De Minimis Tariffs On Chinese Goods: A G-7 Discussion

Table of Contents
The Current State of De Minimis Tariffs on Chinese Imports
The current de minimis thresholds for imported goods vary widely across G7 nations, creating a complex and often unfair playing field for importers. These discrepancies lead to inconsistencies in the application of tariffs and pose challenges for businesses trying to navigate international trade. Understanding these variations is crucial for businesses operating in this landscape.
-
Current de minimis levels: The US currently has a de minimis threshold of $800, while Canada sits at CAD 20, the UK at £135, France at €150, Germany at €22, Italy at €22, and Japan at ¥200,000. These substantial differences impact how small businesses operate.
-
Impact on small businesses: Small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) importing from China are disproportionately affected by these inconsistent regulations. The fluctuating thresholds make it difficult to predict costs and manage inventory efficiently, creating uncertainty and increased administrative burdens.
-
Challenges faced by businesses: Businesses face difficulties with accurate cost estimations, compliance complexities, and increased paperwork due to inconsistent thresholds. This often leads to higher operational costs and decreased competitiveness.
-
Examples of affected goods: A wide range of goods, from clothing and electronics to small machinery parts and craft supplies, are subject to these varying de minimis thresholds, creating uneven market conditions.
G-7 Discussions and Potential Harmonization of De Minimis Tariffs
The G7 nations are actively engaged in discussions about the harmonization of de minimis tariffs on Chinese goods. The aim is to establish a more consistent and predictable system that simplifies international trade, promotes fair competition, and reduces administrative burdens. However, the path to harmonization is fraught with challenges.
-
Arguments for harmonization: Proponents of harmonization argue for a level playing field for businesses, regardless of their origin. A standardized system would reduce administrative complexities and increase predictability for both importers and customs authorities. This fosters increased transparency and trust within the global marketplace.
-
Arguments against harmonization: Opponents of harmonization raise concerns about potential negative impacts on domestic industries. Lowering tariffs across the board might negatively affect certain sectors, leading to job losses and reduced revenue for domestic businesses. Concerns also exist over revenue loss for governments.
-
G7 initiatives: While specific proposals remain largely confidential during ongoing negotiations, the G7 is exploring options for a more coordinated approach, potentially through recommendations and best practices shared among member nations.
Economic Impacts and Implications of De Minimis Tariffs on Chinese Goods
The current system of de minimis tariffs on Chinese goods has significant economic consequences, influencing consumer prices, business profitability, and employment. Changes to this system will undoubtedly have further ripple effects.
-
Impact on consumer prices: Varying tariff levels can directly affect consumer prices, as inconsistent regulations may lead to higher costs for imported goods. Consumers might pay more for similar products depending on the country of origin and the applicable tariff.
-
Effects on SMEs: SMEs are particularly vulnerable to fluctuations in tariff levels, impacting their ability to compete and grow. The added complexity and unpredictability of tariffs can be detrimental to their financial stability and sustainability.
-
Potential job creation or loss: Harmonization, or lack thereof, could lead to job creation in certain sectors and job losses in others. A reduction in tariffs might benefit some industries by lowering costs while potentially displacing others that are less efficient.
-
Impact on trade relations: The ongoing discussion about de minimis tariffs reflects broader trade tensions between the G7 nations and China. A lack of consensus on these issues could negatively impact overall trade relations and international cooperation.
Future Outlook and Policy Recommendations
The future of de minimis tariffs on Chinese goods depends on the actions taken by G7 nations and the ongoing international dialogue. A coordinated and transparent approach is essential for ensuring a stable and competitive global trade environment.
-
Predictions for future tariff adjustments: Predicting future adjustments is challenging given the ongoing negotiations. However, we anticipate gradual adjustments, likely leaning towards harmonization to simplify the system and minimize disputes.
-
Recommendations for a balanced system: A balanced approach involves considering the interests of all stakeholders, including businesses, consumers, and governments. This necessitates a careful assessment of economic impacts and potential job displacement. Transparency and engagement with stakeholders are crucial.
-
Addressing stakeholder concerns: Open dialogue and collaboration between government agencies, industry representatives, and consumer advocacy groups are essential for navigating the complexities of de minimis tariff adjustments.
-
The role of the WTO: The World Trade Organization (WTO) can play a significant role in mediating disputes and providing a framework for resolving disagreements related to de minimis tariffs. International cooperation and adherence to WTO guidelines are key.
The Path Forward for De Minimis Tariffs on Chinese Goods within the G-7
The complexities surrounding de minimis tariffs on Chinese goods highlight the need for a coordinated and balanced approach within the G7. The inconsistencies in current regulations present significant challenges for businesses, impact consumer prices, and affect overall trade relations. The ongoing discussions within the G7 represent a crucial step towards establishing a more predictable and equitable system. Harmonization, though challenging, offers the potential for a more stable and transparent global trade environment. Stay informed about developments regarding de minimis tariffs on Chinese goods and related policies from relevant government and international trade organizations to ensure your business remains competitive in this evolving landscape. Engage in the ongoing discussion to contribute to the creation of a more effective and fair international trade system.

Featured Posts
-
 Trade War Fears Trigger 7 Plunge In Amsterdam Stock Market
May 24, 2025
Trade War Fears Trigger 7 Plunge In Amsterdam Stock Market
May 24, 2025 -
 Escape To The Country Building A Community In Your New Rural Home
May 24, 2025
Escape To The Country Building A Community In Your New Rural Home
May 24, 2025 -
 Ftc Launches Probe Into Open Ai And Chat Gpt Data Privacy Concerns
May 24, 2025
Ftc Launches Probe Into Open Ai And Chat Gpt Data Privacy Concerns
May 24, 2025 -
 M56 Motorway Incident Overturned Car Paramedic Treatment Of Casualty
May 24, 2025
M56 Motorway Incident Overturned Car Paramedic Treatment Of Casualty
May 24, 2025 -
 Promoting Growth Through Collaboration The 2nd Best Of Bangladesh In Europe
May 24, 2025
Promoting Growth Through Collaboration The 2nd Best Of Bangladesh In Europe
May 24, 2025
Latest Posts
-
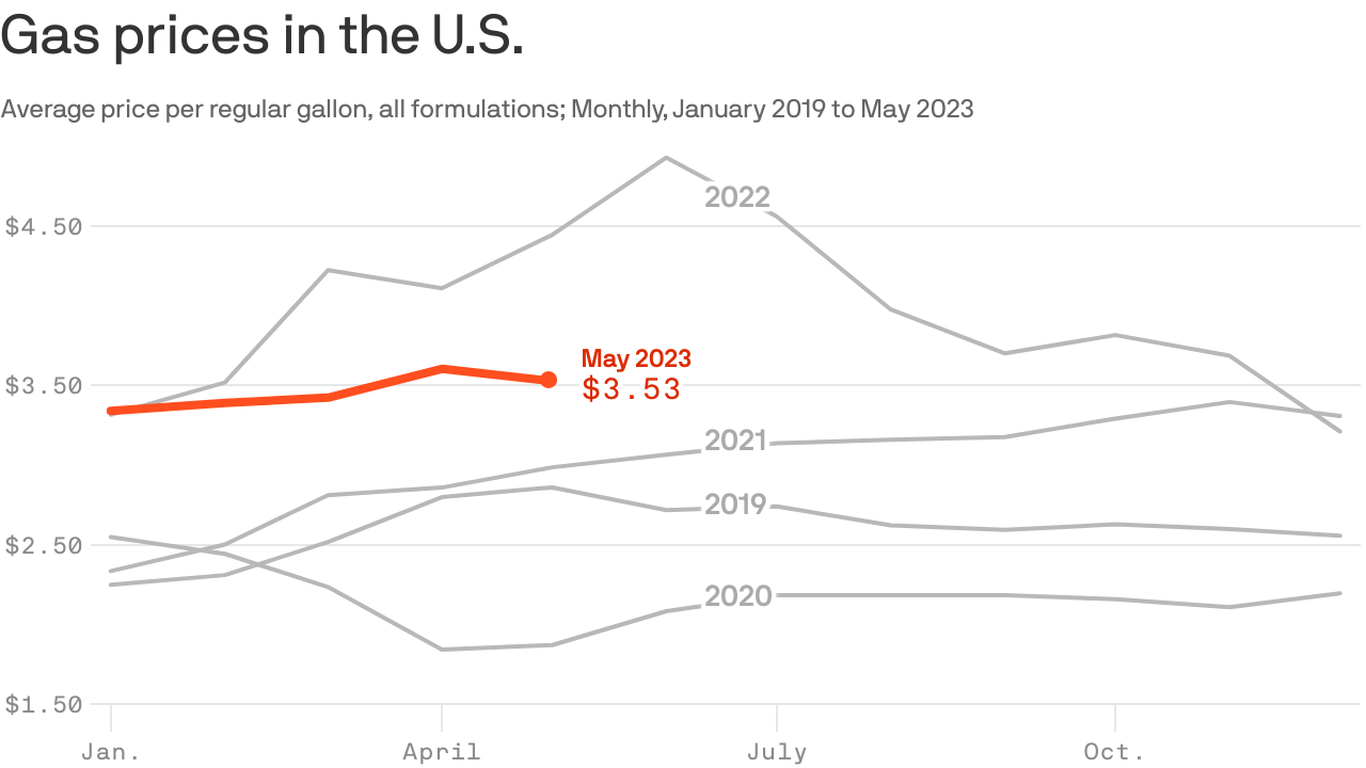 Record Low Gas Prices Predicted For Memorial Day Weekend
May 24, 2025
Record Low Gas Prices Predicted For Memorial Day Weekend
May 24, 2025 -
 New York City Memorial Day Weekend Weather Prediction And Rain Outlook
May 24, 2025
New York City Memorial Day Weekend Weather Prediction And Rain Outlook
May 24, 2025 -
 Stitchpossibles Weekend Success A Look At The Potential For A Historic 2025 Box Office
May 24, 2025
Stitchpossibles Weekend Success A Look At The Potential For A Historic 2025 Box Office
May 24, 2025 -
 Best Memorial Day 2025 Sales Laptops Beauty And More
May 24, 2025
Best Memorial Day 2025 Sales Laptops Beauty And More
May 24, 2025 -
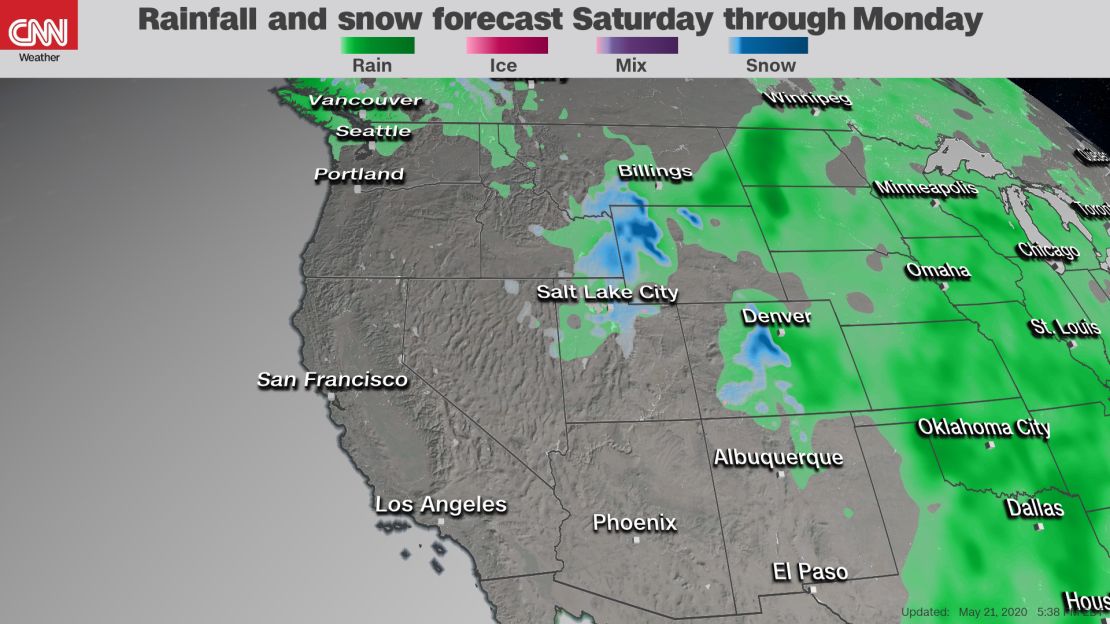 Memorial Day Weekend Rain Forecast For New York City
May 24, 2025
Memorial Day Weekend Rain Forecast For New York City
May 24, 2025
