Justice Department's Decision: The Fall Of School Desegregation Orders
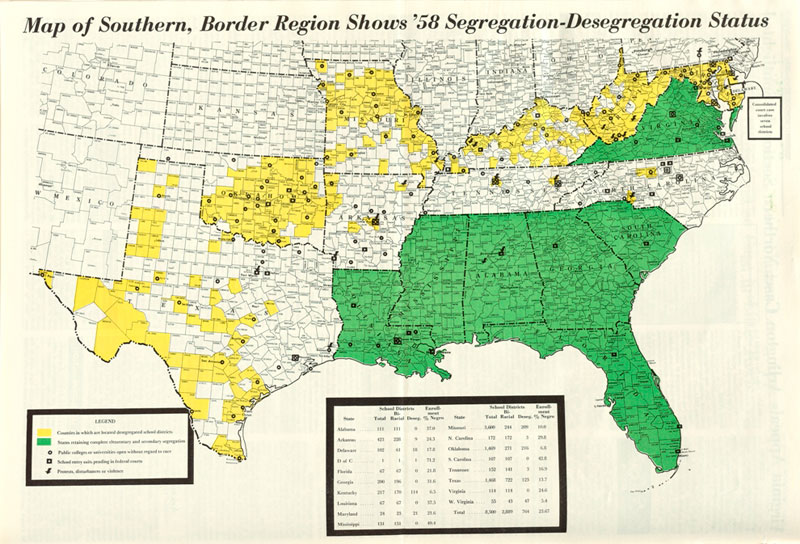
Table of Contents
The Changing Legal Landscape: Weakening of Federal Enforcement
The Justice Department's approach to enforcing school desegregation orders has undergone a dramatic transformation. Initially, the DOJ played a proactive role, actively investigating school districts and pursuing court-ordered remedies to achieve integration. However, over time, this vigorous enforcement has waned, leading to a significant weakening of federal oversight.
This shift is reflected in several key areas:
-
Court Cases and Overturned Orders: Numerous court cases have seen desegregation orders modified or completely overturned. These rulings often cite a lack of current evidence of intentional segregation, shifting the focus away from historical injustices. The consequences include the re-segregation of many schools.
-
Changes in DOJ Policies: The Justice Department’s policies regarding school district compliance monitoring have become significantly less stringent. Resources allocated to desegregation enforcement have been reduced, limiting the agency's ability to effectively monitor and address violations. This decreased oversight has allowed many districts to fall short of their integration goals.
-
Supreme Court Rulings: Supreme Court decisions have increasingly narrowed the scope of acceptable desegregation remedies. This has made it more difficult to address deeply ingrained racial disparities and achieve meaningful integration in schools. The Court’s interpretation of what constitutes justifiable remedies has significantly impacted the efficacy of desegregation orders.
The Rise of "Racial Isolation" vs. "De Jure" Segregation
A critical distinction exists between de jure segregation (segregation by law) and de facto segregation (segregation in fact). While the fight against de jure segregation—the legally mandated separation of races—has largely been won, the more complex problem of de facto segregation persists.
This shift in focus has created significant challenges:
-
Proving Intentional Segregation: Demonstrating intentional segregation in today's context is exceedingly difficult. While historical patterns of segregation are undeniable, proving current discriminatory intent requires substantial evidence, a hurdle that often proves insurmountable.
-
Socioeconomic Factors and Housing Patterns: Racial isolation is often intertwined with socioeconomic factors and residential segregation. Addressing these complex issues requires multifaceted solutions beyond the scope of traditional desegregation remedies. The interplay between housing policy and school segregation presents significant obstacles to achieving racial integration.
-
Limitations of Legal Remedies: Legal remedies, even when successfully implemented, have limited efficacy in addressing deeply ingrained racial disparities rooted in historical injustices and socioeconomic inequalities. The pervasive nature of these disparities often transcends the reach of legal action.
Political and Ideological Influences on Desegregation Enforcement
The Justice Department's approach to school desegregation has been significantly influenced by broader political shifts and ideological changes.
-
Shifting Priorities of Administrations: Different administrations have prioritized or de-prioritized desegregation enforcement based on their political ideologies and broader policy agendas. This inconsistency has undermined the consistency and effectiveness of desegregation efforts.
-
Conservative Legal Movements: The rise of conservative legal movements has significantly impacted desegregation policy. These groups have actively challenged desegregation orders and advocated for policies that limit federal intervention in education. Their influence is undeniable in the shaping of legal precedent regarding school desegregation.
-
Lobbying and Political Pressure: Various groups have exerted considerable lobbying pressure on policymakers, influencing the political climate surrounding desegregation and impacting the allocation of resources towards enforcement. This political maneuvering has often worked against the interests of achieving racial equality in education.
The Impact on Students and Communities: The Legacy of Unequal Educational Opportunities
The weakening of desegregation orders has had a devastating impact on students and communities across the nation.
-
Persistent Achievement Gaps: Racial disparities in educational outcomes remain stark, with students in predominantly minority schools consistently lagging behind their peers in predominantly white schools. This achievement gap reflects a legacy of unequal educational opportunities.
-
Impact on Social Mobility: Segregation limits social mobility and economic opportunities for students in under-resourced schools, perpetuating cycles of poverty and inequality. The lack of access to quality education hinders upward mobility for many minority students.
-
Psychological and Social Effects: Attending segregated schools can have profound negative psychological and social effects on students, impacting self-esteem, academic motivation, and future prospects. The isolation and limited exposure to diverse perspectives can have long-lasting consequences.
Conclusion: The Future of School Desegregation and the Justice Department's Role
The decline of school desegregation orders is a consequence of several intertwined factors: shifting legal interpretations, the complexities of addressing de facto segregation, and the influence of political and ideological forces. The Justice Department's decision to scale back enforcement has significantly contributed to this decline. The critical role of the Justice Department in upholding equal educational opportunities cannot be overstated. The future of equitable education hinges on a renewed commitment from the Justice Department and active engagement from citizens. Demand accountability and support organizations fighting for an end to the legacy of the Justice Department's decision to weaken school desegregation orders. We must strive for truly integrated schools and equal educational opportunities for all children, regardless of race.

Featured Posts
-
 Tuerkiye Nin Avrupa Ile Is Birligi Vizyonu
May 03, 2025
Tuerkiye Nin Avrupa Ile Is Birligi Vizyonu
May 03, 2025 -
 Breaking The Silence Why Mental Health Awareness Matters Dr Shradha Malik
May 03, 2025
Breaking The Silence Why Mental Health Awareness Matters Dr Shradha Malik
May 03, 2025 -
 Mother And Daughter Duo Kate And Lila Moss Shine In Black Dresses At London Fashion Week
May 03, 2025
Mother And Daughter Duo Kate And Lila Moss Shine In Black Dresses At London Fashion Week
May 03, 2025 -
 Informacion I Fundit Sulm Me Thike Ne Qender Tregtare Ne Ceki Dy Te Vdekur
May 03, 2025
Informacion I Fundit Sulm Me Thike Ne Qender Tregtare Ne Ceki Dy Te Vdekur
May 03, 2025 -
 Securing A Place In The Sun Tips For Buying Overseas Property
May 03, 2025
Securing A Place In The Sun Tips For Buying Overseas Property
May 03, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 The Future Of Expensive Offshore Wind Energy Projects
May 04, 2025
The Future Of Expensive Offshore Wind Energy Projects
May 04, 2025 -
 Rising Costs Jeopardize Offshore Wind Farm Investments
May 04, 2025
Rising Costs Jeopardize Offshore Wind Farm Investments
May 04, 2025 -
 Offshore Wind Farm Economics A Turning Point For The Industry
May 04, 2025
Offshore Wind Farm Economics A Turning Point For The Industry
May 04, 2025 -
 The High Cost Of Offshore Wind Why Energy Firms Are Reconsidering
May 04, 2025
The High Cost Of Offshore Wind Why Energy Firms Are Reconsidering
May 04, 2025 -
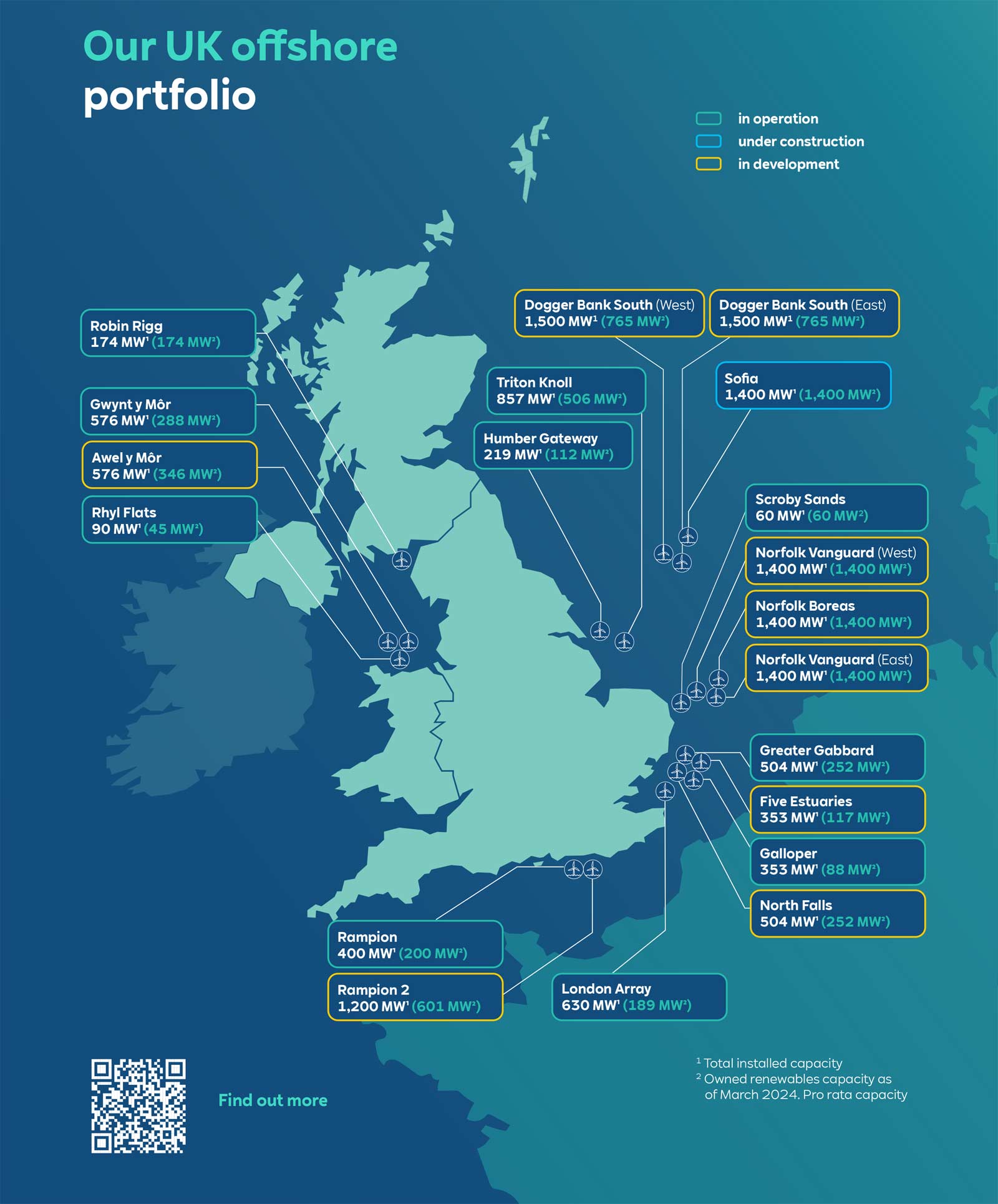 Expensive Offshore Wind Farms A Shift In Industry Favor
May 04, 2025
Expensive Offshore Wind Farms A Shift In Industry Favor
May 04, 2025
