Investor Behavior In Leveraged Semiconductor ETFs: A Case Study
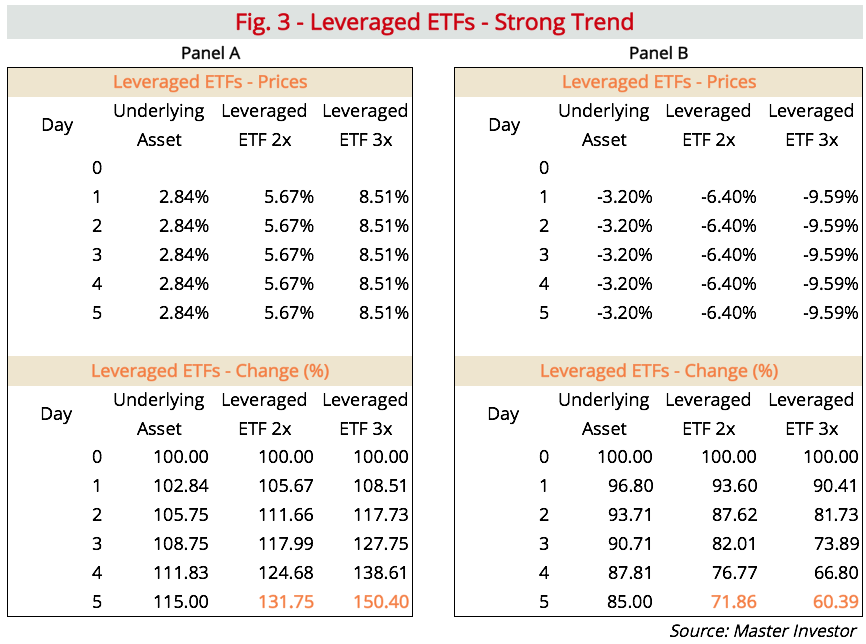
Table of Contents
The Appeal of Leveraged Semiconductor ETFs
The attraction of leveraged semiconductor ETFs stems from their potential for amplified returns and the inherent growth opportunities within the semiconductor sector.
Amplified Returns and Potential for High Growth
Leveraged ETFs, unlike traditional ETFs, aim to deliver a multiple of the daily performance of their underlying index. For example, a 2x leveraged semiconductor ETF aims to provide double the daily return of the benchmark semiconductor index. This magnification of returns is appealing to investors seeking exposure to potentially high-growth sectors like semiconductors. During periods of significant market upswings, these ETFs can yield substantial profits. However, it's crucial to remember that past performance is not indicative of future results.
- Daily resetting of leverage: Leverage is recalculated daily, meaning the ETF’s returns are reset at the close of each trading day. This daily resetting can lead to significant deviations from the intended multiple return over longer periods.
- Impact of compounding on long-term performance: While daily resetting offers the benefit of daily adjustments, it can also negatively impact long-term performance, especially in volatile markets. Compounding effects can lead to a considerable difference between the stated leverage and the actual accumulated returns.
- Higher potential for gains compared to unleveraged ETFs: The inherent leverage offers the potential for higher gains during periods of market growth, attracting investors seeking higher returns.
Speculative Trading and Short-Term Strategies
Leveraged semiconductor ETFs are frequently employed for speculative trading and short-term strategies. Investors often leverage these ETFs to capitalize on short-term market fluctuations and predicted movements. Successful utilization hinges heavily on accurate market timing and a deep understanding of the underlying semiconductor market dynamics.
- Day trading and swing trading approaches: Many investors use these ETFs for both day trading (holding positions for hours or less) and swing trading (holding positions for days or weeks).
- Leveraging market news and analyst predictions: Investors often base their trading decisions on market news, such as earnings reports, technological advancements, and geopolitical events affecting the semiconductor industry, along with analyst predictions and ratings.
- Use of technical analysis in trading decisions: Technical analysis, focusing on chart patterns, indicators, and other quantitative data, plays a significant role in trading decisions with these volatile instruments.
Risks Associated with Leveraged Semiconductor ETFs
While offering the allure of amplified returns, leveraged semiconductor ETFs carry significant risks that investors must fully understand.
Volatility and the Risk of Significant Losses
The inherent leverage amplifies not only gains but also losses. During market downturns, investors in leveraged semiconductor ETFs can experience losses far exceeding those of unleveraged counterparts. The compounding effect of daily losses can quickly erode capital. The semiconductor sector's historical volatility underscores the substantial risk involved.
- Increased risk compared to unleveraged ETFs: The risk profile of leveraged ETFs is substantially higher than unleveraged ETFs due to the amplified price movements.
- The impact of volatility decay: Over longer periods, volatility decay can significantly reduce the overall return of a leveraged ETF, often leading to underperformance compared to the intended leverage multiple.
- The importance of risk tolerance: Investors must possess a high risk tolerance to consider investing in leveraged semiconductor ETFs. The potential for significant losses must be carefully considered against one's overall investment strategy.
Understanding the Impact of Fees and Expenses
Leveraged ETFs typically carry higher expense ratios than their unleveraged counterparts. These fees, though seemingly small on a percentage basis, can significantly erode returns over time. It's crucial to compare the expense ratios of different leveraged semiconductor ETFs before making an investment.
- Expense ratio calculations and impact on returns: The expense ratio is an annual fee charged as a percentage of the ETF's assets under management. Even a seemingly small expense ratio can significantly reduce long-term returns, especially for leveraged products.
- Comparison of fees among different leveraged semiconductor ETFs: Investors should carefully compare the expense ratios and other fees associated with various leveraged semiconductor ETFs before investing.
- The importance of considering fees when making investment decisions: Fees are a crucial factor to consider when evaluating the overall performance and profitability of leveraged ETF investments.
Analyzing Investor Behavior Data
Analyzing investor behavior data provides valuable insights into the market dynamics surrounding leveraged semiconductor ETFs.
Trading Volume and Market Sentiment
Examining trading volume in leveraged semiconductor ETFs reveals significant trends in investor behavior. High trading volume often coincides with periods of heightened volatility and strong market sentiment, either positive or negative. Analyzing this data alongside news events and market sentiment indicators paints a clearer picture of investor psychology.
- Increased trading volume during periods of high volatility: Trading activity tends to spike during periods of significant market movements, reflecting investor reactions to price changes.
- The relationship between news events and investor behavior: Major news events, such as earnings announcements or regulatory changes, can significantly impact investor sentiment and trading activity.
- Use of sentiment indicators to gauge market mood: Analyzing sentiment indicators, such as social media mentions and news headlines, can offer insights into the overall market mood and investor confidence.
Investor Profile and Risk Appetite
Understanding the typical investor profile for leveraged semiconductor ETFs is essential. These investors often have a higher risk tolerance and a more active trading style than those investing in less volatile instruments.
- Survey data on investor profiles and risk tolerance: Data collected from investor surveys can reveal the demographic and risk tolerance profiles of those investing in leveraged semiconductor ETFs.
- The role of financial literacy in investment decisions: Financial literacy and understanding of the complexities of leveraged products are crucial factors influencing investment choices.
- The influence of past experience on future investment choices: Past investment successes and failures can shape an investor's future decisions and risk appetite.
Conclusion
Leveraged semiconductor ETFs present a high-risk, high-reward investment opportunity. Understanding investor behavior, encompassing both the allure and the inherent dangers, is crucial for making informed decisions. This case study underscores the importance of thoroughly understanding leveraged ETFs, including the mechanics of leverage, the impact of volatility, and the significance of fees. Before investing in leveraged semiconductor ETFs, carefully assess your risk tolerance and investment goals. Consider consulting with a financial advisor to determine if this investment aligns with your overall financial strategy. Remember, a keen analysis of investor behavior in leveraged semiconductor ETFs is paramount to successful and responsible investing.

Featured Posts
-
 The End Of An Era Fords Brazil Departure And Byds Ev Opportunity
May 13, 2025
The End Of An Era Fords Brazil Departure And Byds Ev Opportunity
May 13, 2025 -
 Sue Crane 1931 2023 A Legacy Of Service To Portola Valley
May 13, 2025
Sue Crane 1931 2023 A Legacy Of Service To Portola Valley
May 13, 2025 -
 Eva Longoria Faces Road Trip Mayhem In Alexander And The Terrible Horrible No Good Very Bad Day
May 13, 2025
Eva Longoria Faces Road Trip Mayhem In Alexander And The Terrible Horrible No Good Very Bad Day
May 13, 2025 -
 The Beyonce Effect Five Script Changes Demanded Before Film Role Acceptance
May 13, 2025
The Beyonce Effect Five Script Changes Demanded Before Film Role Acceptance
May 13, 2025 -
 The House Republican Plan A Deep Dive Into Trumps Proposed Tax Cuts
May 13, 2025
The House Republican Plan A Deep Dive Into Trumps Proposed Tax Cuts
May 13, 2025
