A Conclave: The Process Of Electing The Pope
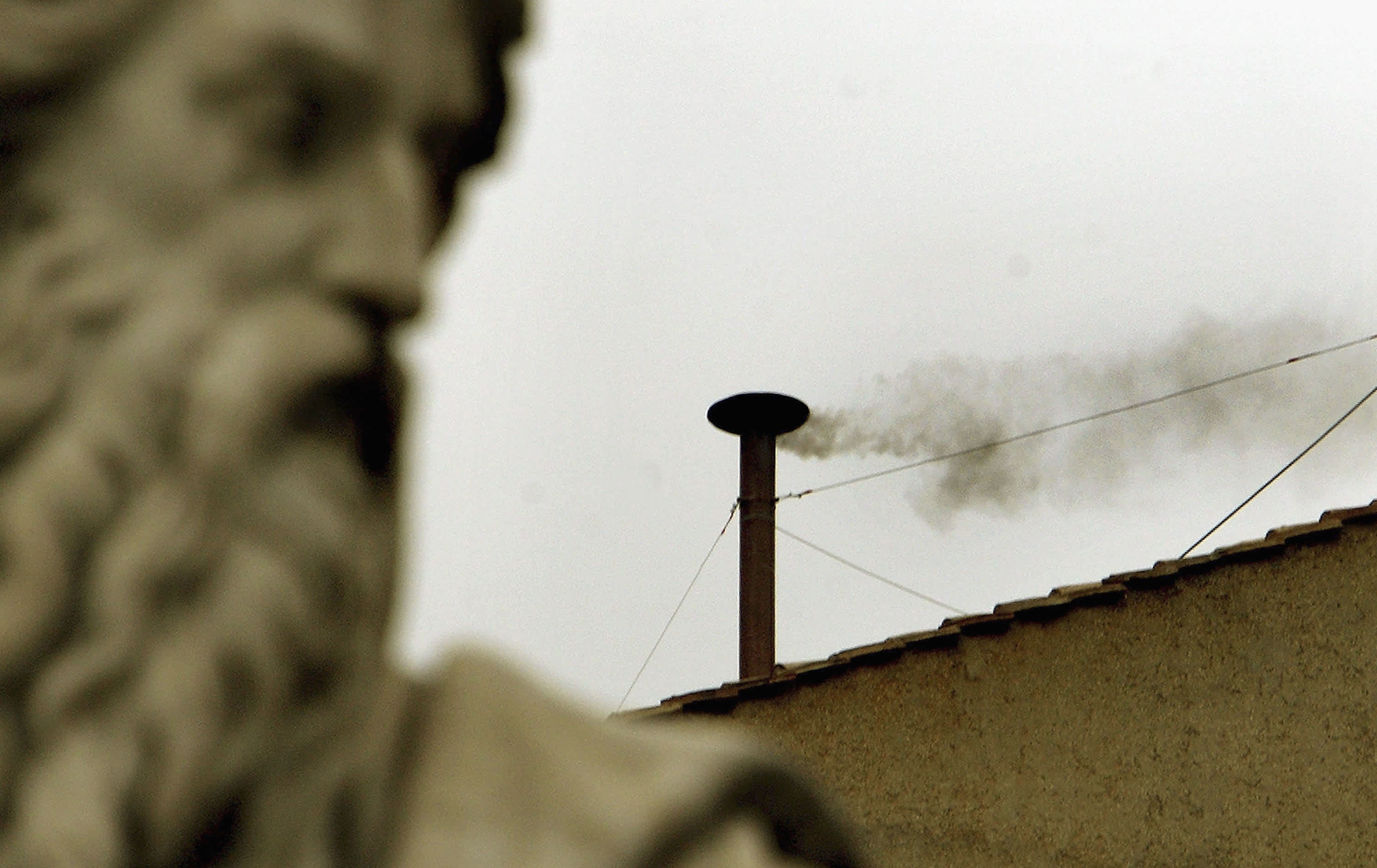

Table of Contents
The Prerequisites to a Papal Conclave
Death or Resignation of the Pope
The death or resignation of the reigning Pope automatically initiates the Conclave process. Historically, papal resignations were extremely rare, but the resignation of Pope Benedict XVI in 2013 marked a significant departure from tradition. This event highlighted the evolving understanding of the papacy and the possibility of a Pope stepping down due to age or health concerns.
- Official Announcement: The death of a Pope is officially announced by the Cardinal Camerlengo, who temporarily administers the Church during the Sede Vacante.
- Sede Vacante: The period between the death or resignation of a Pope and the election of his successor is known as the Sede Vacante ("Vacant See"). During this time, the governance of the Church is entrusted to the College of Cardinals.
- Role of the Camerlengo: The Camerlengo manages the temporal affairs of the Holy See during the Sede Vacante, ensuring the smooth functioning of the Vatican City State.
The College of Cardinals
The Conclave is exclusively composed of Cardinals under the age of 80. These Cardinals are key figures within the Catholic Church's hierarchical structure, advising the Pope and playing a critical role in its governance. The selection of Cardinals themselves is a complex process, often involving extensive consultations and considerations by the reigning Pope.
- Cardinal-Bishops: These Cardinals typically hold the highest positions within the Church hierarchy. They are usually the bishops of the seven suburbicarian dioceses surrounding Rome.
- Cardinal-Priests: These Cardinals typically serve as archbishops or bishops of various dioceses around the world.
- Cardinal-Deacons: These Cardinals typically serve as heads of various departments within the Roman Curia (the central government of the Catholic Church). Their role in the Conclave is primarily advisory.
Preparation for the Conclave
The period leading up to the Conclave involves significant logistical preparations, including the gathering of eligible Cardinals in Rome. This necessitates meticulous planning and coordination to ensure the smooth operation of the Conclave.
- Security Measures: The Vatican implements stringent security measures to protect the Cardinals and maintain the secrecy of the Conclave.
- Accommodation: The Cardinals are housed within the Apostolic Palace during the Conclave, often in relatively simple accommodations.
- Sealing of the Sistine Chapel: The Sistine Chapel, where the voting takes place, is meticulously prepared and sealed to prevent any external interference.
The Conclave Process Itself
Seclusion and the Oath of Secrecy
Once the Cardinals have assembled, they are sequestered within the Apostolic Palace and take a solemn oath of secrecy. This oath, steeped in centuries of tradition, ensures the confidentiality of the deliberations and prevents external influence on the election.
- Living Conditions: The Cardinals live under strict conditions, with limited access to outside communication and a regulated daily routine.
- Communications Restrictions: Contact with the outside world is strictly limited to essential matters only.
- Integrity of the Process: The oath of secrecy ensures the integrity of the Conclave and prevents any compromise to the process.
The Voting Process
The voting process involves multiple rounds of balloting (known as "scrutinies"). The Cardinals cast their votes secretly and the ballots are meticulously counted by appointed scrutineers. A two-thirds majority is required for a valid election.
- Scrutinies: Each voting round is called a scrutiny. Multiple scrutinies may be necessary before a Pope is elected.
- Role of Scrutineers: The scrutineers ensure the secrecy and integrity of the voting process.
- Invalid Ballots: Ballots that are invalidated due to error or improper markings are removed from the count.
The Election of the Pope
When a candidate receives the required two-thirds majority of votes, the election is declared. The announcement, "Habemus Papam!" ("We have a Pope!") is made from the balcony of St. Peter's Basilica.
- White Smoke Signal: The appearance of white smoke from the Sistine Chapel chimney signifies the election of a new Pope.
- Formal Announcement: The new Pope is formally presented to the world from the balcony of St. Peter's Basilica.
- Urbi et Orbi: The new Pope delivers his first address (Urbi et Orbi – "to the city and to the world").
Post-Conclave Procedures
The Inauguration Mass
The newly elected Pope's formal installation takes place during a special Inauguration Mass in St. Peter's Square. This ceremony is a significant event attended by many dignitaries and members of the Catholic faithful.
- Ceremony Details: The Mass features specific prayers, rites and rituals that symbolize the commencement of the new Pope’s papacy.
- Attendance: The Mass typically draws a large crowd of faithful and world leaders.
- Official Acts: The newly elected Pope begins to exercise his responsibilities as the head of the Catholic Church.
The Papal Name and Seal
The Pope traditionally selects a new name upon his election. This name can be significant, reflecting a spiritual aspiration or honoring a saint. The Papal Seal is also created at this time.
- Tradition of Choosing a Name: The selection of a papal name often reflects the chosen Pope's aspirations for his papacy or honors a significant figure in church history.
- Meaning of the Papal Name: The significance of the name is often discussed and analyzed following its selection.
- Papal Seal: The Papal Seal is a symbol of the Pope's authority.
Conclusion
The Conclave, a process steeped in tradition and secrecy, is a pivotal event in the Catholic Church. Understanding its intricacies provides insight into the selection of the leader of over a billion Catholics worldwide. From the preparations leading up to the Conclave to the election and installation of the new Pope, every step carries immense weight and historical significance. To learn more about the fascinating history and details of Papal elections, further research into the intricacies of the Conclave is highly recommended. Deepen your knowledge of this important process by exploring other resources on the Conclave and the election of the Pope.

Featured Posts
-
 Analyzing The Seattle Mariners Retention Of Their Starting Pitchers
May 07, 2025
Analyzing The Seattle Mariners Retention Of Their Starting Pitchers
May 07, 2025 -
 Revealing The Voice Actor Behind Kenny In The White Lotus Season 3
May 07, 2025
Revealing The Voice Actor Behind Kenny In The White Lotus Season 3
May 07, 2025 -
 Who Wants To Be A Millionaire Celebrity Special Behind The Scenes Look At The Popular Show
May 07, 2025
Who Wants To Be A Millionaire Celebrity Special Behind The Scenes Look At The Popular Show
May 07, 2025 -
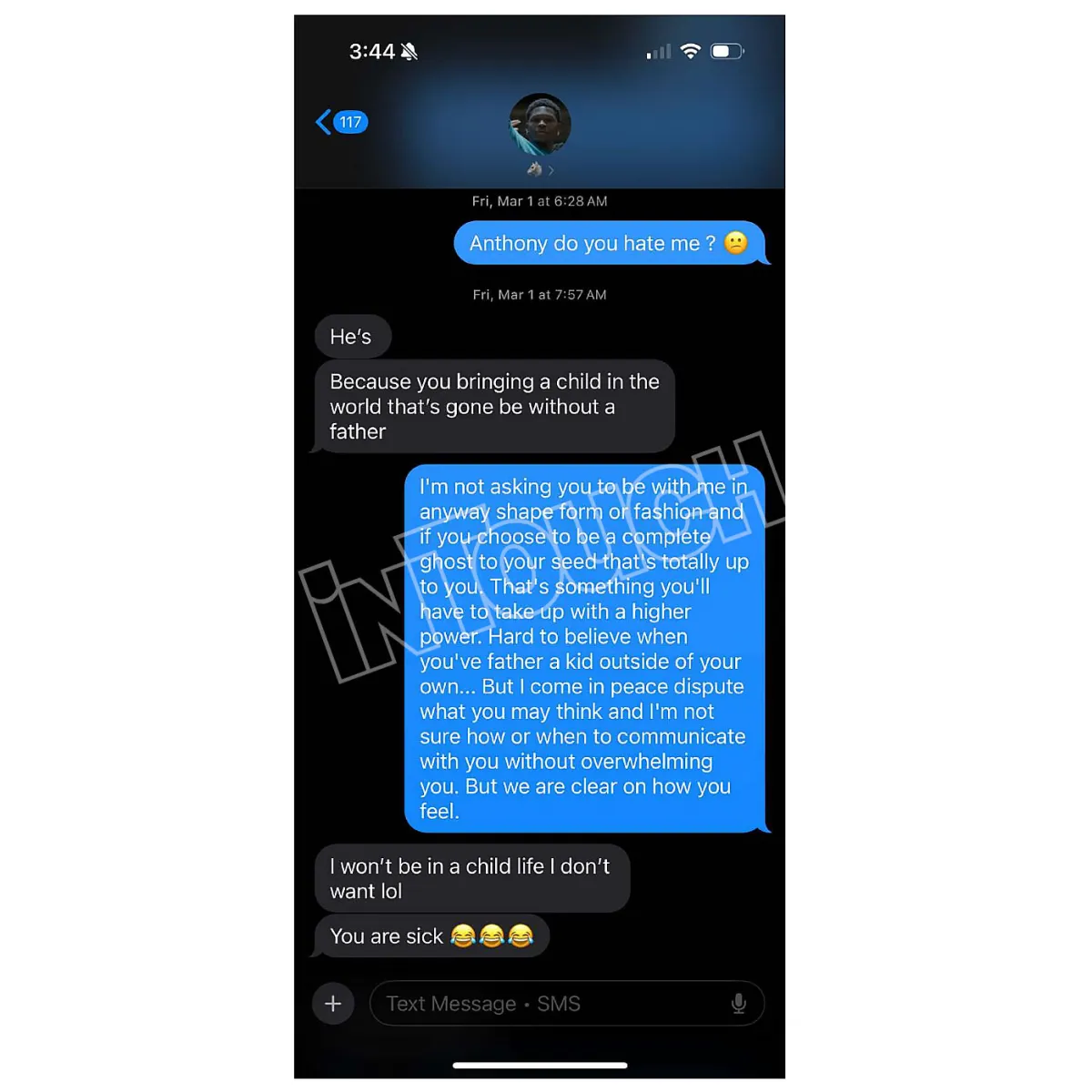 The Anthony Edwards Baby Mama Saga Unfolding Online
May 07, 2025
The Anthony Edwards Baby Mama Saga Unfolding Online
May 07, 2025 -
 Ms Hokej Svedi S Hvezdnou Nhl Sestavou Cesi Narazi Na Nemecko
May 07, 2025
Ms Hokej Svedi S Hvezdnou Nhl Sestavou Cesi Narazi Na Nemecko
May 07, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Bitcoin Rebound Investing Strategies For The Future
May 08, 2025
Bitcoin Rebound Investing Strategies For The Future
May 08, 2025 -
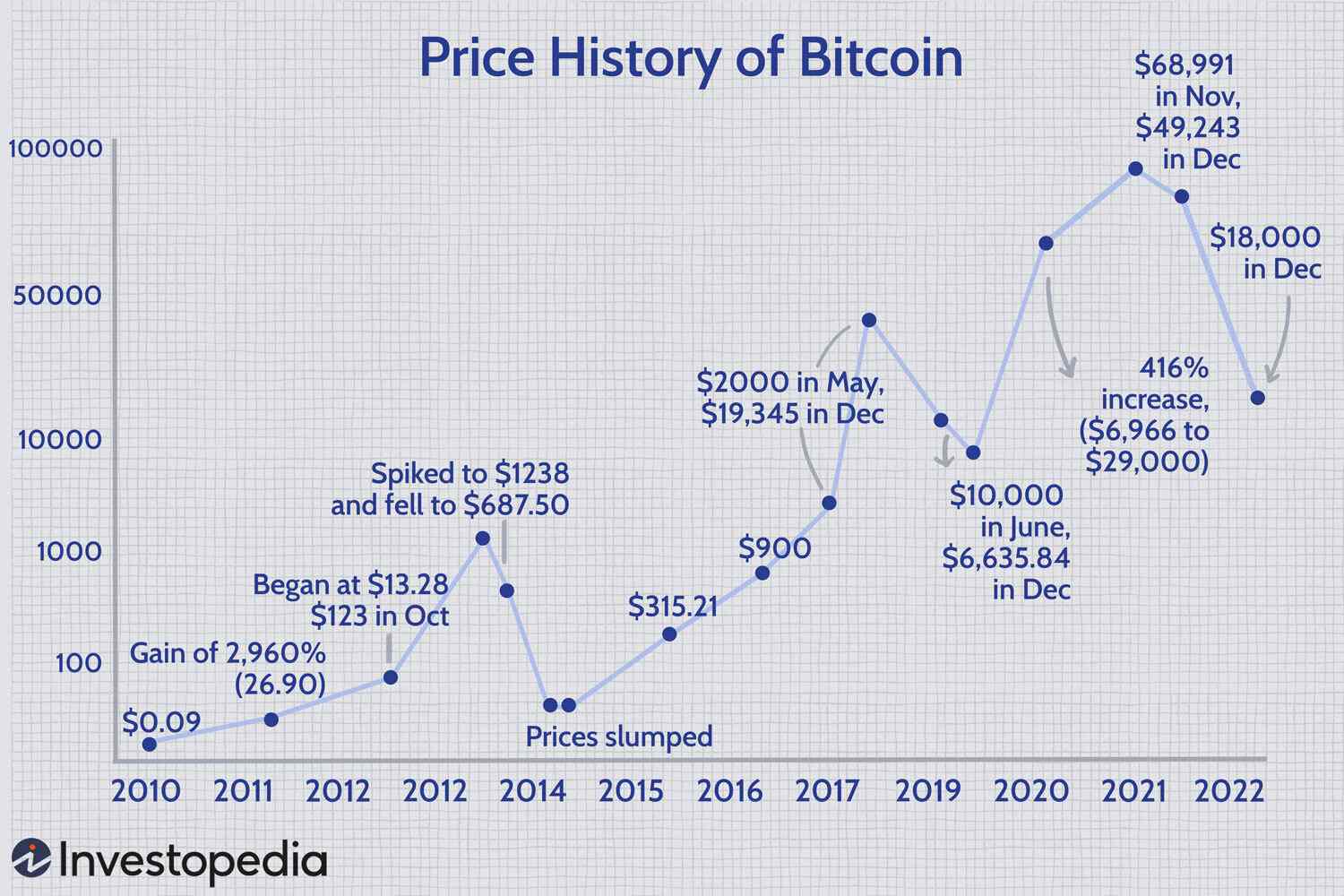 1 500 Bitcoin Growth Analyzing The Prediction And Its Implications
May 08, 2025
1 500 Bitcoin Growth Analyzing The Prediction And Its Implications
May 08, 2025 -
 Understanding Bitcoins Rebound Risks And Opportunities
May 08, 2025
Understanding Bitcoins Rebound Risks And Opportunities
May 08, 2025 -
 2024
May 08, 2025
2024
May 08, 2025 -
 The Bitcoin Rebound Signs Of A Lasting Recovery
May 08, 2025
The Bitcoin Rebound Signs Of A Lasting Recovery
May 08, 2025
