Multiple Studies Link Shingles Vaccine To Lower Dementia Risk
Table of Contents
The Shingles Vaccine: A Closer Look
The shingles vaccine is designed to protect against herpes zoster, the virus responsible for chickenpox and its reactivation as shingles. Many misunderstand the vaccine, believing it's only for older adults or that it carries significant risks. In reality, the vaccine is a safe and effective preventative measure available in several formulations, including Zostavax and Shingrix.
- How it Works: The vaccine stimulates the immune system to produce antibodies against the varicella-zoster virus, preventing shingles outbreaks and their complications, such as postherpetic neuralgia (PHN).
- Effectiveness: The Shingrix vaccine, a newer version, boasts a significantly higher effectiveness rate (over 90%) in preventing shingles compared to its predecessor.
- Side Effects: Common side effects are typically mild and temporary, including pain, redness, or swelling at the injection site. More serious side effects are rare.
Dementia: Understanding the Growing Threat
Dementia encompasses a range of neurological disorders characterized by progressive cognitive decline. Alzheimer's disease is the most common type, but others include vascular dementia, frontotemporal dementia, and Lewy body dementia. Dementia profoundly impacts individuals, affecting their memory, thinking, and ability to perform daily tasks. It also places a significant burden on families and caregivers.
- Global Impact: Dementia affects tens of millions globally, and its prevalence is projected to rise dramatically due to the aging population.
- Risk Factors: Age is the most significant risk factor, but genetics, lifestyle choices (including diet, exercise, and smoking), and underlying health conditions also play crucial roles.
- Economic Burden: The cost of dementia care is staggering, impacting healthcare systems and economies worldwide. Current treatment options primarily focus on managing symptoms and slowing progression, but there's no cure.
The Connection Between Shingles Vaccine and Reduced Dementia Risk: Evidence from Multiple Studies
Several studies have hinted at a correlation between shingles vaccination and a reduced risk of developing dementia. While more research is needed to establish causality, the findings are intriguing. These studies, though varying in methodology and sample size, consistently suggest a potential protective effect. (Specific studies and links would be inserted here if available.)
- Key Findings: Studies have reported a statistically significant association between shingles vaccination and a lower incidence of dementia, particularly Alzheimer's disease.
- Potential Mechanisms: Researchers hypothesize that the vaccine's impact on immune function and inflammation may contribute to its neuroprotective effects. A strong immune system might help combat the inflammatory processes implicated in dementia development.
- Limitations: The research is ongoing, and more large-scale, longitudinal studies are needed to confirm these findings and explore the underlying mechanisms.
Is it a Direct Cause-and-Effect Relationship?
It's crucial to distinguish between correlation and causation. While studies show an association between shingles vaccination and reduced dementia risk, it doesn't definitively prove a direct causal link. Other factors could be at play, such as overall health status and lifestyle choices influencing both vaccination uptake and dementia risk. Further research is essential to determine if the shingles vaccine directly impacts dementia development or if it's an indirect association.
Conclusion: Protecting Your Brain Health: The Role of the Shingles Vaccine
Emerging evidence suggests a potential link between the shingles vaccine and a reduced risk of developing dementia. While more research is required to establish a definitive causal relationship, the findings highlight the importance of preventative measures in combating this devastating disease. The shingles vaccine offers benefits beyond preventing shingles; it may also play a role in promoting brain health and potentially reducing dementia risk.
Call to action: Discuss shingles vaccination with your healthcare provider to assess your suitability. Take proactive steps towards dementia prevention, including healthy lifestyle choices and exploring the potential benefits of the shingles vaccine in reducing dementia risk. Don't hesitate to ask your doctor about the shingles vaccination and its potential role in preventing dementia. Protecting your brain health should be a priority, and the shingles vaccine might be a significant part of that strategy.

Featured Posts
-
 The Unraveling Of Elon Musks Autonomous Taxi Plans
Apr 25, 2025
The Unraveling Of Elon Musks Autonomous Taxi Plans
Apr 25, 2025 -
 Zuckerbergs New Chapter Navigating The Trump Presidency
Apr 25, 2025
Zuckerbergs New Chapter Navigating The Trump Presidency
Apr 25, 2025 -
 Planning Your Stagecoach 2025 Trip What You Need To Know
Apr 25, 2025
Planning Your Stagecoach 2025 Trip What You Need To Know
Apr 25, 2025 -
 New Dope Thief Trailer Shows Brian Tyree Henry And Wagner Moura As Undercover Agents
Apr 25, 2025
New Dope Thief Trailer Shows Brian Tyree Henry And Wagner Moura As Undercover Agents
Apr 25, 2025 -
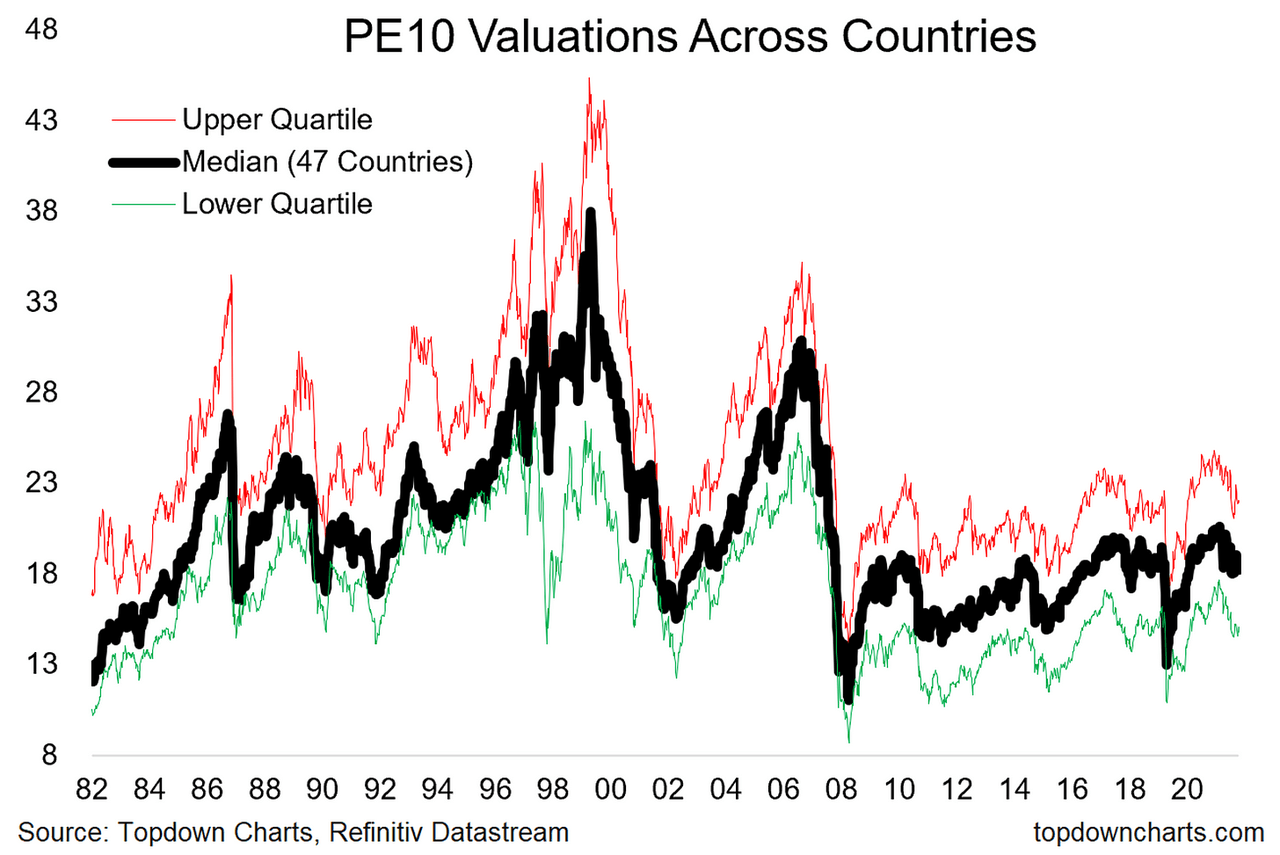 Why Current Stock Market Valuations Shouldnt Deter Investors Bof A Analysis
Apr 25, 2025
Why Current Stock Market Valuations Shouldnt Deter Investors Bof A Analysis
Apr 25, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Dzilijan Anderson Ikona Stila U Retro Haljini
Apr 30, 2025
Dzilijan Anderson Ikona Stila U Retro Haljini
Apr 30, 2025 -
 50
Apr 30, 2025
50
Apr 30, 2025 -
 Is Age Just A Number Perspectives On Aging And Relationships
Apr 30, 2025
Is Age Just A Number Perspectives On Aging And Relationships
Apr 30, 2025 -
 Elegantna Dzilijan Anderson U Novoj Retro Kreaciji
Apr 30, 2025
Elegantna Dzilijan Anderson U Novoj Retro Kreaciji
Apr 30, 2025 -
 Analyzing Remember Monday The Uks Response To Online Hate Through Eurovision
Apr 30, 2025
Analyzing Remember Monday The Uks Response To Online Hate Through Eurovision
Apr 30, 2025
