare, or other reasons. This highlights the importance of community-based vaccination campaigns.
Understanding the Spread of Measles
Measles transmission is highly efficient, making it a significant public health concern. Understanding measles contagiousness is essential for prevention.
-
Explanation of the airborne nature of measles transmission: Measles is spread through the air via respiratory droplets produced when an infected person coughs or sneezes. These droplets can remain suspended in the air for a considerable period.
-
The incubation period of the disease and its implications for spread: The incubation period – the time between infection and symptom onset – is typically 7-14 days. This means infected individuals can unknowingly spread the virus for several days before they even realize they are ill.
-
The impact of community immunity and herd immunity on outbreak control: High vaccination rates lead to herd immunity, protecting even those who cannot be vaccinated. Herd immunity significantly reduces the likelihood and severity of outbreaks.
-
Risk factors associated with increased susceptibility (e.g., unvaccinated individuals, weakened immune systems): Unvaccinated individuals and those with weakened immune systems are at significantly higher risk of contracting measles.
Public Health Response and Prevention Measures
A multi-pronged approach is necessary to control measles outbreaks. Measles prevention relies heavily on vaccination and public health interventions.
-
Measures taken by public health agencies to contain the spread (e.g., contact tracing, vaccination campaigns): Public health agencies utilize contact tracing to identify and isolate individuals exposed to the virus. Mass vaccination campaigns are crucial to building community immunity.
-
Importance of the MMR vaccine in preventing measles: The MMR vaccine is highly effective in preventing measles, mumps, and rubella. It is a safe and effective way to protect individuals and the wider community.
-
Addressing concerns and misinformation surrounding vaccination: Addressing vaccine hesitancy and misinformation is crucial. Public health initiatives should focus on providing accurate, evidence-based information to build trust.
-
Strategies for improving vaccination rates in vulnerable populations: Targeted outreach programs and initiatives are needed to ensure vulnerable populations, such as low-income communities, have access to the MMR vaccine.
Conclusion
Understanding the data and locations associated with the U.S. measles outbreak is crucial for implementing effective public health strategies. By analyzing the spread of measles cases, identifying affected areas, and promoting vaccination, we can collectively work to reduce the risk of future outbreaks and protect vulnerable populations. Staying informed about the latest U.S. measles outbreak data and taking preventative measures, like getting vaccinated, is vital to controlling this highly contagious disease. Learn more about the U.S. measles outbreak data and protect yourself and your community. Get vaccinated today!

Featured Posts
-
 Undertale 10th Anniversary Orchestral Concert A Single Night Event
May 30, 2025
Undertale 10th Anniversary Orchestral Concert A Single Night Event
May 30, 2025 -
 Top Riders And Hondas Winning Bikes A Perfect Match
May 30, 2025
Top Riders And Hondas Winning Bikes A Perfect Match
May 30, 2025 -
 The Ultimate Bargain Hunt A Comprehensive Guide To Saving Money
May 30, 2025
The Ultimate Bargain Hunt A Comprehensive Guide To Saving Money
May 30, 2025 -
 Strong Q1 Performance For Cts Eventim Adjusted Ebitda And Revenue Climb
May 30, 2025
Strong Q1 Performance For Cts Eventim Adjusted Ebitda And Revenue Climb
May 30, 2025 -
 Elon Musks Response To Bill Gates Child Poverty Accusation
May 30, 2025
Elon Musks Response To Bill Gates Child Poverty Accusation
May 30, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Munichs Bmw Open 2025 Zverev Battles Griekspoor In Quarter Finals
May 31, 2025
Munichs Bmw Open 2025 Zverev Battles Griekspoor In Quarter Finals
May 31, 2025 -
 May Day Rally In Kingston Images Show Strength And Solidarity Daily Freeman
May 31, 2025
May Day Rally In Kingston Images Show Strength And Solidarity Daily Freeman
May 31, 2025 -
 Bmw Open 2025 Zverev Griekspoor Quarter Final Showdown In Munich
May 31, 2025
Bmw Open 2025 Zverev Griekspoor Quarter Final Showdown In Munich
May 31, 2025 -
 Indian Wells Surprise Zverevs First Match Exit And His Honest Assessment
May 31, 2025
Indian Wells Surprise Zverevs First Match Exit And His Honest Assessment
May 31, 2025 -
 Trump Administration Loses Key Advisor Elon Musks Resignation Explained
May 31, 2025
Trump Administration Loses Key Advisor Elon Musks Resignation Explained
May 31, 2025
