The Often Overlooked Value Of Middle Managers: A Critical Analysis
Table of Contents
The Bridge Between Leadership and Employees
Middle managers serve as a vital bridge, connecting the strategic vision of senior leadership with the day-to-day operations of employee teams. Their ability to effectively navigate this space is crucial for organizational success.
Facilitating Communication and Information Flow
Effective middle managers are masters of communication, translating complex, top-down strategies into actionable plans for their teams. They ensure that directives are clear, expectations are understood, and progress is tracked effectively. Equally important, they act as a conduit for upward communication, relaying employee feedback, concerns, and suggestions to senior leadership. This two-way communication flow is essential for fostering a healthy and productive work environment.
- Examples of communication challenges solved by effective middle managers:
- Clarifying ambiguous directives from upper management.
- Addressing employee concerns about new policies or procedures.
- Managing conflicts between team members or departments.
- Translating complex data into easily understandable reports for team members.
- Effectively communicating company-wide changes and their impact on individual teams.
Mentorship and Employee Development
Beyond communication, middle managers play a crucial role in fostering employee growth and engagement. They act as mentors, coaches, and trainers, providing guidance and support to help their team members develop their skills and advance their careers. This investment in talent development contributes directly to increased productivity and retention.
- Specific examples of mentoring activities:
- Conducting regular performance reviews and providing constructive feedback.
- Identifying training needs and providing access to relevant resources.
- Guiding employees in their career development, offering advice and support.
- Delegating tasks strategically to foster skill development.
- Recognizing and rewarding employee achievements.
Driving Operational Efficiency and Productivity
Middle managers are not simply messengers; they are the engines of operational efficiency and productivity. Their daily activities directly impact the organization's ability to achieve its goals.
Resource Allocation and Project Management
Effective middle managers are adept at resource allocation, ensuring that projects are appropriately staffed, funded, and equipped for success. They oversee project timelines, manage budgets, and prioritize tasks to ensure that resources are used efficiently and effectively.
- Examples of effective resource management and project oversight:
- Prioritizing tasks based on urgency and importance.
- Managing project deadlines and milestones.
- Optimizing workflows to eliminate bottlenecks.
- Allocating resources effectively to meet project demands.
- Monitoring progress and adjusting plans as needed.
Problem-Solving and Decision-Making
Middle managers are constantly confronted with problems requiring immediate attention and decisive action. They are responsible for resolving team conflicts, addressing operational bottlenecks, and adapting to unexpected changes. Their ability to make sound decisions quickly and efficiently is crucial for maintaining operational effectiveness.
- Types of problems commonly addressed by middle managers:
- Resolving conflicts between team members.
- Addressing operational bottlenecks and inefficiencies.
- Adapting to unexpected changes in project scope or deadlines.
- Identifying and resolving technical issues.
- Making decisions about resource allocation in the face of competing priorities.
Championing Innovation and Adaptability
Contrary to the stereotype of rigid adherence to rules, effective middle managers are often champions of innovation and adaptability. Their proximity to daily operations allows them to identify areas for improvement and proactively drive positive change.
Identifying Opportunities for Improvement
Middle managers are uniquely positioned to identify opportunities for process improvement and innovation. Their hands-on experience allows them to see inefficiencies and suggest solutions that streamline workflows, reduce costs, and boost productivity.
- Examples of process improvements initiated by middle managers:
- Streamlining workflows to reduce processing time.
- Implementing new technologies to increase efficiency.
- Suggesting cost-saving measures.
- Identifying and eliminating redundant tasks.
- Developing new training programs to improve employee skills.
Driving Change and Embracing New Strategies
Middle managers are crucial in the successful implementation of new strategies and organizational change. They translate high-level directives into practical action plans for their teams, providing support and guidance throughout the transition.
- Examples of successful change management initiatives led or supported by middle managers:
- Implementing new software or systems.
- Introducing new work processes or procedures.
- Managing organizational restructuring.
- Leading team through mergers or acquisitions.
- Successfully navigating periods of significant organizational change.
Conclusion
Middle managers are far more than just a link in the chain of command. They are vital contributors to organizational success, acting as communication hubs, mentors, problem-solvers, and drivers of innovation. While criticisms of middle management exist, this analysis highlights their critical role in bridging leadership and employees, driving operational efficiency, and championing adaptability. To dismiss their value is to overlook a significant source of organizational strength. Recognize and invest in the often-overlooked value of your middle managers for a more productive and successful organization. Investing in effective middle management translates directly into improved employee engagement, increased productivity, and a more adaptable and innovative organization. Don't underestimate the power of your middle managers—empower them!

Featured Posts
-
 Hamas October 7 Attacks A Bid To Sabotage The Israel Saudi Deal
May 19, 2025
Hamas October 7 Attacks A Bid To Sabotage The Israel Saudi Deal
May 19, 2025 -
 Last Minute Eurovision Host Change Unforeseen Circumstances Force Cancellation
May 19, 2025
Last Minute Eurovision Host Change Unforeseen Circumstances Force Cancellation
May 19, 2025 -
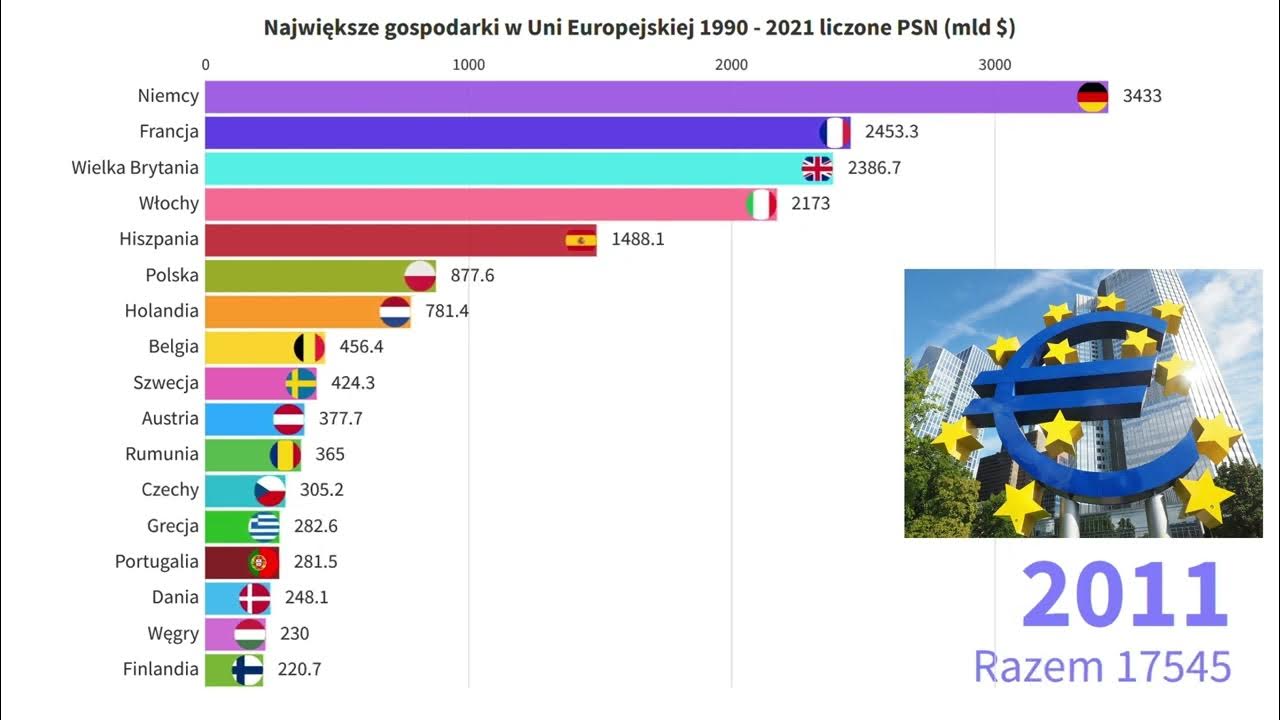 Preselectio Do Eurowizji Ranking Najwiekszych Rozczarowan
May 19, 2025
Preselectio Do Eurowizji Ranking Najwiekszych Rozczarowan
May 19, 2025 -
 Russias Largest Drone Attack On Ukraine Military Reports
May 19, 2025
Russias Largest Drone Attack On Ukraine Military Reports
May 19, 2025 -
 Will Ubers Autonomous Vehicles Drive Etf Returns
May 19, 2025
Will Ubers Autonomous Vehicles Drive Etf Returns
May 19, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 1050 V Mware Price Hike At And T Sounds The Alarm On Broadcoms Acquisition
May 19, 2025
1050 V Mware Price Hike At And T Sounds The Alarm On Broadcoms Acquisition
May 19, 2025 -
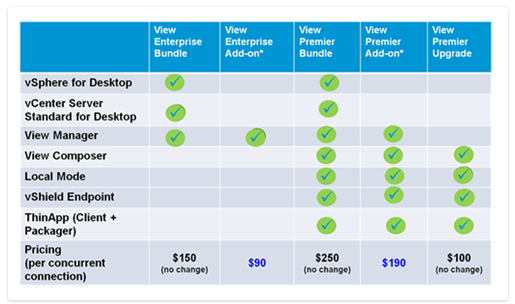 Extreme V Mware Price Increase At And T Highlights 1050 Cost Jump Due To Broadcom
May 19, 2025
Extreme V Mware Price Increase At And T Highlights 1050 Cost Jump Due To Broadcom
May 19, 2025 -
 V Mware Costs To Skyrocket At And T Details A 1050 Price Increase From Broadcom
May 19, 2025
V Mware Costs To Skyrocket At And T Details A 1050 Price Increase From Broadcom
May 19, 2025 -
 Is Canadian Tires Pursuit Of Hudsons Bay A Wise Move
May 19, 2025
Is Canadian Tires Pursuit Of Hudsons Bay A Wise Move
May 19, 2025 -
 Will A Canadian Tire Hudsons Bay Partnership Succeed A Detailed Analysis
May 19, 2025
Will A Canadian Tire Hudsons Bay Partnership Succeed A Detailed Analysis
May 19, 2025
