Asian Currency Volatility: The Impact Of A Weakening Dollar
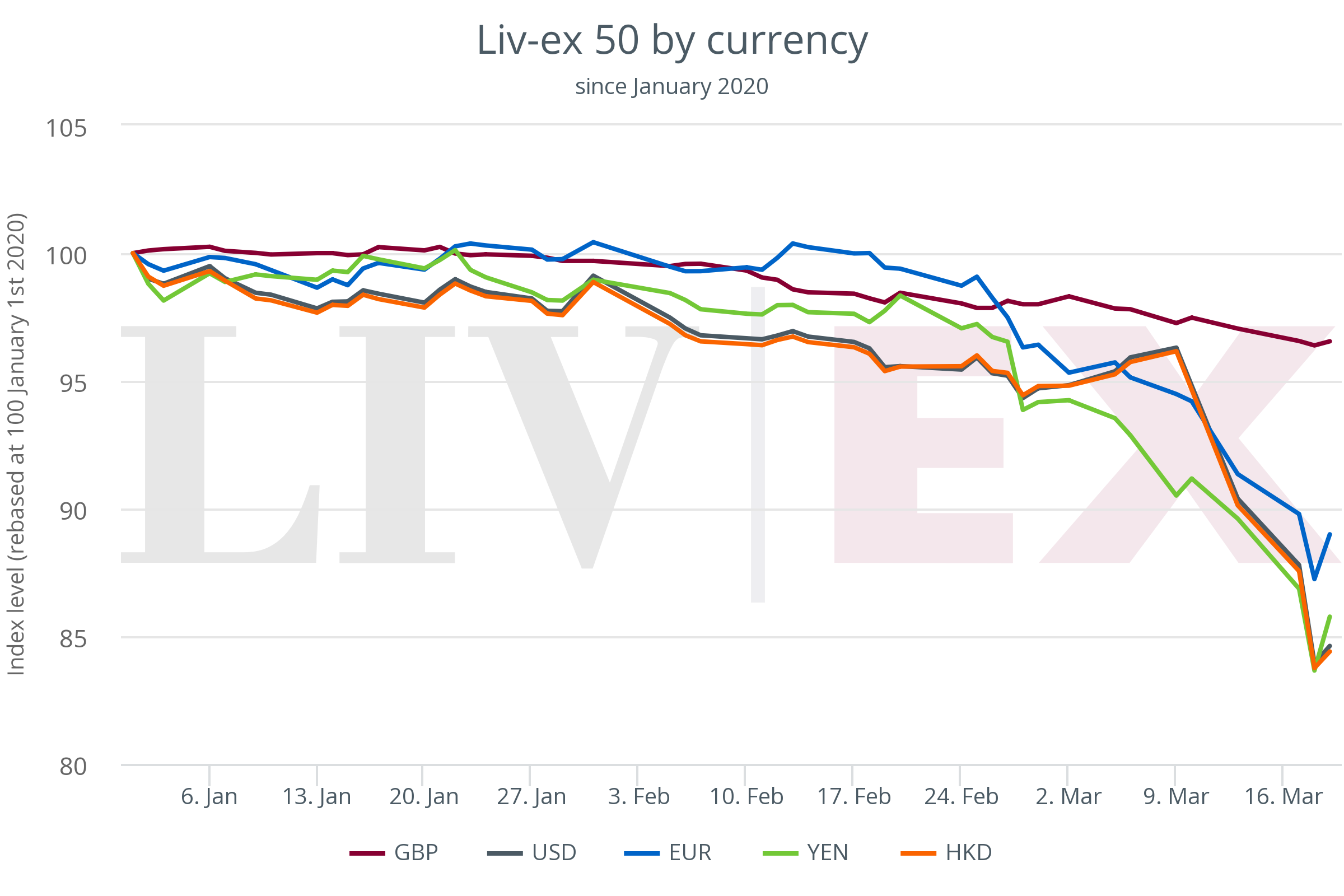
Table of Contents
Understanding the Dollar's Influence on Asian Currencies
The US dollar's role as the world's primary reserve currency profoundly influences trade and investment flows in Asia. Many Asian nations peg their currencies to the dollar or maintain substantial dollar reserves as part of their foreign exchange reserves. This close relationship means that fluctuations in the dollar's value directly impact Asian currencies.
-
Currency Pegs and Reserves: A weaker dollar makes US goods cheaper for Asian consumers, boosting imports. However, it simultaneously increases import costs for Asian nations reliant on dollar-denominated goods. This can lead to inflationary pressures and impact trade balances.
-
Foreign Direct Investment (FDI): A weakening dollar can affect foreign direct investment (FDI) flows. A decline in the dollar's value may make investments in Asian markets more attractive to foreign investors seeking higher returns, but it can also impact the value of existing investments denominated in dollars.
-
Exchange Rate Mechanisms: Asia employs various exchange rate mechanisms, including managed floats (where central banks intervene to influence exchange rates) and pegged exchange rates (where a currency's value is fixed to another currency). These mechanisms play a critical role in managing Asian currency volatility in response to dollar fluctuations.
Causes of the Weakening Dollar and Subsequent Asian Currency Volatility
Several factors contribute to the dollar's decline and the resulting Asian currency volatility. Understanding these factors is crucial for anticipating future trends.
-
US Monetary Policy: The US Federal Reserve's monetary policy decisions, including interest rate changes and quantitative easing (QE) programs, significantly impact the dollar's value. Lower interest rates generally weaken the dollar, making it less attractive to foreign investors. Conversely, interest rate hikes tend to strengthen the dollar.
-
Global Economic Uncertainty and Geopolitical Risks: Global economic uncertainty, such as recessions or trade wars, and geopolitical risks often lead investors to seek the safety of the dollar, temporarily strengthening it. However, prolonged uncertainty can also erode confidence in the dollar, leading to a weakening trend.
-
Increased US Debt and Budget Deficits: High levels of US debt and persistent budget deficits can weaken investor confidence in the dollar, putting downward pressure on its value.
-
Competition from Other Global Currencies: The rise of other global currencies, such as the Euro, Japanese Yen, and Chinese Yuan, challenges the dollar's dominance and contributes to increased volatility in the foreign exchange market.
Impact on Specific Asian Economies
The weakening dollar's impact varies across Asian economies. Let's examine a few key examples:
-
China: A weaker dollar can boost Chinese exports, making them more competitive globally. However, it could also increase the cost of imported raw materials and potentially fuel inflation. The volatility of the Chinese Yuan (RMB) in response to dollar fluctuations is a significant concern for China's economy and its global trade relationships.
-
Japan: Japan's export-oriented economy is sensitive to dollar movements. A weaker dollar generally benefits Japanese exporters but can also lead to increased import costs and inflationary pressures. The Japanese Yen's value significantly fluctuates depending on the dollar's performance.
-
South Korea: South Korea, like Japan, is export-dependent and therefore vulnerable to currency fluctuations driven by the dollar. A weaker dollar can be a double-edged sword, benefiting exporters while increasing import costs.
-
India: India’s economy is also susceptible to dollar movements, although its reliance on dollar-denominated imports is a key factor. The Indian Rupee's movement in relation to the dollar impacts trade and inflation within the country.
The Case of China and the Renminbi (RMB)
China's role in global trade makes the Renminbi (RMB) volatility particularly significant. Fluctuations in the RMB directly influence the cost of Chinese goods in international markets, impacting global trade balances and potentially triggering competitive devaluations by other countries. Understanding RMB movements and their relationship to the weakening dollar is paramount for navigating the complexities of the global economy.
Opportunities and Risks for Investors
Asian currency volatility presents both opportunities and risks for investors. Navigating this requires a well-defined investment strategy and effective risk management.
-
Currency Hedging: Investors can use hedging strategies like forward contracts or currency options to mitigate currency risk. This involves minimizing potential losses stemming from unexpected fluctuations.
-
Potential for Higher Returns: Volatile markets can offer opportunities for higher returns, particularly for investors skilled in identifying undervalued assets or capitalizing on short-term price swings.
-
Increased Risk of Losses: The inherent risk in volatile markets is that unexpected currency fluctuations can lead to significant losses if investments are not appropriately hedged or diversified.
Conclusion
The weakening dollar has a significant impact on Asian currency volatility, creating both challenges and opportunities. Factors such as US monetary policy, global economic uncertainty, and the rise of other global currencies all play a role in shaping this volatility. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for businesses and investors alike. Developing a robust strategy that incorporates effective risk management and currency hedging techniques is essential for navigating the complexities of Asian currency volatility. Learn more about managing Asian currency volatility today and protect your investments!

Featured Posts
-
 Short And Sweet A Fantastic Stephen King Series You Can Watch In Under 5 Hours
May 06, 2025
Short And Sweet A Fantastic Stephen King Series You Can Watch In Under 5 Hours
May 06, 2025 -
 Erdogan Aliyev Goeruesmesi Boelgesel Isbirligi Ve Ikili Iliskiler
May 06, 2025
Erdogan Aliyev Goeruesmesi Boelgesel Isbirligi Ve Ikili Iliskiler
May 06, 2025 -
 Affordable And Effective Products
May 06, 2025
Affordable And Effective Products
May 06, 2025 -
 Smart Shopping For Budget Conscious Consumers
May 06, 2025
Smart Shopping For Budget Conscious Consumers
May 06, 2025 -
 Nude Scene Controversy Arnold Schwarzenegger And Son Patrick
May 06, 2025
Nude Scene Controversy Arnold Schwarzenegger And Son Patrick
May 06, 2025
