Ontario's $14.6 Billion Deficit: Tariff Impacts And Economic Outlook
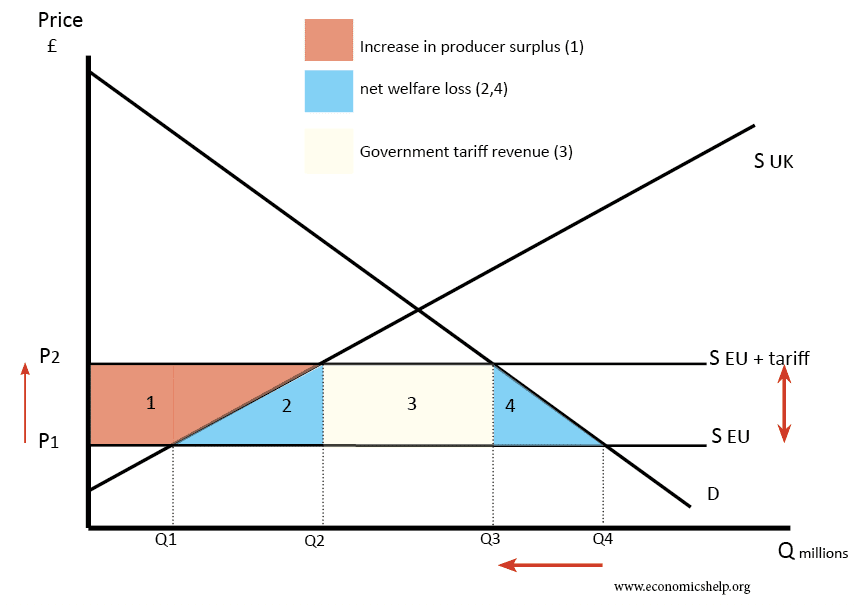
Table of Contents
The Role of Tariffs in Ontario's Deficit
Tariffs, essentially taxes on imported goods, have significantly contributed to Ontario's burgeoning deficit. Their impact reverberates across various sectors, creating a ripple effect throughout the provincial economy.
Impact on Key Industries
Tariffs have disproportionately affected several key Ontario industries, leading to reduced competitiveness and job losses. The increased cost of imported materials and goods directly impacts production costs, making Ontario businesses less able to compete in both domestic and international markets.
- Automotive manufacturing: The automotive sector, a cornerstone of the Ontario economy, has been particularly hard hit. Higher tariffs on imported parts have increased production costs, forcing manufacturers to either absorb the increased expense or pass it on to consumers through higher vehicle prices, impacting sales and profitability. This has led to plant closures and job losses in several communities.
- Manufacturing: Many manufacturing businesses rely on imported components and raw materials. Tariffs on these inputs increase the cost of production, reducing profit margins and competitiveness. This has led to a decline in manufacturing output and employment in Ontario.
- Agriculture: The agricultural sector, while less directly impacted by tariffs on manufactured goods, faces challenges due to retaliatory tariffs imposed by other countries on Canadian agricultural exports. This reduces export opportunities and negatively affects farm incomes.
The reduced competitiveness caused by tariffs has led to:
- Loss of market share to foreign competitors.
- Decreased investment in Ontario businesses.
- Job losses across multiple sectors.
Trade Wars and Their Ripple Effect
Trade disputes and retaliatory tariffs have significantly exacerbated Ontario's economic woes. The interconnectedness of the global economy means that tariffs imposed in one area create a chain reaction, impacting numerous sectors. For example, retaliatory tariffs imposed by other countries on Canadian goods have reduced export revenue, contributing to the deficit. Statistics from [Insert Source – e.g., Statistics Canada] show a [Insert Data – e.g., X% decrease] in exports due to these trade disputes, resulting in [Insert Data – e.g., Y number] job losses.
Increased Costs for Consumers
Tariffs don't just impact businesses; they also directly affect consumers through increased prices for goods and services. Higher import costs are passed on to consumers, reducing their purchasing power and impacting consumer spending. For example, tariffs on steel have increased the cost of construction, while tariffs on certain consumer electronics have increased their retail prices. This decreased consumer confidence and spending contributes to slower economic growth and adds further pressure to Ontario's deficit.
Analyzing Ontario's Economic Outlook
Ontario's economic outlook is complex, intertwined with the challenges of the current deficit and the ongoing impact of tariffs.
Government Spending and Revenue Projections
The Ontario government has announced plans to address the deficit, including [Insert Specific Government Plans – e.g., spending cuts in specific areas, potential tax increases]. However, the realism and effectiveness of these plans are subject to debate. Critics argue that [Insert Criticisms – e.g., spending cuts may negatively impact essential services, tax increases could stifle economic growth]. The success of these measures will significantly influence Ontario's economic outlook.
Job Creation and Economic Growth Strategies
The province is implementing various job creation and economic growth strategies, focusing on [Insert Specific Strategies – e.g., investment in specific sectors, support for small and medium-sized enterprises]. However, the effectiveness of these strategies amidst the current economic climate remains uncertain. The challenge lies in balancing the need for fiscal responsibility with the need to stimulate economic growth and job creation. Diversification away from sectors heavily reliant on international trade is key to mitigating future tariff risks.
Long-Term Economic Sustainability
The long-term implications of Ontario's deficit are significant. Failure to address the underlying issues could lead to [Insert Potential Negative Consequences – e.g., reduced credit rating, increased borrowing costs, decreased investment]. However, with strategic planning and effective implementation of economic policies, Ontario can achieve long-term economic sustainability. This requires careful management of government finances, promotion of innovation, and investment in human capital.
Potential Solutions and Mitigation Strategies
Addressing Ontario's deficit and mitigating the impact of tariffs requires a multi-pronged approach.
Diversification of Trade Partners
Reducing reliance on trade partners prone to imposing tariffs is crucial. Ontario should actively explore new trade relationships and diversify its export markets, reducing its vulnerability to trade disputes. This includes strengthening trade ties with countries less likely to engage in protectionist trade policies.
Investing in Innovation and Technology
Investments in research and development, technological innovation, and advanced manufacturing can improve productivity and competitiveness, helping Ontario businesses better withstand external economic shocks such as tariffs. Government support programs aimed at fostering innovation are crucial.
Strengthening Social Safety Nets
Providing support for workers and industries affected by tariffs is essential. This involves investing in retraining programs, providing financial assistance to businesses, and strengthening social safety nets to help workers transition to new jobs.
Conclusion
Ontario's $14.6 billion deficit presents a significant challenge, exacerbated by the impact of tariffs on key industries and the broader economy. Addressing this requires a multifaceted approach that includes diversification of trade, investment in innovation, and strategic government spending. Understanding the complexities of Ontario's deficit and the influence of tariffs is crucial for both policymakers and citizens alike. Stay informed on developments regarding Ontario's deficit and its implications for the future economic stability of the province. Further research into the specific impacts of tariffs on your industry or sector is recommended to understand its effect on your business and develop strategies for navigating this challenging economic climate. Effective management of Ontario's deficit is vital for the province's long-term economic health.

Featured Posts
-
 Understanding The Investment Potential Of Uber Uber
May 17, 2025
Understanding The Investment Potential Of Uber Uber
May 17, 2025 -
 Rune Pobeduje Alcarasa U Finalu U Barceloni Uprkos Alcarasovoj Povredi
May 17, 2025
Rune Pobeduje Alcarasa U Finalu U Barceloni Uprkos Alcarasovoj Povredi
May 17, 2025 -
 Everything We Know About Andor Season 2 Release Date And Trailer
May 17, 2025
Everything We Know About Andor Season 2 Release Date And Trailer
May 17, 2025 -
 New York Knicks Suffer Devastating Loss Thibodeau Calls For More Resolve
May 17, 2025
New York Knicks Suffer Devastating Loss Thibodeau Calls For More Resolve
May 17, 2025 -
 The Wnbas Future Angel Reeses Perspective On Player Demands
May 17, 2025
The Wnbas Future Angel Reeses Perspective On Player Demands
May 17, 2025
