U.S. Federal Reserve Rate Decision: A Deep Dive Into Current Economic Conditions
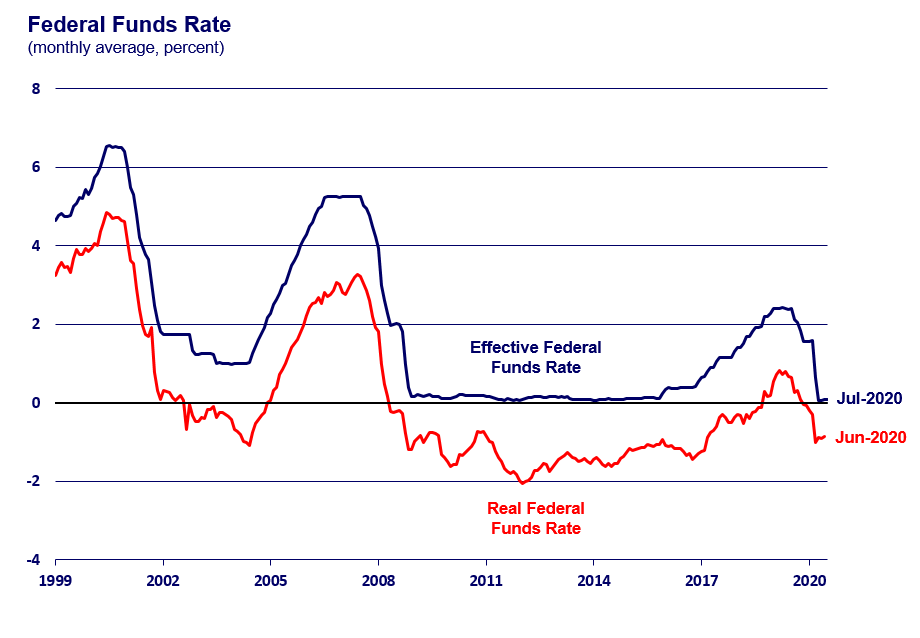
Table of Contents
Inflationary Pressures and the Fed's Response
Current inflation rates are a primary concern for the Federal Reserve. High inflation erodes purchasing power, impacting consumer spending and overall economic stability. The Fed's mandate includes maintaining price stability, and its response to inflation is a key factor in its interest rate decisions.
- Current CPI and PPI figures: Recent data shows [Insert latest CPI and PPI figures and their percentage changes. Source the data with a reputable link]. These figures indicate [Interpret the figures – e.g., persistent inflationary pressure, signs of easing inflation, etc.].
- Analysis of core inflation vs. headline inflation: Core inflation, which excludes volatile food and energy prices, provides a clearer picture of underlying inflationary pressures. [Compare and contrast core and headline inflation figures, and explain the significance of the difference].
- Impact of supply chain disruptions on inflation: Supply chain bottlenecks continue to contribute to inflationary pressures by limiting the availability of goods and increasing prices. [Explain how specific supply chain issues are impacting inflation, citing examples].
- Discussion of wage growth and its contribution to inflation: Strong wage growth can fuel inflation if businesses pass increased labor costs onto consumers. [Discuss the current state of wage growth and its potential impact on inflation. Provide data to support your analysis].
The Fed's response to inflation often involves adjusting interest rates. Higher interest rates make borrowing more expensive, slowing down economic activity and reducing demand-pull inflation. The effectiveness of this monetary policy tool depends on various economic factors.
Employment Data and Labor Market Dynamics
The U.S. labor market is another key indicator the Fed considers when making interest rate decisions. A strong labor market typically suggests a healthy economy, but it can also contribute to inflationary pressures if wage growth outpaces productivity gains.
- Unemployment rate and its significance: The current unemployment rate is [Insert latest unemployment rate and source]. A low unemployment rate often indicates a tight labor market, which can lead to upward pressure on wages.
- Job growth figures and sector-specific analysis: Job growth figures for [Insert latest month/quarter] show [Insert job growth figures and source]. Analyzing job growth across different sectors provides insights into the overall health of the economy. [Provide a brief analysis of job growth in key sectors].
- Labor force participation rate and its trends: The labor force participation rate is [Insert latest data and source]. Changes in this rate reflect shifts in the workforce and can impact both unemployment and inflation.
- Wage growth and its implications for inflation: As mentioned earlier, wage growth is a crucial factor in the inflation equation. [Analyze current wage growth trends and their potential inflationary impact].
The Federal Reserve closely monitors employment data to assess the overall health of the economy and to gauge the potential for inflationary pressures.
Economic Growth and GDP Projections
The pace of economic growth is a critical element in the Fed's decision-making process. Strong economic growth can be positive, but excessively rapid growth can fuel inflation. Conversely, weak growth can signal a potential recession.
- Recent GDP growth figures: The most recent GDP growth figures show [Insert latest GDP growth figures and source]. This indicates [Interpret the figures – e.g., strong growth, slowing growth, contraction].
- Forecasts for future economic growth: Economic forecasters predict [Insert forecasts and source] for future GDP growth. These projections take into account various factors, including interest rates, consumer spending, and business investment.
- Impact of global economic factors on U.S. growth: Global economic conditions significantly impact the U.S. economy. [Discuss the influence of global factors, such as trade wars, geopolitical instability, or global recessions].
- Discussion of potential recessionary risks: [Analyze the current risks of a recession, citing relevant economic indicators and expert opinions].
Geopolitical Factors and Their Influence
Geopolitical events exert considerable influence on the U.S. economy and the Federal Reserve's policy decisions.
- Impact of the war in Ukraine on energy prices and inflation: The war in Ukraine has significantly disrupted global energy markets, leading to higher energy prices and contributing to inflation. [Elaborate on the impact of the war on energy prices and inflation, providing data].
- Effects of global supply chain disruptions: Ongoing supply chain disruptions continue to impact the availability and prices of goods, exacerbating inflationary pressures. [Explain how geopolitical instability influences supply chains and inflation].
- Influence of international trade relations: Changes in international trade relations, such as trade wars or sanctions, can significantly impact the U.S. economy and influence the Fed's policy decisions. [Provide examples of how trade relations affect the U.S. economy and the Fed's decisions].
The Federal Reserve's Policy Tools and Their Effectiveness
The Federal Reserve employs several policy tools to influence the economy and manage inflation.
- Federal funds rate and its mechanism: The federal funds rate is the target rate that the Fed sets for overnight lending between banks. Changes to this rate directly impact other interest rates in the economy.
- Quantitative easing (QE) and quantitative tightening (QT): QE involves the Fed buying securities to increase the money supply, while QT is the opposite, reducing the money supply. These actions influence interest rates and credit availability.
- Forward guidance and its role in managing expectations: The Fed uses forward guidance to communicate its intentions and manage market expectations about future interest rate changes.
The effectiveness of these policy tools depends on various economic factors and can have unintended consequences.
Conclusion
The U.S. Federal Reserve rate decision is a complex process influenced by a multitude of interacting economic factors. Understanding the current inflationary pressures, labor market dynamics, economic growth projections, and geopolitical influences is vital for interpreting the Fed's actions. By analyzing these elements, we can better anticipate future interest rate decisions and their potential impact on the economy. Staying informed about the U.S. Federal Reserve Rate Decision and its implications is crucial for navigating the ever-changing economic landscape. Keep following reputable financial news sources for the latest updates and analysis of the Federal Reserve's monetary policy to make informed decisions. Understanding the intricacies of the interest rate decision allows for better financial planning and strategic investments.

Featured Posts
-
 Jazz Cash And K Trade A New Era Of Accessible Stock Trading
May 09, 2025
Jazz Cash And K Trade A New Era Of Accessible Stock Trading
May 09, 2025 -
 Rethinking Stephen King 4 Unexpected Randall Flagg Theories
May 09, 2025
Rethinking Stephen King 4 Unexpected Randall Flagg Theories
May 09, 2025 -
 Knights Edge Wild In Overtime Barbashev Scores Game Winner
May 09, 2025
Knights Edge Wild In Overtime Barbashev Scores Game Winner
May 09, 2025 -
 56 M In Funding To Address Nursing Shortages At Community Colleges
May 09, 2025
56 M In Funding To Address Nursing Shortages At Community Colleges
May 09, 2025 -
 Dogecoins Price Volatility The Impact Of Elon Musks Recent Activities
May 09, 2025
Dogecoins Price Volatility The Impact Of Elon Musks Recent Activities
May 09, 2025
