Texas Measles Cases Rise: Unlinked To Major Outbreak
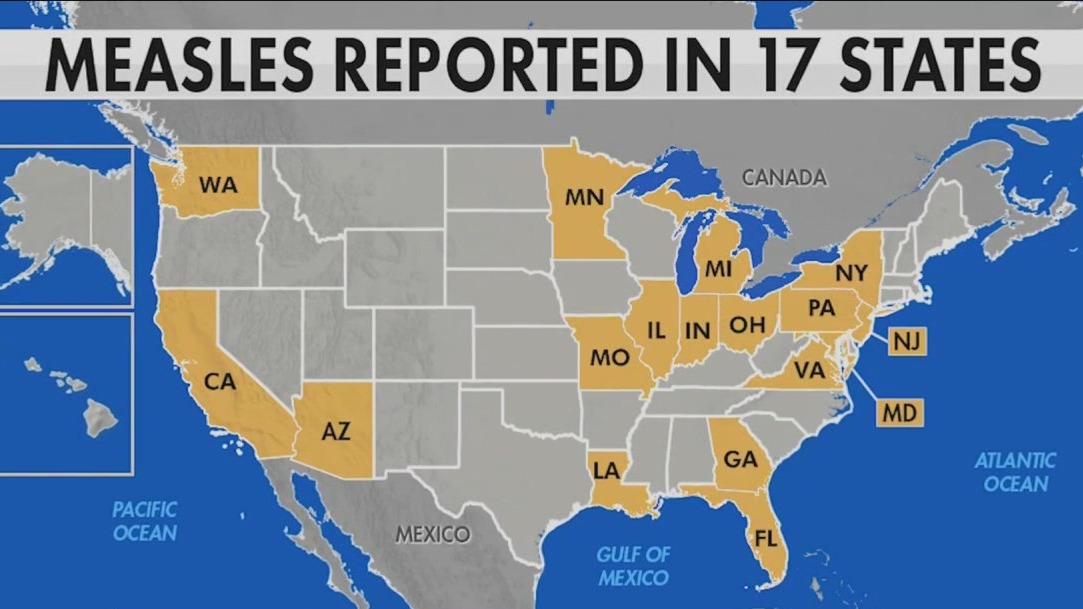
Table of Contents
Current Statistics and Geographic Distribution of Texas Measles Cases
The recent increase in Texas measles cases is alarming. Data from the Texas Department of State Health Services (DSHS) shows a [Insert Percentage]% increase in reported cases compared to the same period last year, totaling [Insert Number] confirmed cases. The affected areas are primarily concentrated in [List Specific Counties or Regions], indicating potential localized outbreaks rather than a widespread epidemic.
Key data points highlight the severity of the situation:
- Total number of cases reported: [Insert Number]
- Age range of affected individuals: Primarily [Specify Age Range], with a notable number of cases among unvaccinated individuals.
- Vaccination status of affected individuals: [Insert Data on Vaccination Status – if available; otherwise, state "Data on vaccination status is currently being collected and analyzed."]
- Hospitalizations and complications related to measles cases: [Insert Number] hospitalizations have been reported, with [mention any complications like pneumonia or encephalitis, if available].
Investigation into the Cause: Why are Texas Measles Cases Rising Independently?
Health officials are actively investigating the reasons behind this independent rise in Texas measles cases. While the cases are not linked to larger outbreaks, several factors may be contributing:
- Low vaccination rates in specific communities: Pockets of low vaccination rates, particularly in certain counties, leave communities vulnerable to measles outbreaks. This highlights the importance of targeted vaccination campaigns in these areas.
- International travel and potential exposure: Travel to regions with higher measles incidence could be a factor, though currently, investigations haven't established a clear link.
- Decreased herd immunity in certain areas: Lower vaccination rates translate to decreased herd immunity, making it easier for the virus to spread.
- Spread within unvaccinated populations: The virus is highly contagious, and spread within unvaccinated populations can lead to rapid increases in cases.
The lack of connection to major outbreaks elsewhere suggests that localized factors within Texas are the primary drivers of this recent increase.
Public Health Response and Prevention Measures
The Texas Department of State Health Services (DSHS) and local health authorities are implementing several measures to control the spread of measles:
- Enhanced surveillance: Increased monitoring of measles cases and potential outbreaks.
- Targeted vaccination campaigns: Focused efforts to increase vaccination rates in affected areas.
- Public health messaging: Dissemination of information about measles symptoms, prevention, and vaccination.
Recommended preventative measures include:
- MMR vaccination: The measles-mumps-rubella (MMR) vaccine is highly effective in preventing measles. Two doses are recommended for complete protection.
- Avoiding contact with infected individuals: Stay away from individuals exhibiting measles symptoms.
- Steps to take if symptoms appear: Seek immediate medical attention if you suspect measles.
- Information on accessing MMR vaccines: Contact your doctor or local health department to schedule your MMR vaccination.
You can find more information and locate vaccination resources at: [Link to Texas DSHS website] and [Link to CDC website].
The Importance of Vaccination in Preventing Measles Outbreaks
The MMR vaccine is highly effective, reducing the risk of measles by [Insert Percentage]%. Despite its safety and effectiveness, some misconceptions persist. The MMR vaccine has been rigorously tested and is safe for most individuals. Achieving high vaccination rates is crucial for establishing herd immunity, protecting even those who cannot receive the vaccine due to medical reasons. Community immunity significantly reduces the risk of widespread measles outbreaks.
Conclusion: Understanding and Preventing Future Texas Measles Cases
The rise in Texas measles cases is a serious concern, but thankfully, it's currently unrelated to larger national or international outbreaks. However, this underscores the need for continued vigilance and proactive measures. Vaccination remains the most effective tool in preventing measles and protecting communities. Addressing low vaccination rates through targeted campaigns and public education is vital.
Protect yourself and your community from measles. Get vaccinated today and help prevent further increases in Texas measles cases. Visit [Link to Texas DSHS website] and [Link to CDC website] for more information on measles and vaccination.

Featured Posts
-
 Vaer Og Badetemperaturer Hopp I Sjoen
May 30, 2025
Vaer Og Badetemperaturer Hopp I Sjoen
May 30, 2025 -
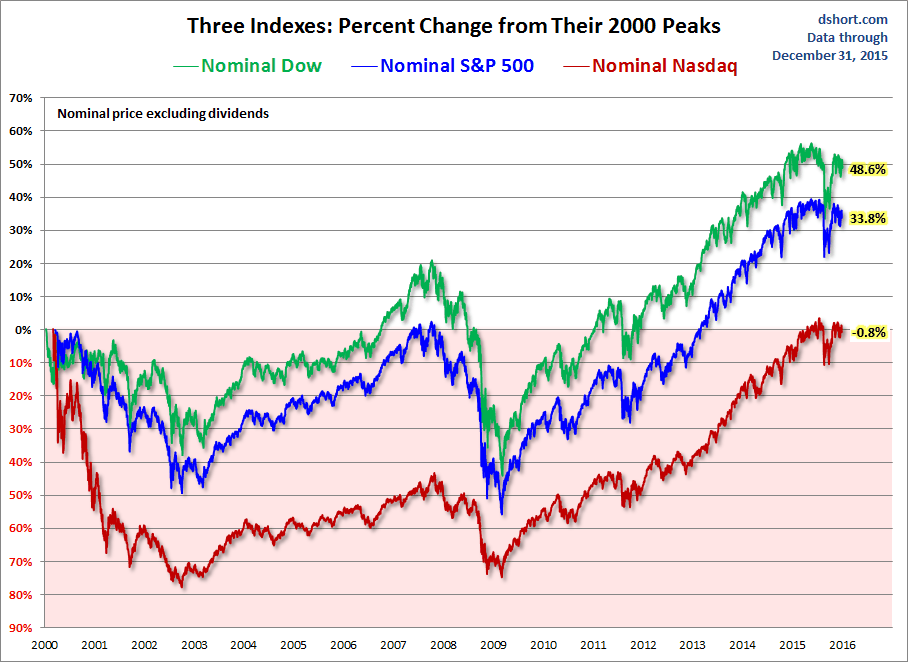 Tracking The Markets Dow And S And P 500 On May 29
May 30, 2025
Tracking The Markets Dow And S And P 500 On May 29
May 30, 2025 -
 A69 L Etat Saisit La Justice Pour Relancer Le Chantier Sud Ouest
May 30, 2025
A69 L Etat Saisit La Justice Pour Relancer Le Chantier Sud Ouest
May 30, 2025 -
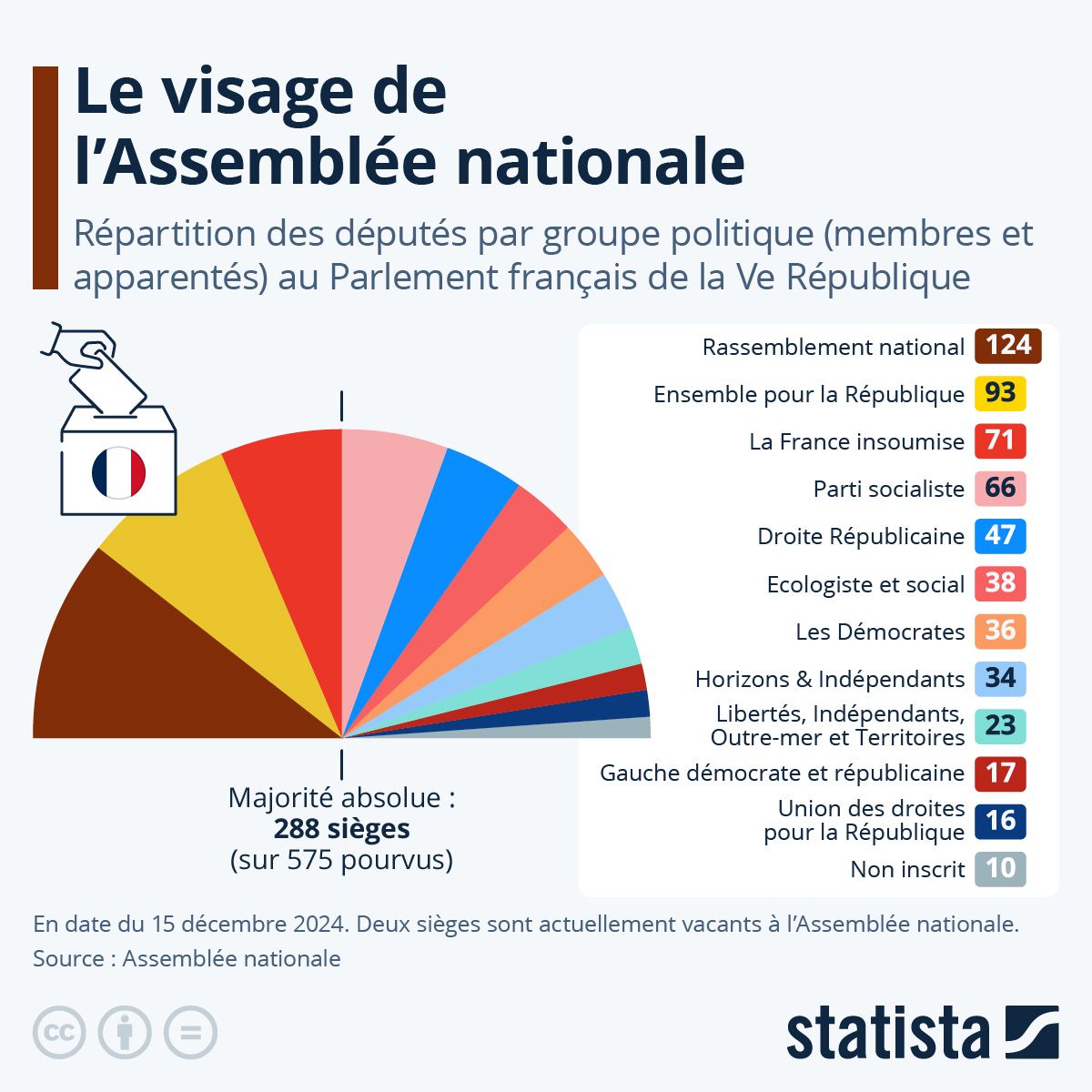 Rn A L Assemblee Nationale La Strategie De La Confrontation Face A Lfi
May 30, 2025
Rn A L Assemblee Nationale La Strategie De La Confrontation Face A Lfi
May 30, 2025 -
 The Dark Side Of French Open Spectators Abuse And Distraction Tactics Against Visiting Players
May 30, 2025
The Dark Side Of French Open Spectators Abuse And Distraction Tactics Against Visiting Players
May 30, 2025
