The Future Of Chinese-Iranian Plastics Trade Under US Pressure
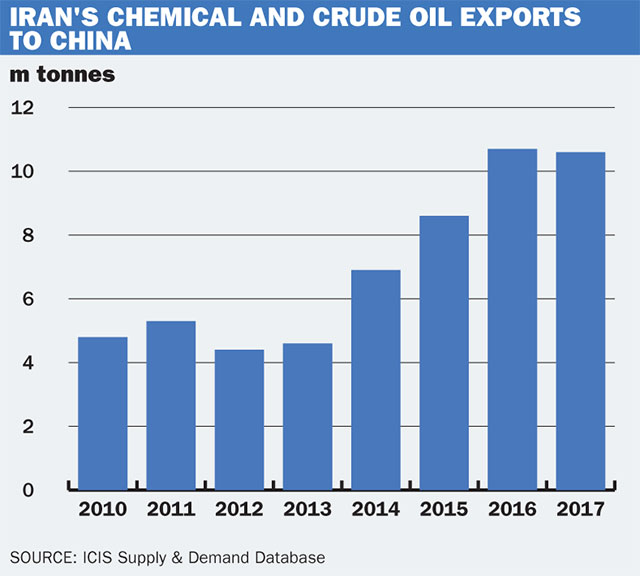
Table of Contents
The Current State of Chinese-Iranian Plastics Trade
Iran's Plastics Industry: Production Capacity and Export Potential
Iran possesses a substantial plastics industry, boasting significant production capacity and export potential. Before the intensification of US sanctions, Iran was a key exporter of various plastics, including polyethylene and polypropylene, to numerous global markets. However, sanctions have significantly impacted its export capabilities.
- Current Production: Iran's petrochemical sector, a significant contributor to its plastics industry, produces millions of tons of plastics annually.
- Key Export Markets (Pre-Sanctions): Significant exports were directed to countries in the Middle East, Asia, and Africa.
- Types of Plastics Exported: Polyethylene (PE), Polypropylene (PP), Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC), and other petrochemical-based plastics were major export items.
- Key Players: Several Iranian companies, including the National Petrochemical Company (NPC) and its subsidiaries, play a dominant role in the production and export of plastics.
- Raw Material Reliance: Iran's plastics industry relies heavily on domestically sourced natural gas and oil for raw materials, although some specialized additives may need to be imported. This dependence creates vulnerability to international pressure and supply chain disruptions.
China's Demand for Plastics and its Sourcing Strategies
China, as the world's largest plastics consumer and a global manufacturing powerhouse, has an enormous and ever-growing demand for plastics. This demand fuels a massive import market, making China a crucial player in the global plastics trade.
- Massive Demand: China's manufacturing sector, construction industry, and consumer goods market drive immense demand for various types of plastics.
- Existing Import Sources: China currently sources plastics from a wide array of countries, including Southeast Asian nations, the Middle East, and the Americas.
- Dependence on Iranian Imports: While not a primary source, Iran has historically supplied China with certain specialized plastics. The exact quantities and types are often kept confidential due to sanctions-related concerns.
- Sourcing Strategies: China employs diverse sourcing strategies, including long-term contracts with established suppliers, spot purchases from various markets, and investment in overseas petrochemical production facilities to secure its supply chain.
The Impact of US Sanctions on the Trade Relationship
Direct Sanctions and their Effect
US sanctions imposed on Iran have significantly impacted the Chinese-Iranian plastics trade. These sanctions aim to limit Iran's access to the international financial system and restrict its ability to export goods.
- Financial Restrictions: Sanctions make it difficult for Iranian companies to receive payments from Chinese buyers and for Chinese companies to make payments to Iranian suppliers.
- Shipping Limitations: Sanctions complicate the shipping of plastics between the two countries due to restrictions on insurance and the use of international shipping routes. This leads to increased transportation costs and delays.
- Legal and Regulatory Challenges: Chinese companies face substantial legal and regulatory risks when engaging in trade with Iran, fearing secondary sanctions imposed by the US.
Indirect Impacts and Circumvention Strategies
The impact of sanctions extends beyond direct restrictions. Indirect consequences include higher costs, longer delivery times, and reliance on complex and opaque financial mechanisms.
- Increased Costs: The need for alternative, often more expensive, shipping routes and financial transactions adds to the overall cost of plastics trade.
- Delays: Sanctions create delays in shipments due to additional scrutiny and complicated logistics.
- Circumvention Strategies: Despite sanctions, some trade continues through the use of third-party countries (e.g., using intermediary companies in other nations to mask the origin and destination of goods) and shadow banking systems. This creates additional risks and vulnerabilities.
- Sanctions Evasion Risks: Both Chinese and Iranian companies involved in circumventing sanctions face significant legal and financial penalties if discovered.
Potential Future Scenarios for Chinese-Iranian Plastics Trade
Adaptation and Resilience
Both China and Iran have shown remarkable resilience in the face of sanctions. Adaptation and diversification are key to navigating the ongoing challenges.
- Diversification of Trade Partners: Both countries are actively seeking alternative trade partners to reduce their dependence on each other and avoid sanctions-related risks.
- Development of Alternative Trade Routes: The exploration of land-based routes and alternative shipping lanes is crucial to bypass sanctions-related limitations on maritime trade.
- Investment in Domestic Capacity: Investing in domestic production capacity within both countries to reduce reliance on international trade is a long-term strategic goal.
- Technological Advancements: Technologies improving efficiency and reducing dependence on specific materials can mitigate the impact of sanctions.
- Regional Cooperation: Enhanced regional cooperation within the Middle East and Asia can provide support for alternative trade routes and financial mechanisms.
Geopolitical Uncertainties and their Influence
The future of Chinese-Iranian plastics trade remains inextricably linked to broader geopolitical developments.
- Nuclear Deal Outcomes: A successful nuclear deal with Iran could significantly ease sanctions, leading to a surge in trade.
- Role of Other Global Players: The actions and policies of other major global players (like Russia and the European Union) will influence the overall geopolitical environment and impact trade dynamics.
- Shifts in Global Plastics Demand: Changes in global demand for specific plastics types will affect trade flows and prices, independently of sanctions.
Conclusion
The future of Chinese-Iranian plastics trade remains uncertain under the pressure of US sanctions. The resilience of both economies, their capacity for adaptation, and the evolving geopolitical landscape will shape the trajectory of this vital trade relationship. While sanctions present significant hurdles, both China and Iran are demonstrating adaptability by diversifying their trade partners and exploring alternative routes and strategies. Understanding the intricate interplay between sanctions, geopolitical shifts, and market forces is critical to predicting future trends. Continued monitoring of US sanctions, trade policies, and the resilience of both economies is crucial for comprehending the dynamics of Chinese-Iranian plastics trade and mitigating associated risks. Further research into the specifics of Chinese-Iranian plastics trade is crucial for predicting future trends and mitigating risks.

Featured Posts
-
 Mnenieto Na Ed Shiyrn Za Riana
May 07, 2025
Mnenieto Na Ed Shiyrn Za Riana
May 07, 2025 -
 Kogda Ovechkin Pobet Rekord Grettski Noviy Prognoz Ot N Kh L
May 07, 2025
Kogda Ovechkin Pobet Rekord Grettski Noviy Prognoz Ot N Kh L
May 07, 2025 -
 Tigers Opening Win 9 6 Victory Against Mariners
May 07, 2025
Tigers Opening Win 9 6 Victory Against Mariners
May 07, 2025 -
 George Pickens Steelers Future Uncertain Could He Be Gone Before 2026
May 07, 2025
George Pickens Steelers Future Uncertain Could He Be Gone Before 2026
May 07, 2025 -
 Cavaliers Vs Knicks Prediction Will The Knicks Triumph At Msg
May 07, 2025
Cavaliers Vs Knicks Prediction Will The Knicks Triumph At Msg
May 07, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 New Mlb Rankings Angels Farm System Faces Criticism
May 08, 2025
New Mlb Rankings Angels Farm System Faces Criticism
May 08, 2025 -
 Bitcoin Market Reversal Binance Buying Volume Dominates Selling
May 08, 2025
Bitcoin Market Reversal Binance Buying Volume Dominates Selling
May 08, 2025 -
 Angels Farm System Receives Scathing Review From Mlb Insiders
May 08, 2025
Angels Farm System Receives Scathing Review From Mlb Insiders
May 08, 2025 -
 Bitcoin Buying Volume Surges On Binance First Time In Six Months
May 08, 2025
Bitcoin Buying Volume Surges On Binance First Time In Six Months
May 08, 2025 -
 Stream La Angels Baseball No Cable Needed 2025
May 08, 2025
Stream La Angels Baseball No Cable Needed 2025
May 08, 2025
