Internal Fungal Infections: A Growing Threat In A Warming World
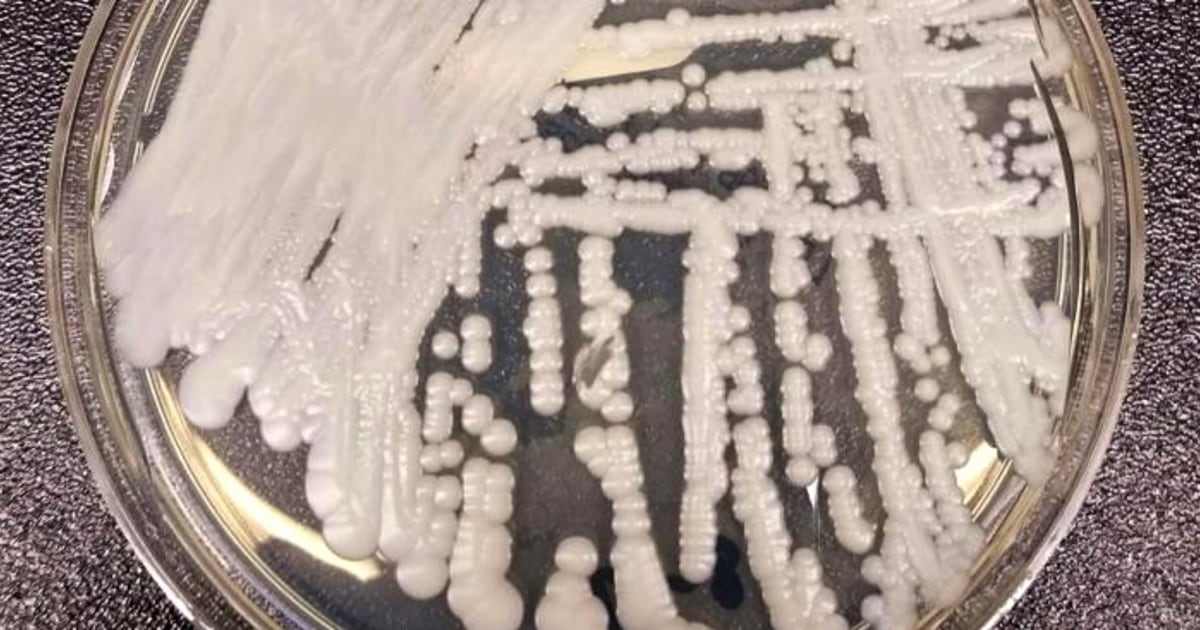
Table of Contents
The World Health Organization (WHO) lists fungal infections as one of the top ten leading causes of death globally. A chilling statistic, but one that underscores the urgency of addressing the escalating threat of internal fungal infections. These infections, once considered relatively uncommon, are rapidly emerging as a significant public health concern, with climate change playing a major role in their proliferation. This article will explore the escalating threat posed by internal fungal infections, highlighting the impact of climate change, the challenges in diagnosis and treatment, and the crucial need for preventative measures and increased research.
The Impact of Climate Change on Fungal Growth:
Climate change is creating a perfect storm for fungal growth. Rising global temperatures and increased humidity are expanding the geographical range of many fungi, allowing them to thrive in previously unsuitable environments. This leads to a higher risk of human exposure and subsequent infection.
Rising Temperatures and Humidity:
- Many fungal species, including Candida and Aspergillus, flourish in warmer, more humid conditions.
- Geographical areas experiencing significant climate change impacts, such as tropical and subtropical regions, are seeing increased incidences of fungal infections.
- The immunocompromised—including individuals with HIV/AIDS, those undergoing chemotherapy, and organ transplant recipients—are particularly vulnerable to severe fungal infections in these changing conditions. Their weakened immune systems struggle to fight off opportunistic fungi that proliferate in warmer climates.
Altered Ecosystems and Increased Exposure:
Climate change dramatically alters ecosystems, increasing human contact with fungal spores.
- Deforestation increases exposure to soil-borne fungi, like Histoplasma capsulatum.
- Flooding creates damp environments ideal for fungal growth and spread, increasing the risk of exposure to waterborne fungi.
- Changes in insect populations can influence the transmission of certain fungal infections; some insects act as vectors, carrying fungal spores and spreading them to humans and animals. This vector-borne transmission is another significant concern amplified by climate change.
Types of Invasive Fungal Infections:
Several types of internal fungal infections pose significant threats, and their prevalence is increasing.
Candidiasis (Yeast Infections):
- Candida species, most commonly Candida albicans, cause a range of infections, from superficial thrush to life-threatening bloodstream infections (candidemia).
- Symptoms vary depending on the location of infection and can include oral thrush, vaginal yeast infections, or more serious symptoms like fever, chills, and organ failure in cases of invasive candidiasis.
- Treatment challenges include the increasing prevalence of antifungal resistance, making certain Candida species difficult to treat effectively.
Aspergillosis:
- Aspergillus species, such as Aspergillus fumigatus, are ubiquitous airborne fungi that cause aspergillosis, a serious infection primarily affecting individuals with weakened immune systems.
- Symptoms range from mild allergic reactions to severe invasive aspergillosis, which can be fatal.
- Invasive aspergillosis carries a high mortality rate, underscoring the need for early diagnosis and aggressive treatment.
Other Emerging Fungal Threats:
- Cryptococcosis: Caused by Cryptococcus species, primarily affecting individuals with weakened immune systems, it can cause meningitis and other severe complications.
- Mucormycosis: Also known as zygomycosis, this aggressive fungal infection often affects individuals with diabetes or other immunocompromising conditions, leading to serious tissue damage.
Challenges in Diagnosis and Treatment of Internal Fungal Infections:
Early and accurate diagnosis is crucial for effective treatment, yet this remains a major challenge.
Diagnostic Difficulties:
- Diagnosing internal fungal infections can be challenging due to non-specific symptoms, often mimicking other illnesses.
- Specialized laboratory tests, such as fungal cultures and PCR assays, are necessary, but these can be time-consuming and not readily available in many healthcare settings.
- Improved diagnostic tools and techniques are urgently needed to facilitate faster and more accurate identification of fungal pathogens.
Antifungal Resistance:
- The increasing use of antifungals has led to the development of resistance in several fungal species, making treatment more complex and less effective.
- Mechanisms of antifungal resistance are varied and complex, hindering the development of new drugs.
- The development of new antifungal drugs and alternative treatment strategies is vital to combat this growing problem of antifungal resistance.
Prevention and Public Health Measures:
Preventing internal fungal infections requires a multi-pronged approach.
Promoting Hygiene and Sanitation:
- Good hygiene practices, such as regular handwashing, proper food handling, and maintaining a clean living environment, are crucial in reducing exposure to fungal spores.
- Improved sanitation in healthcare settings and communities can significantly reduce the risk of fungal infections.
Surveillance and Early Detection:
- Robust surveillance systems are essential for tracking the occurrence and spread of fungal infections, allowing for early detection of outbreaks.
- Early intervention is crucial in managing fungal infections and preventing severe complications.
- Public health agencies play a vital role in educating the public about fungal infections and implementing strategies to control their spread.
Conclusion:
Internal fungal infections represent a significant and growing threat to global health, with climate change exacerbating this challenge. The difficulties in diagnosis, the emergence of antifungal resistance, and the vulnerability of certain populations underscore the urgent need for increased research, improved diagnostic tools, and effective public health initiatives. To combat this escalating threat, we must prioritize funding for research into new antifungals, enhance surveillance programs, and promote public awareness about the prevention of internal fungal infections. Support organizations dedicated to researching and combating internal fungal infections; your action can help save lives.

Featured Posts
-
 Traffic Delays Of Up To 60 Minutes On M6 Southbound
May 25, 2025
Traffic Delays Of Up To 60 Minutes On M6 Southbound
May 25, 2025 -
 Nws Flood Warning Protecting Yourself And Your Property
May 25, 2025
Nws Flood Warning Protecting Yourself And Your Property
May 25, 2025 -
 Naomi Kempbell I Millioner Foto Detey Podtverzhdayut Slukhi
May 25, 2025
Naomi Kempbell I Millioner Foto Detey Podtverzhdayut Slukhi
May 25, 2025 -
 7 Drop For Amsterdam Stocks As Trade War Fears Grip Markets
May 25, 2025
7 Drop For Amsterdam Stocks As Trade War Fears Grip Markets
May 25, 2025 -
 Eala Eyes Impressive French Open Performance
May 25, 2025
Eala Eyes Impressive French Open Performance
May 25, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Iga Swiatek Overcomes Keys Reaches Madrid Semifinal Against Gauff
May 25, 2025
Iga Swiatek Overcomes Keys Reaches Madrid Semifinal Against Gauff
May 25, 2025 -
 French Open Alex Ealas Path To Success
May 25, 2025
French Open Alex Ealas Path To Success
May 25, 2025 -
 Swiateks Comeback Victory From 0 6 To Madrid Semifinal
May 25, 2025
Swiateks Comeback Victory From 0 6 To Madrid Semifinal
May 25, 2025 -
 Eala Eyes Impressive French Open Performance
May 25, 2025
Eala Eyes Impressive French Open Performance
May 25, 2025 -
 Alex Ealas French Open Aspirations A Dream Start
May 25, 2025
Alex Ealas French Open Aspirations A Dream Start
May 25, 2025
