The End Of A School Desegregation Order: A Turning Point?
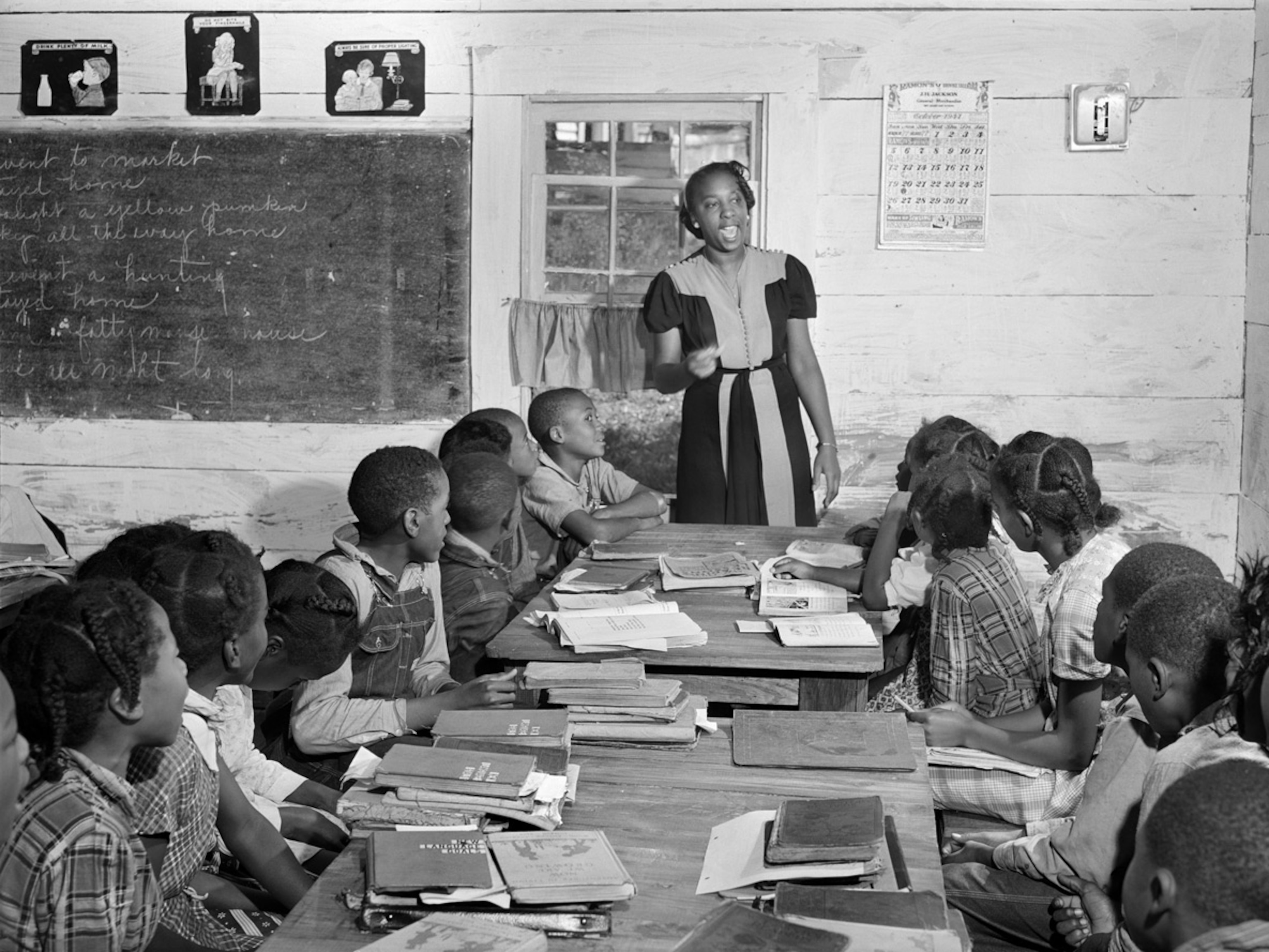

Table of Contents
The Legal Landscape and the Rationale Behind Ending Desegregation Orders
The history of school desegregation is a long and arduous struggle. Brown v. Board of Education (1954) declared state laws establishing separate public schools for black and white students unconstitutional. However, implementation was slow and often met with resistance, leading to decades of court-ordered desegregation plans. The legal arguments for ending these orders often centered around the concept of "unitary status," suggesting that school districts had achieved racial balance and eliminated the vestiges of segregation.
- Specific Cases: Many cases saw desegregation orders lifted, often after lengthy litigation and monitoring by federal courts. These rulings, while based on the claim of achieving unitary status, often overlooked persistent inequalities.
- Supreme Court Decisions: Supreme Court decisions played a pivotal role, shaping the interpretation of unitary status and influencing the pace at which desegregation orders were terminated. These rulings, while aiming for legal closure, often left significant social and educational challenges unaddressed.
- Unitary Status: The concept of "unitary status," while seemingly straightforward, proved difficult to define and measure consistently. Its application frequently led to the premature termination of desegregation orders before genuine integration was achieved, leaving room for de facto segregation to flourish.
Socioeconomic Implications: Re-segregation and its Impact
The ending of desegregation orders has raised serious concerns about re-segregation, particularly along socioeconomic lines. Historically, school segregation has been deeply intertwined with socioeconomic disparities, with marginalized communities disproportionately concentrated in under-resourced schools. The lifting of desegregation orders has, in many instances, exacerbated these inequalities.
- Statistics on Segregation: Data consistently shows a resurgence of racial and economic segregation in schools across the nation. These statistics highlight a stark reality: while legally mandated segregation has been dismantled, de facto segregation continues to thrive.
- Impact on Educational Outcomes: School segregation profoundly impacts educational outcomes. Students in under-resourced schools often lack access to quality teachers, advanced coursework, and vital resources, leading to persistent achievement gaps. This disparity directly results from the end of school desegregation orders in many districts.
- Access to Resources: Segregation limits access to quality resources and opportunities. This includes everything from well-equipped classrooms and technology to extracurricular activities and college preparatory programs, further perpetuating the cycle of inequality.
Educational Outcomes: Assessing the Effects on Student Achievement and Diversity
The impact of ending desegregation orders on student achievement is a subject of ongoing debate. While some argue that the removal of court oversight has led to improved educational outcomes in certain contexts, others point to a widening achievement gap between students of different racial and socioeconomic backgrounds.
- Data Comparison: Comparative studies examining student achievement before and after the termination of desegregation orders reveal mixed results. However, many studies indicate that the achievement gap has not narrowed and, in some cases, has widened significantly, especially in previously integrated school districts.
- School Climate and Intergroup Relations: The end of desegregation orders has, in many cases, negatively impacted school climate and intergroup relations. Increased racial and socioeconomic segregation contributes to a less diverse and inclusive learning environment.
- Role of School Choice: School choice initiatives, while often presented as promoting diversity, have in some cases exacerbated segregation by allowing families to opt out of integrated schools. This highlights the complexity of addressing segregation through policy interventions.
The Role of Community and Policy Responses in Addressing Segregation
Addressing school segregation requires a multi-faceted approach involving both community engagement and effective policy interventions. Local communities play a crucial role in shaping school integration efforts, while federal and state policies significantly impact the landscape of school segregation.
- Community-Based Programs: Successful community-based integration programs often rely on strong parent involvement, collaboration between schools and community organizations, and a commitment to inclusive practices. Conversely, unsuccessful programs often lack these vital elements.
- Federal and State Policies: Federal and state-level policies play a crucial role in shaping school segregation. Policies promoting school integration, such as magnet schools or controlled choice plans, can be effective, while policies that exacerbate segregation, such as funding disparities or inadequate oversight, need to be addressed.
- School Choice and Segregation: The unintended consequences of school choice initiatives need careful consideration. While choice can theoretically lead to greater diversity, it often leads to increased segregation when families opt for schools that align with their socioeconomic and racial preferences.
Conclusion: Has the End of a School Desegregation Order Truly Marked a Turning Point?
The end of school desegregation orders has undeniably had a profound and complex impact on American education. While the legal rationale behind ending these orders often cited the achievement of "unitary status," the reality is far more nuanced. The data suggests that re-segregation, particularly along socioeconomic lines, has significantly impacted educational outcomes, creating and perpetuating achievement gaps. While some communities have successfully maintained integration efforts, others have seen a resurgence of segregation, highlighting the ongoing need for vigilance and proactive policies. Therefore, while the end of school desegregation orders might mark a legal turning point, the fight for true educational equality continues, demanding continued focus on dismantling de facto segregation and ensuring equitable opportunities for all students. Further research and a national dialogue are crucial to addressing the long-term effects of the end of school desegregation orders and to fostering equitable educational opportunities for all. This requires continued vigilance and proactive policies to address the lingering effects of the end of school desegregation orders and to ensure true educational equality.

Featured Posts
-
 Fortnite Fans Outraged Latest Item Shop Update Criticized
May 02, 2025
Fortnite Fans Outraged Latest Item Shop Update Criticized
May 02, 2025 -
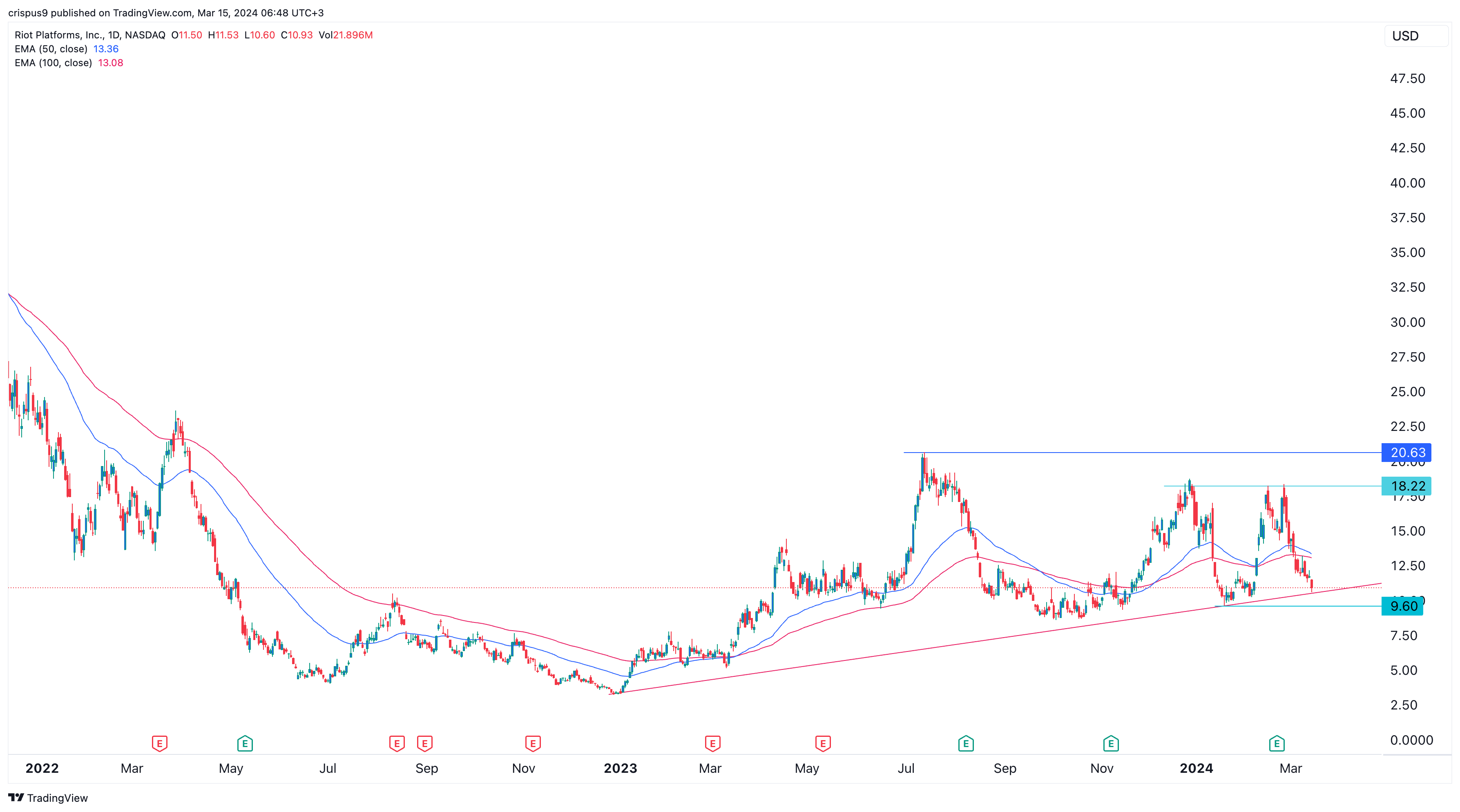 Riot Platforms Riot Stock Price Factors Contributing To The Drop
May 02, 2025
Riot Platforms Riot Stock Price Factors Contributing To The Drop
May 02, 2025 -
 Grote Stroomstoring Breda 30 000 Huishoudens Zonder Elektriciteit
May 02, 2025
Grote Stroomstoring Breda 30 000 Huishoudens Zonder Elektriciteit
May 02, 2025 -
 A Travelers Guide To This Country Practical Tips And Information
May 02, 2025
A Travelers Guide To This Country Practical Tips And Information
May 02, 2025 -
 Daisy May Cooper Shows Off Huge Engagement Ring At The Cinema
May 02, 2025
Daisy May Cooper Shows Off Huge Engagement Ring At The Cinema
May 02, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Lee Anderson Welcomes Councillor Defection To Reform Party
May 03, 2025
Lee Anderson Welcomes Councillor Defection To Reform Party
May 03, 2025 -
 Gaza Bound Aid Ship Attacked By Drones Ngo Account
May 03, 2025
Gaza Bound Aid Ship Attacked By Drones Ngo Account
May 03, 2025 -
 Sos From Gaza Bound Aid Ship Drone Attack Alleged Off Malta Coast
May 03, 2025
Sos From Gaza Bound Aid Ship Drone Attack Alleged Off Malta Coast
May 03, 2025 -
 Drones Attack Aid Ship Bound For Gaza Ngo Reports
May 03, 2025
Drones Attack Aid Ship Bound For Gaza Ngo Reports
May 03, 2025 -
 Malta Coast Aid Ship To Gaza Reports Drone Attack Issues Sos
May 03, 2025
Malta Coast Aid Ship To Gaza Reports Drone Attack Issues Sos
May 03, 2025
