Elevated Uncertainty: The Growing Risks Of Higher Inflation And Job Losses

Table of Contents
The Inflationary Spiral and its Impact
Understanding the Drivers of Inflation
Inflation, a persistent increase in the general price level of goods and services in an economy, is currently a major global concern. Several factors contribute to this inflationary spiral:
-
Supply Chain Disruptions: The COVID-19 pandemic exposed vulnerabilities in global supply chains, leading to shortages of essential goods and increased transportation costs. This reduced supply, while demand remained high, pushed prices upwards. For example, the semiconductor chip shortage significantly impacted the automotive industry, leading to higher car prices.
-
Increased Energy Prices: The war in Ukraine significantly disrupted global energy markets, leading to a sharp increase in oil and natural gas prices. These energy costs filter through the entire economy, impacting manufacturing, transportation, and heating costs for consumers. This has contributed significantly to the current inflationary pressures.
-
Demand-Pull Inflation: Strong consumer demand, fueled by factors such as government stimulus packages and pent-up demand following pandemic lockdowns, has also contributed to inflation. This increased demand outstrips supply, driving prices higher.
-
Rising Interest Rates: Central banks worldwide are responding to inflation by raising interest rates. While this aims to curb inflation by reducing borrowing and spending, it can also slow economic growth and potentially contribute to job losses. The effectiveness of this measure remains to be seen.
The Consumer Price Index (CPI), a measure that tracks changes in the price of a basket of consumer goods and services, is a key indicator of inflation. A consistently rising CPI signals persistent inflationary pressures.
Inflation's Impact on Consumer Spending and Savings
High inflation erodes purchasing power, meaning consumers can buy less with the same amount of money. This leads to decreased consumer confidence and reduced spending, impacting economic growth.
-
Impact on Different Income Brackets: Low-income households are disproportionately affected by inflation, as a larger portion of their income is spent on necessities like food and energy, which are experiencing the most significant price increases.
-
Decreased Savings Rates: As the cost of living increases, individuals may find it more difficult to save, further hindering economic growth and investment.
Examples of inflation’s impact on everyday expenses include soaring grocery bills, higher rents and mortgage payments, and increased transportation costs. This squeeze on household budgets can have significant long-term consequences.
The Threat of Job Losses and Economic Recession
Inflation's Role in Job Market Instability
High inflation forces businesses to make difficult choices. To maintain profitability in a high-inflation environment, companies may:
-
Reduce Hiring: Businesses may postpone hiring plans or freeze recruitment to control labor costs.
-
Cut Wages: In some cases, companies might attempt to reduce wage increases or even implement wage cuts to offset rising costs.
-
Lay Off Employees: As a last resort, companies may resort to layoffs to reduce their overall payroll expenses.
Industries particularly vulnerable to job losses during inflationary periods include those with high labor costs and low pricing power.
- The Wage-Price Spiral: A dangerous feedback loop can occur where rising wages fuel further inflation, leading to a wage-price spiral. Workers demand higher wages to keep pace with rising prices, which in turn pushes up production costs and further increases prices.
The Recessionary Risk
The combined pressures of high inflation and reduced consumer spending significantly increase the risk of a recession. Economists use various indicators to predict recessions:
-
GDP Growth: A sustained decline in Gross Domestic Product (GDP) is a key indicator of a recession.
-
Unemployment Rate: A sharp increase in the unemployment rate signifies economic downturn and job losses.
A recession triggered by high inflation could be severe and prolonged, depending on the effectiveness of government intervention and the resilience of the global economy.
Strategies for Mitigating Risk in a Time of Elevated Uncertainty
Personal Financial Strategies
Individuals can take steps to protect themselves against the risks of inflation and potential job loss:
-
Budgeting: Creating a detailed budget and tracking expenses is crucial to managing finances effectively during inflationary periods.
-
Diversifying Investments: Spread investments across different asset classes (stocks, bonds, real estate) to mitigate risk. Inflation-protected securities (TIPS) can help hedge against inflation.
-
Building an Emergency Fund: Having 3-6 months' worth of living expenses saved can provide a safety net in case of job loss or unexpected expenses.
-
Financial Planning: Consult a financial advisor to develop a personalized financial plan to navigate the economic uncertainties.
Business Strategies for Navigating Inflation
Businesses can implement strategies to mitigate the impact of inflation on profitability:
-
Efficient Inventory Management: Optimizing inventory levels can help reduce storage costs and minimize losses from price fluctuations.
-
Price Optimization: Carefully adjusting prices to reflect rising costs while remaining competitive is essential.
-
Exploring New Markets: Diversifying into new markets can help reduce reliance on any single market and potentially access lower-cost resources.
-
Managing Employee Costs: Implementing strategies to control labor costs while maintaining employee morale is crucial.
-
Government Support Programs: Explore potential government assistance programs designed to support businesses during economic downturns.
Conclusion
The current period of elevated uncertainty, marked by the interconnected risks of higher inflation and potential job losses, presents significant challenges. The potential for a recession underscores the need for proactive risk management strategies. Individuals must focus on responsible budgeting, diversified investments, and building emergency funds. Businesses need to implement efficient strategies to manage costs, optimize pricing, and explore new markets. Understanding and proactively addressing these challenges is paramount for securing individual and economic stability. Implement effective strategies to navigate this complex economic landscape and build resilience against future uncertainty. Learn more about managing your financial well-being during times of elevated uncertainty.

Featured Posts
-
 Concert De Medine Subventionne En Grand Est Le Rn S Insurge
May 30, 2025
Concert De Medine Subventionne En Grand Est Le Rn S Insurge
May 30, 2025 -
 Ministre Tabarot Confirme L Ouverture Du Tunnel De Tende Pour Juin
May 30, 2025
Ministre Tabarot Confirme L Ouverture Du Tunnel De Tende Pour Juin
May 30, 2025 -
 Ufc Veteran Advocates For Jon Joness 29 Million Demand
May 30, 2025
Ufc Veteran Advocates For Jon Joness 29 Million Demand
May 30, 2025 -
 Le Jugement De Marine Le Pen 5 Ans D Ineligibilite Analyse Et Consequences
May 30, 2025
Le Jugement De Marine Le Pen 5 Ans D Ineligibilite Analyse Et Consequences
May 30, 2025 -
 Israel Faces Measles Surge After Texas Outbreak
May 30, 2025
Israel Faces Measles Surge After Texas Outbreak
May 30, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Wildfires In Canada Severe Air Quality Degradation In Minnesota
May 31, 2025
Wildfires In Canada Severe Air Quality Degradation In Minnesota
May 31, 2025 -
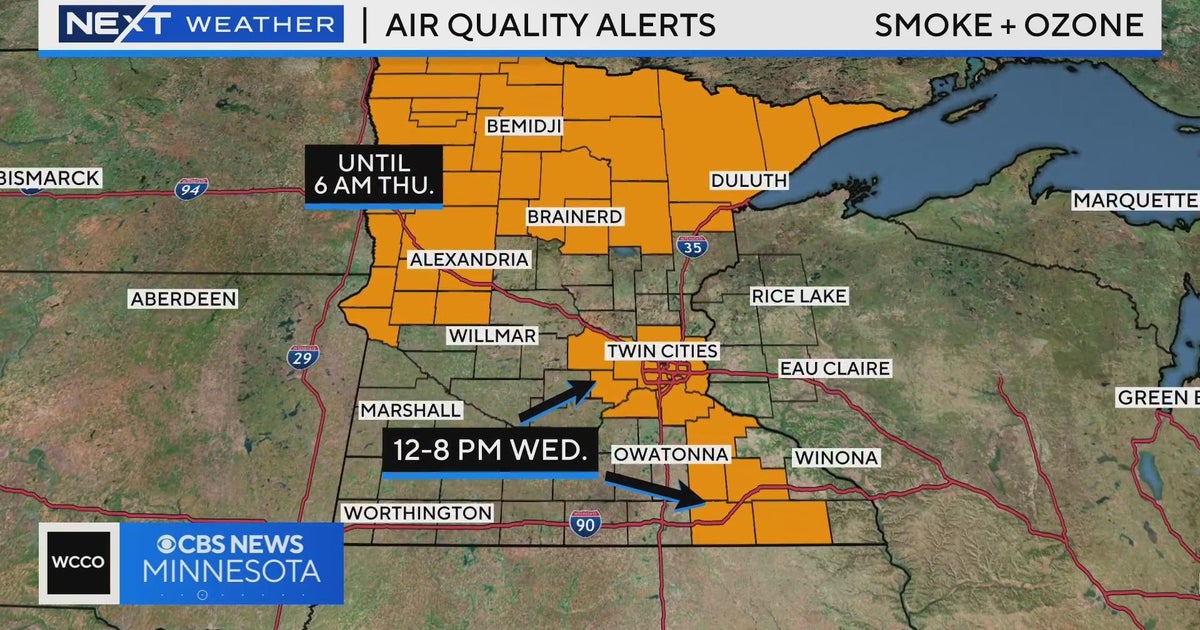 Canadian Wildfire Smoke Impacts Minnesotas Air Quality
May 31, 2025
Canadian Wildfire Smoke Impacts Minnesotas Air Quality
May 31, 2025 -
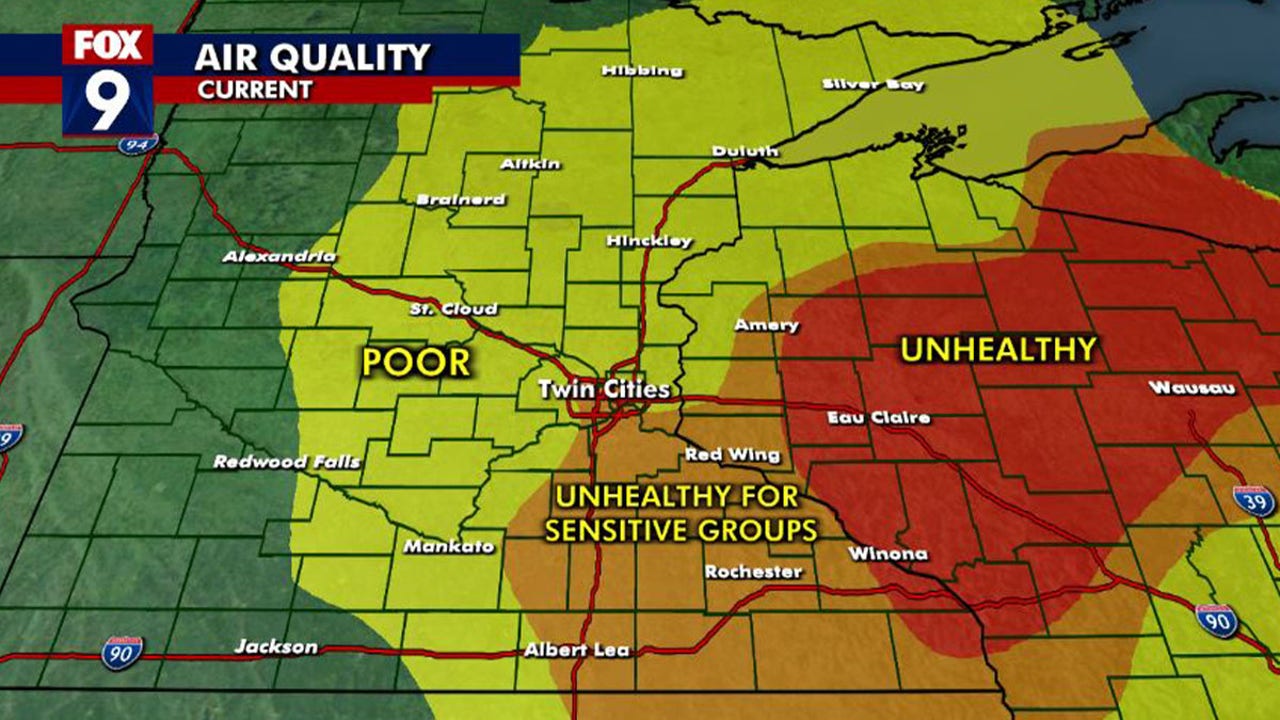 Minnesota Air Quality Crisis Impact Of Canadian Wildfires
May 31, 2025
Minnesota Air Quality Crisis Impact Of Canadian Wildfires
May 31, 2025 -
 Canadian Wildfires Minnesota Air Quality Plummets
May 31, 2025
Canadian Wildfires Minnesota Air Quality Plummets
May 31, 2025 -
 The Texas Panhandle Wildfire A Year Of Recovery And Rebirth
May 31, 2025
The Texas Panhandle Wildfire A Year Of Recovery And Rebirth
May 31, 2025
