Betting On Natural Disasters: Examining The Los Angeles Wildfire Example

Table of Contents
The Economics of Wildfire Risk in Los Angeles
Wildfires in Los Angeles County represent a significant economic burden. The sheer cost of these devastating events extends far beyond immediate property damage, impacting businesses, healthcare systems, and the overall economic well-being of the region. Understanding the financial implications is crucial for effective mitigation strategies.
-
Statistics on average annual wildfire damage costs in Los Angeles County: While precise figures fluctuate yearly, Los Angeles County consistently faces hundreds of millions of dollars in damages from wildfires, encompassing property destruction, firefighting costs, and long-term recovery efforts. This financial strain significantly impacts local budgets and the broader Californian economy.
-
Examples of specific high-cost wildfire events in recent years: The Woolsey Fire (2018) and the Getty Fire (2019) are prime examples of costly wildfire events, resulting in billions of dollars in damage and widespread displacement. These incidents underscore the catastrophic financial implications of unchecked wildfire risk.
-
Mention the role of climate change in increasing wildfire risk and frequency: Climate change is exacerbating the problem. Rising temperatures, prolonged droughts, and shifting weather patterns contribute to increased wildfire frequency and intensity, leading to even greater economic losses in the future. This necessitates a proactive approach to risk management and mitigation.
Insurance and Reinsurance: A Key Player in Wildfire Risk Management
Insurance companies play a critical role in managing wildfire risk. They assess the likelihood of wildfires occurring in specific areas, considering factors such as proximity to wildlands, building materials, and the implementation of defensible space around properties. This assessment directly impacts insurance premiums.
-
Discussion of factors influencing insurance premiums (e.g., proximity to wildlands, building materials, defensible space): Homes located in high-risk areas near wildlands typically face significantly higher premiums than those situated further away. Building materials (e.g., fire-resistant roofing) and the presence of defensible space (cleared areas around homes) also influence premium calculations.
-
Explanation of reinsurance and its role in managing catastrophic losses: Reinsurance acts as a crucial safety net for primary insurers. When catastrophic events like major wildfires occur, reinsurers help primary insurers cover exceptionally large losses, preventing widespread insolvency within the insurance industry.
-
Mention the challenges faced by insurers in accurately predicting wildfire risk and setting appropriate premiums: Accurately predicting wildfire risk and setting fair premiums remains a challenge. The increasing frequency and intensity of wildfires driven by climate change makes accurate prediction more difficult, potentially leading to increasing premiums or even a withdrawal of insurance coverage in high-risk areas.
The Role of Financial Markets and Derivatives in Wildfire Risk
Financial markets offer tools to manage and, controversially, speculate on wildfire risk. Catastrophe bonds (CAT bonds) are a prime example, transferring risk from insurers to investors.
-
Discussion of catastrophe bonds (CAT bonds) and other risk transfer mechanisms: CAT bonds are essentially insurance-linked securities. Investors receive a return on their investment unless a specified catastrophic event, such as a large wildfire, occurs. In such cases, investors may lose part or all of their investment.
-
Mention the limitations and complexities of using financial markets to manage wildfire risk: Financial markets are not a panacea. The complexity of these instruments, the potential for market manipulation, and the inherent uncertainty associated with predicting natural disasters present significant limitations.
-
Ethical considerations and potential for market manipulation: The potential for speculation and market manipulation raises ethical concerns. The possibility of profiting from the misfortune of others necessitates careful regulation and oversight of these financial instruments.
Predictive Modeling and Data Analytics in Wildfire Risk Assessment
Advanced technologies and data analytics are revolutionizing wildfire risk assessment. By analyzing weather patterns, fuel conditions, and historical data, predictive models can forecast wildfire risk with increasing accuracy.
-
Mention the use of weather patterns, fuel conditions, and historical data in predictive modeling: Sophisticated models incorporate real-time weather data, information on vegetation density and dryness (fuel conditions), and historical wildfire patterns to estimate wildfire risk and potential spread.
-
Explain the role of satellite imagery and remote sensing in wildfire detection and monitoring: Satellite imagery provides crucial information for early detection and monitoring of wildfires. Real-time data on fire location and spread enables swift responses and improves resource allocation for firefighting efforts.
-
Discuss the limitations of predictive modeling and the uncertainties inherent in forecasting wildfires: Despite advancements, predictive modeling is not perfect. Unpredictable weather patterns, unexpected changes in fuel conditions, and the inherent complexity of wildfire behavior introduce significant uncertainties into forecasts.
Community Preparedness and Mitigation Strategies
Community preparedness and mitigation are crucial for reducing wildfire risk and the associated financial losses. A comprehensive approach involves a combination of individual actions, community-based programs, and governmental initiatives.
-
Examples of effective community-based wildfire mitigation programs: Community-led programs focused on defensible space creation, controlled burns (under strict supervision), and community education campaigns play a vital role in reducing wildfire risk.
-
Discussion of the role of government agencies and local authorities: Government agencies and local authorities are responsible for developing and enforcing building codes, managing land use, implementing fire prevention measures, and coordinating emergency response efforts.
-
Highlight the importance of individual preparedness and home hardening techniques: Individual preparedness is critical. Home hardening techniques, such as installing fire-resistant roofing and creating defensible space around homes, reduce the risk of property damage. Having an evacuation plan and emergency supplies are also essential.
Conclusion
Predicting and mitigating the financial impact of natural disasters like the Los Angeles wildfires is a complex challenge requiring a multi-faceted approach. While the idea of "betting on natural disasters" through financial markets raises ethical questions, understanding the economic mechanisms at play – from insurance markets to predictive modeling – is crucial. Effective strategies involve a combination of robust insurance mechanisms, sophisticated risk assessment tools, and proactive community preparedness. By acknowledging the intricate interplay between natural disasters and the financial world, we can work towards better preparedness and ultimately, reduce the devastating impact of future events. Continue learning about effective strategies for managing the risk of natural disasters like wildfires, focusing on responsible approaches to betting on natural disasters.

Featured Posts
-
 Anchor Brewing Company Shuts Down Impact On The Craft Beer Industry
Apr 29, 2025
Anchor Brewing Company Shuts Down Impact On The Craft Beer Industry
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Over The Counter Birth Control A New Era Of Reproductive Healthcare
Apr 29, 2025
Over The Counter Birth Control A New Era Of Reproductive Healthcare
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Hengrui Pharma Secures Approval For Hong Kong Share Sale
Apr 29, 2025
Hengrui Pharma Secures Approval For Hong Kong Share Sale
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Exclusive University Group Defies Trump Administration Policies
Apr 29, 2025
Exclusive University Group Defies Trump Administration Policies
Apr 29, 2025 -
 The Ethics Of Betting On The Los Angeles Wildfires A Growing Concern
Apr 29, 2025
The Ethics Of Betting On The Los Angeles Wildfires A Growing Concern
Apr 29, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Understanding High Stock Market Valuations A Bof A Analysis
Apr 29, 2025
Understanding High Stock Market Valuations A Bof A Analysis
Apr 29, 2025 -
 High Stock Valuations Why Bof A Believes Investors Shouldnt Worry
Apr 29, 2025
High Stock Valuations Why Bof A Believes Investors Shouldnt Worry
Apr 29, 2025 -
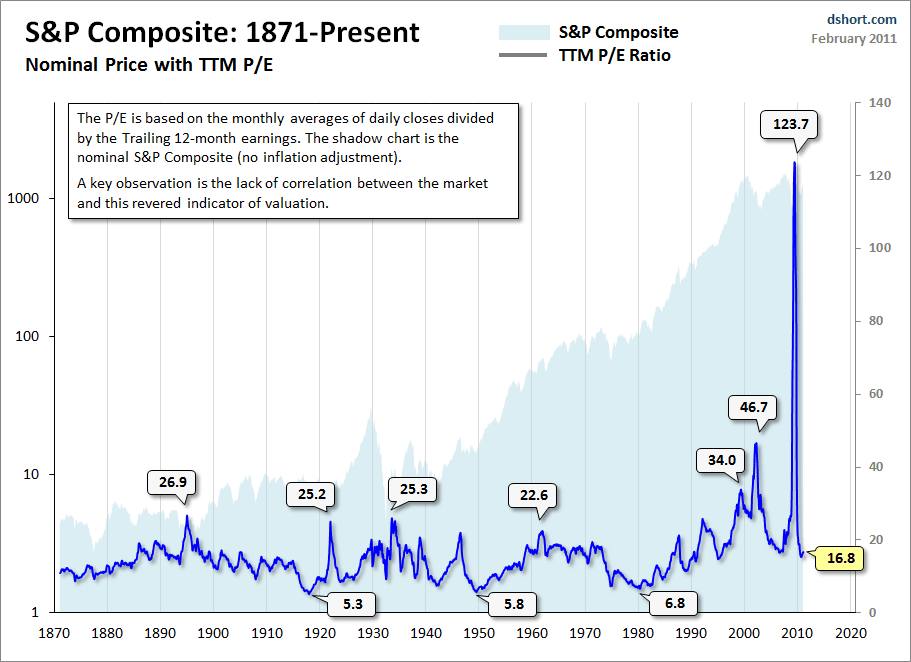 Stock Market Valuations Bof As Reassurance For Investors
Apr 29, 2025
Stock Market Valuations Bof As Reassurance For Investors
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Exploring The Countrys Fastest Growing Business Regions
Apr 29, 2025
Exploring The Countrys Fastest Growing Business Regions
Apr 29, 2025 -
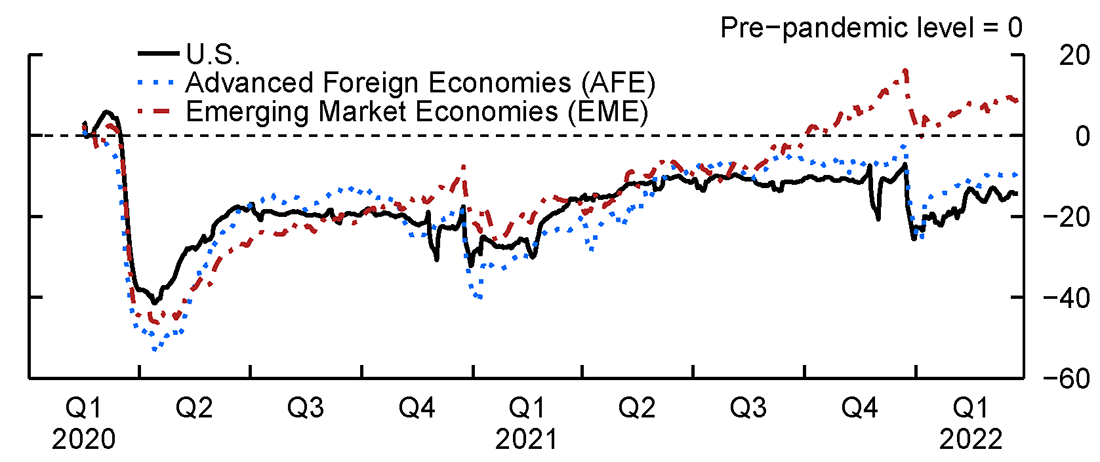 Ecb Report Post Pandemic Fiscal Policies Contribute To Inflation
Apr 29, 2025
Ecb Report Post Pandemic Fiscal Policies Contribute To Inflation
Apr 29, 2025
