Xi's Climate Strategy: China's Unilateral Approach To Emissions Reduction

Table of Contents
Domestic Policy Drivers of Xi's Climate Strategy
Xi's climate strategy is deeply rooted in China's domestic priorities. Two key drivers are energy security and the pursuit of green economic growth.
Energy Security and Self-Reliance
China's pursuit of energy independence is a powerful force shaping its climate policies. Reducing reliance on foreign energy sources is not only a matter of energy security but also strengthens China's economic and geopolitical position. This has led to:
- Increased investment in renewable energy sources: Massive investments in solar, wind, and hydropower are transforming China's energy landscape, making it a global leader in renewable energy production and deployment. This includes substantial government subsidies and supportive regulatory frameworks.
- Development of domestic technology for energy production and storage: China is aggressively developing its domestic technology capabilities in areas like battery storage, smart grids, and advanced renewable energy technologies. This reduces dependence on foreign technology and creates new economic opportunities.
- Gradual phasing out of coal: While coal remains a significant part of China's energy mix, there's a gradual, albeit contested, shift away from coal-fired power plants. The timelines for this transition remain a subject of debate, influenced by economic considerations and regional disparities.
- Focus on energy efficiency improvements: China is implementing policies to improve energy efficiency across various sectors, including industry, transportation, and buildings. This includes stricter building codes, promoting energy-efficient appliances, and investing in public transportation.
Economic Growth and Green Development
Integrating environmental protection with economic goals is central to Xi's vision. The concept of "green development" aims to create a sustainable economic model that balances growth with environmental responsibility. This approach involves:
- Promotion of green technologies and industries for job creation: China views green technology as a driver of economic growth and job creation, investing heavily in sectors like renewable energy manufacturing, electric vehicles, and environmental services.
- Investment in sustainable infrastructure projects: Large-scale investments in green infrastructure, such as high-speed rail, electric vehicle charging stations, and smart grids, are integral to China's green development strategy.
- Emphasis on creating a circular economy to reduce waste: Reducing waste and promoting resource efficiency are key components of the circular economy approach, aiming to minimize environmental impact through resource recycling and reuse.
- Targeting specific sectors for emissions reduction targets: China sets specific emissions reduction targets for various industries and regions, aiming for a more targeted and effective approach to pollution control.
International Implications of a Unilateral Approach
While China participates in international climate negotiations, its approach often prioritizes national interests, leading to criticisms regarding its commitment to global targets.
Limited Engagement with International Agreements
Despite its engagement in international climate forums like the UNFCCC, China's approach is often characterized as cautious and prioritizing national interests over fully embracing global targets. This has led to:
- Cautious approach to emission reduction targets: Compared to some Western nations, China's emission reduction targets have been viewed by some as less ambitious. This is often justified by referencing historical emission differences and developmental needs.
- Emphasis on "common but differentiated responsibilities": China consistently highlights the principle of "common but differentiated responsibilities," emphasizing that developed nations bear a greater historical responsibility for climate change and should take the lead in emission reductions.
- Negotiation tactics focusing on national interests: China's negotiation tactics in international forums are often viewed as prioritizing its national interests, potentially hindering the progress of multilateral agreements.
Belt and Road Initiative and Climate Impacts
The Belt and Road Initiative (BRI), China's massive infrastructure investment program, presents both opportunities and challenges for global climate action.
- Increased investment in infrastructure projects: The BRI’s infrastructure projects in developing nations could lead to increased emissions if not carefully planned and implemented with sustainability in mind.
- Opportunities to promote green infrastructure development: The BRI also presents an opportunity to promote green infrastructure development, potentially transferring technology and best practices to developing countries.
- Potential for technology transfer and sharing best practices: China can leverage the BRI to share its expertise in renewable energy and sustainable infrastructure development, contributing to global climate action.
Challenges and Criticisms of Xi's Climate Strategy
Despite significant progress, Xi's climate strategy faces challenges and criticisms.
Opacity and Lack of Transparency
A lack of transparency surrounding China's emissions data and policy implementation remains a significant concern for international observers.
- Limited access to detailed emission data: Access to comprehensive and verifiable emission data from various sectors remains limited, making independent assessment difficult.
- Difficulty verifying progress towards stated targets: The lack of detailed data makes it challenging to independently verify China's progress towards its stated emissions reduction targets.
- Concerns over the accuracy and reliability of reported data: Concerns persist regarding the accuracy and reliability of the emission data reported by China, hindering international confidence in its climate commitments.
Balancing Economic Growth with Environmental Protection
The simultaneous pursuit of rapid economic growth and significant emissions reductions presents a major challenge.
- Potential trade-offs between economic development and environmental goals: There's a potential for trade-offs between economic development priorities and environmental goals, particularly in the short term.
- Need for innovative solutions that allow for both growth and sustainability: Innovative solutions are needed to allow for both economic growth and sustainable environmental practices.
- Risk of prioritizing economic growth over climate action: There's a risk that economic growth might be prioritized over immediate climate action, particularly in the face of economic challenges.
Conclusion
Xi's climate strategy is a complex and evolving phenomenon. While China has made significant strides in renewable energy development and green technology, its unilateral approach raises questions about its long-term effectiveness and its contribution to global climate cooperation. The success of Xi's Climate Strategy will depend on increased transparency, a stronger commitment to international collaboration, and a more ambitious approach to emissions reduction. Understanding Xi's Climate Strategy is crucial for navigating the future of global climate action. Further research into the nuances of Xi's climate policies is essential for effective international engagement and achieving global climate goals.

Featured Posts
-
 Is Ashton Jeanty The Missing Piece For The Dallas Cowboys
Apr 25, 2025
Is Ashton Jeanty The Missing Piece For The Dallas Cowboys
Apr 25, 2025 -
 Exploring Jack O Connells Sinners Scene A Cultural Analysis
Apr 25, 2025
Exploring Jack O Connells Sinners Scene A Cultural Analysis
Apr 25, 2025 -
 Grammys 2025 Olivia Rodrigos Faithful Fashion Formula
Apr 25, 2025
Grammys 2025 Olivia Rodrigos Faithful Fashion Formula
Apr 25, 2025 -
 Latest Espn Mock Draft Denver Broncos Key Selection
Apr 25, 2025
Latest Espn Mock Draft Denver Broncos Key Selection
Apr 25, 2025 -
 The Casting Coup Of 2025s Breakout Rpg
Apr 25, 2025
The Casting Coup Of 2025s Breakout Rpg
Apr 25, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 How Healthy Is Asparagus Nutritional Benefits And Health Effects
Apr 30, 2025
How Healthy Is Asparagus Nutritional Benefits And Health Effects
Apr 30, 2025 -
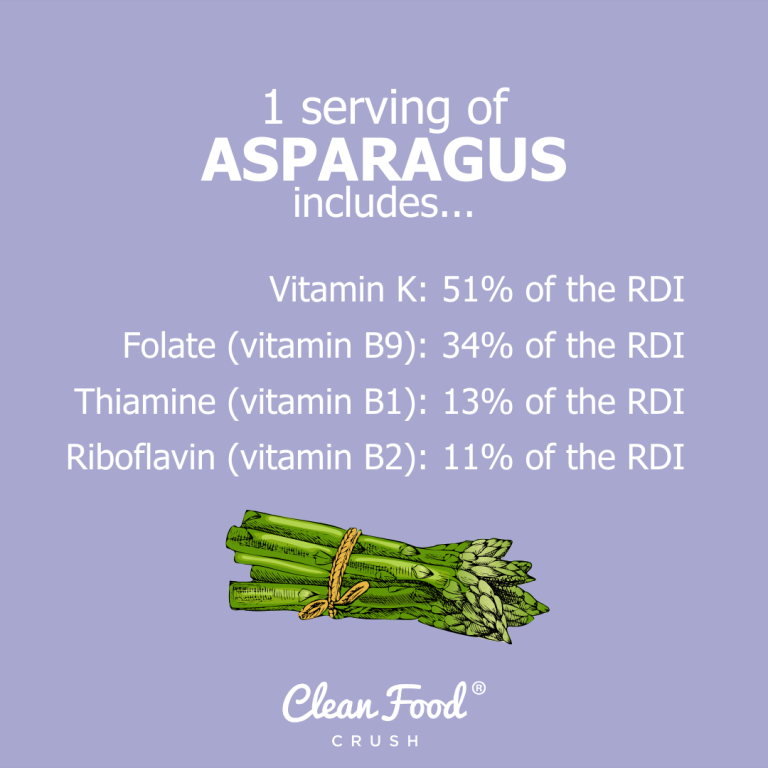 The Complete Guide To Asparagus And Its Health Benefits
Apr 30, 2025
The Complete Guide To Asparagus And Its Health Benefits
Apr 30, 2025 -
 Asparagus And Health Exploring The Positive Impacts
Apr 30, 2025
Asparagus And Health Exploring The Positive Impacts
Apr 30, 2025 -
 Understanding The Nutritional Value Of Asparagus
Apr 30, 2025
Understanding The Nutritional Value Of Asparagus
Apr 30, 2025 -
 Unlocking The Health Benefits Of Asparagus
Apr 30, 2025
Unlocking The Health Benefits Of Asparagus
Apr 30, 2025
