Israel's Blockade Of Gaza: The Impact On Health, Security, And Food Security
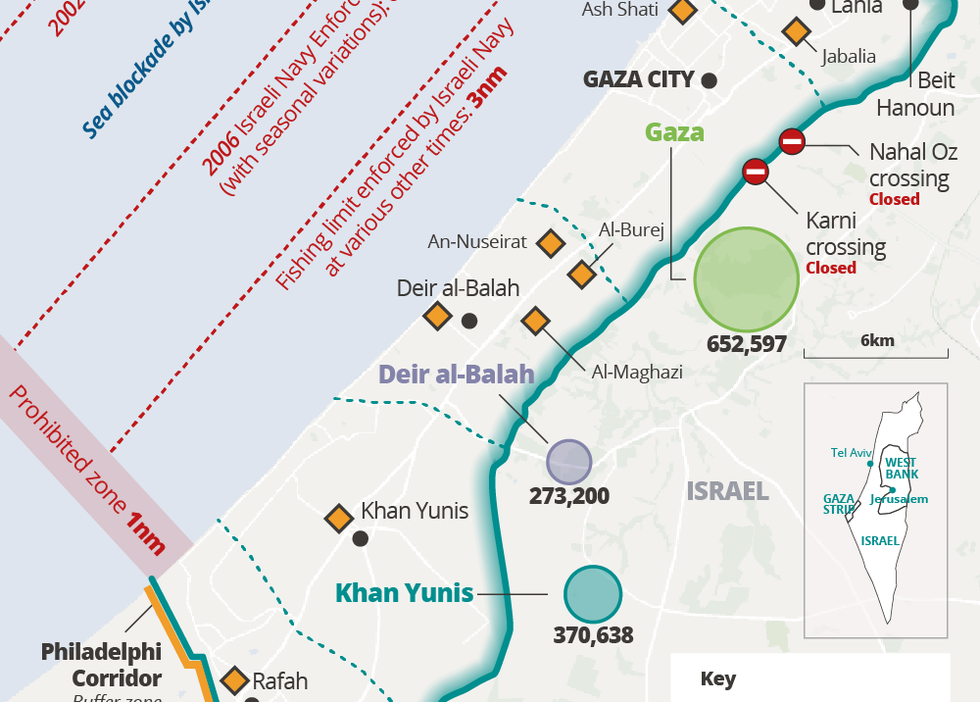
Table of Contents
The Impact on Health in Gaza
The Israeli blockade of Gaza severely restricts access to essential healthcare resources, resulting in a deteriorating public health situation. This includes limitations on movement, import restrictions, and the overall scarcity of resources vital for a functioning healthcare system.
Limited Access to Medical Care
The blockade severely restricts the import of essential medicines, medical equipment, and the movement of patients for specialized treatment. This leads to a range of critical health issues:
- Shortage of critical medications: Many life-saving drugs are in short supply, leaving patients with chronic illnesses vulnerable. The lack of essential medications directly impacts the ability of the medical community to provide adequate care and threatens the lives of countless individuals.
- Lack of advanced medical technology: Gaza's hospitals lack the sophisticated equipment needed for many complex procedures, forcing patients to seek treatment abroad – a process often hampered by the blockade. This lack of technology exacerbates existing health problems and limits the effectiveness of medical care.
- Difficulties in accessing specialists: The movement of medical professionals and patients is heavily restricted, hindering access to specialist care for conditions like oncology, cardiology, and neurology. This lack of access leads to delayed diagnoses, inappropriate treatment and ultimately, higher mortality rates.
- Increased infant and maternal mortality rates: The lack of access to proper prenatal care, essential medicines, and emergency obstetric services contributes to significantly higher rates of infant and maternal mortality compared to other regions. This highlights a fundamental failure in providing basic healthcare services under the existing blockade.
The consequences extend far beyond these immediate issues. The psychological toll on both healthcare providers and patients, constantly facing limitations and shortages, is substantial and deserves further consideration.
Deteriorating Sanitary Conditions
The blockade hinders the import of sanitation materials and the efficient management of waste, creating a breeding ground for disease. This leads to:
- Water shortages: Access to clean drinking water is often limited, increasing the risk of waterborne illnesses. The scarcity of water also affects hygiene practices within households and healthcare facilities.
- Inadequate sewage treatment: The overwhelmed sewage system is incapable of handling the waste, leading to contamination of water sources and increased risk of outbreaks. This poses a significant public health risk.
- Increased risk of infectious diseases: Unsanitary conditions contribute to the spread of infectious diseases like cholera, typhoid, and hepatitis A, placing immense strain on an already weakened healthcare system. Outbreaks are common due to the compromised infrastructure.
- Overcrowded hospitals: Hospitals lack the resources and space to accommodate the increasing number of patients suffering from preventable illnesses due to the poor sanitary conditions. This leads to further complications and reduced quality of care.
The cumulative impact on public health infrastructure is severe, necessitating urgent improvement in waste management and water infrastructure.
Psychological Trauma
The ongoing conflict and the restrictions imposed by the blockade contribute significantly to widespread psychological trauma and mental health issues:
- PTSD: The constant threat of violence and the psychological distress caused by the blockade contribute to a high prevalence of Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) among the population.
- Anxiety disorders and depression: The lack of resources, limited opportunities, and ongoing uncertainty contribute to widespread anxiety and depression.
- Impact on children and families: Children are particularly vulnerable to the psychological impact of the blockade, witnessing violence and experiencing disruption to their education and daily lives. This creates lasting trauma and challenges their development.
- Lack of mental health professionals: The shortage of mental health professionals and limited access to mental healthcare exacerbate the psychological burden on the population. This absence of specialized care leads to untreated mental health issues.
The long-term consequences of untreated trauma are substantial and represent a significant humanitarian concern resulting from the blockade.
The Impact on Security in Gaza
The Israeli blockade of Gaza has significant security implications, contributing to instability and increasing the risk of further conflict.
Increased Tensions and Violence
The blockade fuels resentment and frustration among the population, creating fertile ground for radicalization and violence:
- High unemployment rates: The severely restricted economy has resulted in widespread unemployment, particularly among young people, leading to social unrest and frustration. Economic hardship directly contributes to instability.
- Poverty: The blockade has pushed many families into extreme poverty, increasing their vulnerability to exploitation and radicalization. This desperation enhances the likelihood of engaging in violence.
- Limited opportunities: The lack of economic opportunities and restricted movement stifle hope and contribute to a sense of hopelessness. This limited potential fuels desperation and can lead to risky behavior.
- Potential for radicalization: The dire economic and social conditions create an environment conducive to the recruitment of young people by extremist groups. This increases the risk of further conflicts and violence.
The security implications extend beyond Gaza's borders, impacting regional stability and potentially escalating conflict.
Weakened Infrastructure
The blockade hinders the repair and maintenance of critical infrastructure, leaving the population vulnerable:
- Damage to power plants and water facilities: Repeated conflicts and the lack of access to necessary materials hinder the repair of vital infrastructure, resulting in frequent power outages and water shortages.
- Limited access to building materials: The restriction on imports makes rebuilding after attacks difficult and prolongs the recovery process. This lack of resources hinders reconstruction efforts.
- Inability to rebuild after attacks: The inability to repair damaged infrastructure creates ongoing vulnerabilities and reduces the resilience of the population to future conflicts. The damage is cumulative and impacts the safety and wellbeing of the population.
The cumulative impact of repeated conflicts and the lack of resources for reconstruction contributes to a perpetual cycle of vulnerability.
Limited Law Enforcement Capacity
The blockade affects the capacity of Gaza's law enforcement agencies, leading to increased crime and instability:
- Lack of training and equipment: The blockade restricts access to training and equipment, hindering the effectiveness of law enforcement agencies.
- Difficulty in maintaining order: The weakened capacity of law enforcement agencies contributes to increased crime rates and undermines the rule of law.
- Potential for increased criminal activity: Economic hardship and lack of opportunities can contribute to a rise in criminal activity.
The challenges faced by local authorities in maintaining security and order are compounded by the limitations imposed by the blockade.
The Impact on Food Security in Gaza
The Israeli blockade of Gaza has severely compromised food security, leading to widespread malnutrition and dependence on humanitarian aid.
Restricted Access to Food and Resources
The blockade limits the import of essential food items, agricultural inputs, and fishing equipment, impacting both food production and availability:
- Food shortages: The limited access to food has resulted in frequent shortages of essential commodities, leading to malnutrition and hunger.
- Malnutrition: Widespread malnutrition, particularly among children and pregnant women, is a direct consequence of the limited food availability.
- High food prices: The scarcity of food has driven prices up, making it difficult for many families to afford adequate nutrition.
- Reliance on international aid: A significant portion of the population relies on international humanitarian aid to meet their basic food needs.
The reliance on external aid highlights the critical vulnerability of the food system.
Unemployment and Poverty
The blockade has led to widespread unemployment and poverty, hindering people's ability to access adequate food:
- Lack of economic opportunities: The blockade severely restricts economic activities, leading to high unemployment rates.
- High unemployment rates among youth: Young people are disproportionately affected by unemployment, increasing their vulnerability to poverty and food insecurity.
- Limited income to purchase food: Low income levels make it difficult for families to purchase sufficient food to meet their nutritional needs.
The socio-economic consequences of the blockade directly contribute to food insecurity.
Environmental Degradation
Restrictions on access to resources impact sustainable farming practices and lead to environmental degradation:
- Depleted water resources: Overuse and contamination of water resources further hamper agricultural production.
- Soil degradation: Intensive farming practices, driven by food shortages, contribute to soil degradation and reduced agricultural yields.
- Loss of agricultural land: The ongoing conflict and limitations on access to land for farming reduces agricultural productivity.
- Impact on fishing: Restrictions on fishing activities limit access to an important source of protein and income.
The long-term sustainability of food production under the current conditions is severely compromised.
Conclusion
The Israeli blockade of Gaza has created a complex and devastating humanitarian crisis, significantly impacting the health, security, and food security of its residents. The long-term consequences of this blockade are dire, requiring urgent international attention and intervention. Addressing this complex issue requires a multifaceted approach, including lifting the blockade, improving access to essential goods and services, and fostering economic development and sustainable peace. We must act now to alleviate the suffering of the people of Gaza and find a lasting solution to end Israel's blockade of Gaza and its devastating effects. The continued suffering demands immediate action to lift the blockade and address the humanitarian crisis.

Featured Posts
-
 Tracking Injuries Rays Vs Yankees Series April 17 20
May 11, 2025
Tracking Injuries Rays Vs Yankees Series April 17 20
May 11, 2025 -
 Selena Gomezs Sassy Leather Dress Channel Your Inner Movie Star
May 11, 2025
Selena Gomezs Sassy Leather Dress Channel Your Inner Movie Star
May 11, 2025 -
 Experience Rotorua Immerse Yourself In Maori Culture And Geothermal Activity
May 11, 2025
Experience Rotorua Immerse Yourself In Maori Culture And Geothermal Activity
May 11, 2025 -
 Jessica Simpson Delights Fans With Performance After 15 Year Break
May 11, 2025
Jessica Simpson Delights Fans With Performance After 15 Year Break
May 11, 2025 -
 Unexpected Nsfw Moment Selena Gomez And Benny Blancos Tmi Share
May 11, 2025
Unexpected Nsfw Moment Selena Gomez And Benny Blancos Tmi Share
May 11, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Why Did Investors Sell Leveraged Semiconductor Etfs Before The Rally
May 13, 2025
Why Did Investors Sell Leveraged Semiconductor Etfs Before The Rally
May 13, 2025 -
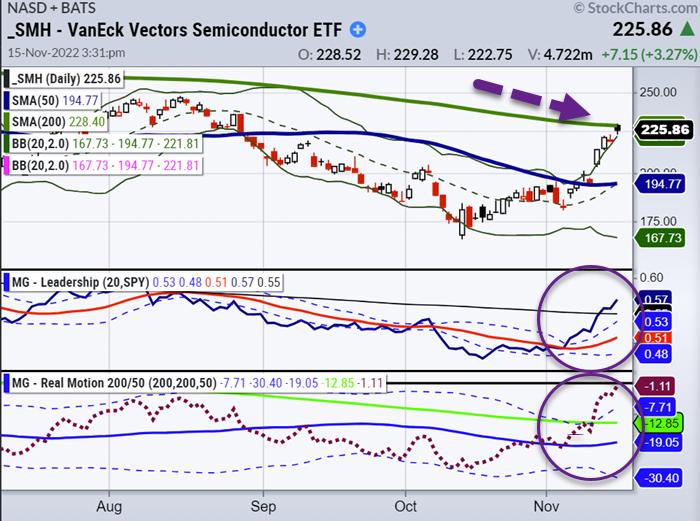 Semiconductor Etf Losses Investors Pre Surge Reactions Analyzed
May 13, 2025
Semiconductor Etf Losses Investors Pre Surge Reactions Analyzed
May 13, 2025 -
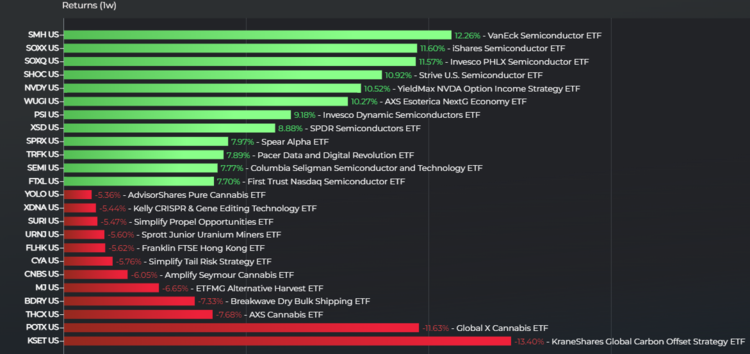 Leveraged Semiconductor Etfs A Pre Surge Sell Off Explained
May 13, 2025
Leveraged Semiconductor Etfs A Pre Surge Sell Off Explained
May 13, 2025 -
 Etf Investors Dumped Leveraged Semiconductor Funds Before Surge What Happened
May 13, 2025
Etf Investors Dumped Leveraged Semiconductor Funds Before Surge What Happened
May 13, 2025 -
 Analyzing The Walleye Credit Cut Realigning Commodities Teams With Core Group Priorities
May 13, 2025
Analyzing The Walleye Credit Cut Realigning Commodities Teams With Core Group Priorities
May 13, 2025
