Unveiling The Mechanisms: How AI Functions And Why It's Not Really Thinking
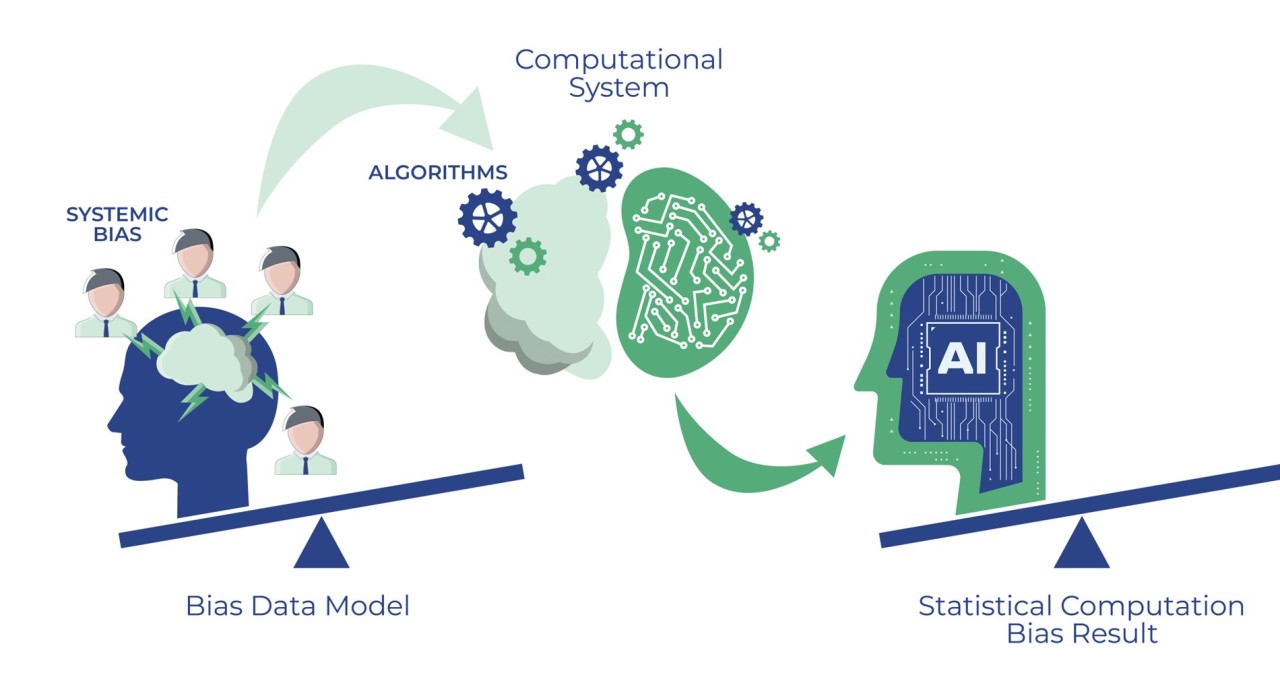
Table of Contents
Understanding the Core of AI: Machine Learning
Many AI systems are built upon the foundation of machine learning (ML). Machine learning allows computers to learn from data without being explicitly programmed. Instead of relying on hard-coded rules, ML algorithms identify patterns and make predictions based on the data they are trained on. There are several key types of machine learning:
-
Supervised learning: This approach involves training an AI model on a large dataset of labeled data. Each data point is tagged with the correct answer, allowing the algorithm to learn the relationship between the input data and the desired output. A classic example is image recognition, where an AI is trained on thousands of images labeled with the objects they contain (e.g., "cat," "dog," "car"). The AI learns to identify these objects in new, unseen images. This is a crucial aspect of understanding how AI functions in image processing.
-
Unsupervised learning: In contrast to supervised learning, unsupervised learning uses unlabeled data. The algorithm's task is to identify patterns, structures, and relationships within the data without any prior knowledge of the correct answers. A common application is customer segmentation, where an AI can group customers based on their purchasing behavior or demographics. The algorithm discovers underlying patterns within the data itself, showing another facet of AI functions.
-
Reinforcement learning: This type of machine learning involves an AI agent interacting with an environment. The agent learns through trial and error, receiving rewards for desirable actions and penalties for undesirable ones. This approach is often used to train AI agents to play games, such as chess or Go, where the AI learns optimal strategies through repeated interactions with the game environment. This demonstrates a different way AI functions, learning through experience.
These diverse AI algorithms, including those used in supervised, unsupervised, and reinforcement learning, form the backbone of many AI applications.
The Role of Algorithms and Data in AI Functions
The effectiveness of any AI system hinges on two crucial elements: algorithms and data. Algorithms are sets of instructions that define how the AI processes data and makes predictions. Different types of algorithms are used in AI, each with its own strengths and weaknesses:
-
Neural networks: Inspired by the structure of the human brain, neural networks consist of interconnected nodes (neurons) organized in layers. They are particularly effective at processing complex data, such as images and speech. Deep learning, a subfield of machine learning, utilizes deep neural networks with many layers to learn intricate patterns.
-
Decision trees: These algorithms create a tree-like model of decisions and their possible consequences. They are relatively simple to understand and interpret, making them suitable for tasks where explainability is important.
Training effective AI systems requires vast amounts of data. The more data an algorithm is trained on, the better it becomes at identifying patterns and making accurate predictions. This is often referred to as "big data." The quality of this data is paramount.
- Data bias: A significant challenge in AI is data bias. If the training data reflects existing biases in society, the AI system will likely perpetuate and even amplify those biases in its predictions. This highlights a critical aspect of understanding how AI functions and its potential societal implications. Addressing data bias is a crucial area of ongoing research in the field.
Deep Dive into Neural Networks: The Architecture of AI
Artificial neural networks (ANNs) are a key component of many powerful AI systems. While inspired by the biological brain, it's important to understand the crucial differences. ANNs are composed of interconnected nodes organized into layers:
-
Layers of interconnected nodes (neurons): These nodes process information and pass it on to subsequent layers. The connections between nodes have associated weights, which determine the strength of the signal passed between them.
-
Weight adjustments and learning through backpropagation: The learning process in an ANN involves adjusting these weights based on the errors made in predictions. Backpropagation is a common algorithm used to calculate these adjustments, allowing the network to gradually improve its accuracy.
-
Limitations of current neural network architectures: Despite their power, current neural network architectures have limitations. They can be computationally expensive to train, and their decision-making processes can be difficult to interpret, often referred to as the "black box" problem. This lack of transparency is a major area of concern.
Why AI Isn't Truly Thinking: The Absence of Consciousness and General Intelligence
While AI excels at pattern recognition and specific tasks, it's crucial to distinguish its capabilities from true human intelligence and consciousness. AI currently lacks several key attributes:
-
AI lacks subjective experience and self-awareness: AI systems operate based on algorithms and data; they do not possess feelings, consciousness, or self-awareness.
-
AI operates based on pre-programmed rules and data, not genuine understanding: AI can perform complex calculations and make accurate predictions, but it doesn't genuinely understand the meaning or context of the data it processes.
-
The challenge of achieving Artificial General Intelligence (AGI): Creating AI with human-level general intelligence (AGI) remains a significant challenge. AGI would possess the ability to learn and apply knowledge across a wide range of tasks, unlike current AI systems, which are typically specialized for specific purposes. This highlights the significant difference between how AI currently functions and the potential for future AI development.
Conclusion
This exploration of how AI functions reveals a sophisticated but ultimately deterministic system. While AI excels at pattern recognition and specific tasks, it currently lacks the consciousness and general intelligence of humans. Understanding the mechanisms of AI—from machine learning algorithms to the architecture of neural networks—is crucial to harnessing its potential responsibly. Further research into AI functions and the development of ethical guidelines are vital as we navigate this rapidly evolving technological landscape. Continue to explore the fascinating world of AI functions to stay informed about its advancements and limitations.

Featured Posts
-
 160km H Mlb
Apr 29, 2025
160km H Mlb
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Israel Faces Pressure To Lift Gaza Aid Ban Amidst Shortages
Apr 29, 2025
Israel Faces Pressure To Lift Gaza Aid Ban Amidst Shortages
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Global Competition Heats Up The Race To Attract Us Researchers
Apr 29, 2025
Global Competition Heats Up The Race To Attract Us Researchers
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Actors And Writers Strike The Complete Impact On Hollywood
Apr 29, 2025
Actors And Writers Strike The Complete Impact On Hollywood
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Astedwa Lfn Abwzby 19 Nwfmbr
Apr 29, 2025
Astedwa Lfn Abwzby 19 Nwfmbr
Apr 29, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Kentucky Severe Weather Awareness Week Nws Preparations
Apr 29, 2025
Kentucky Severe Weather Awareness Week Nws Preparations
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Emergency High Levels Of Natural Gas Force Louisville City Center Evacuation
Apr 29, 2025
Emergency High Levels Of Natural Gas Force Louisville City Center Evacuation
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Fatal D C Black Hawk Crash Examining The Pilots Pre Crash Decisions
Apr 29, 2025
Fatal D C Black Hawk Crash Examining The Pilots Pre Crash Decisions
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Firefighters Investigate Gas Leak Downtown Louisville Buildings Evacuated
Apr 29, 2025
Firefighters Investigate Gas Leak Downtown Louisville Buildings Evacuated
Apr 29, 2025 -
 D C Helicopter Crash Investigation Reveals Pilot Error As Cause Of 67 Fatalities
Apr 29, 2025
D C Helicopter Crash Investigation Reveals Pilot Error As Cause Of 67 Fatalities
Apr 29, 2025
