Justice Department Ends School Desegregation Order: What Happens Next?
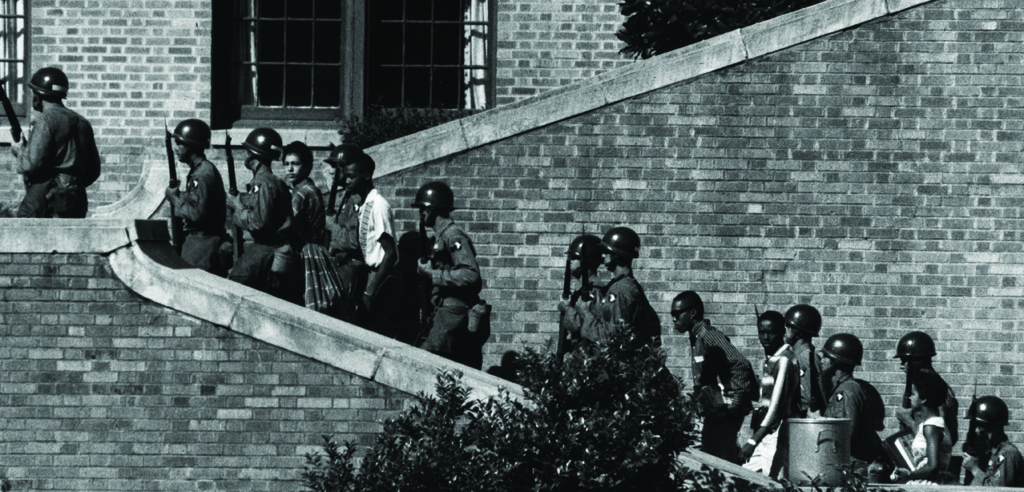

Table of Contents
The History of the School Desegregation Order
The fight for school desegregation is deeply rooted in American history, culminating in the landmark 1954 Brown v. Board of Education Supreme Court decision, which declared state laws establishing separate public schools for black and white students to be unconstitutional. This ruling, however, faced significant resistance, leading to decades of legal battles and ongoing struggles to achieve meaningful integration. The specific order in question, implemented [Insert Year and relevant details about the order, e.g., under the Civil Rights Act of 1964], aimed to address persistent segregation within specific school districts by mandating specific measures such as busing and redrawing school district boundaries.
- Key milestones in the desegregation process: Brown v. Board of Education (1954), the Civil Rights Act of 1964, numerous court cases challenging resistance to desegregation.
- Significant legal challenges faced: Resistance from states and local governments, legal challenges arguing against busing and other desegregation methods, ongoing battles over funding disparities.
- Successes and shortcomings of the order: While the order achieved some progress in integrating schools in certain areas, significant racial disparities persist in many districts, highlighting the limitations of the order's impact and the enduring legacy of segregation.
The Justice Department's Rationale for Ending the Order
The Justice Department's official statement cited [Insert specific reasons cited by the DOJ, e.g., the belief that the order has achieved its goals, the need for local control over education, and claims of the order's ineffectiveness or obsolescence]. Critics, however, argue that these justifications are insufficient, pointing to the continuing racial achievement gap and the persistence of de facto segregation in many schools.
- Specific reasons cited by the DOJ: [List the specific points from the DOJ statement].
- Claims of the order's ineffectiveness or obsolescence: [Summarize the arguments presented by the DOJ regarding the order's perceived lack of effectiveness].
- Potential political motivations behind the decision: [Discuss potential political motivations, acknowledging various perspectives and avoiding biased language].
Potential Consequences of Ending the Order
Ending the school desegregation order carries significant risks, most notably the potential for increased segregation in affected school districts. This could lead to a widening achievement gap, exacerbating existing inequalities in educational resources and opportunities.
- Increased racial disparities in school funding: With federal oversight diminished, disparities in funding between predominantly white and minority schools may increase.
- Potential decline in academic achievement for minority students: Segregation often correlates with lower academic achievement for minority students due to factors such as access to resources, teacher quality, and curriculum.
- Challenges in maintaining diverse learning environments: A lack of federal oversight may lead to a decline in diversity in many schools, limiting exposure to different perspectives and hindering social development.
The Role of Local Governments and School Boards
The responsibility for maintaining desegregated schools now rests largely with local governments and school boards. This necessitates a proactive approach that goes beyond simply complying with anti-discrimination laws. School districts must actively develop and implement strategies to promote diversity and inclusion.
- Legal obligations of school districts regarding equal access to education: School districts remain legally obligated to provide equal educational opportunities to all students, regardless of race.
- Strategies to promote diversity and inclusion within schools: This includes initiatives such as magnet schools, school choice programs, and targeted resource allocation to address historical inequities.
- Resources available to local governments to support desegregation efforts: State and local governments should dedicate resources to support desegregation efforts through funding, professional development, and community engagement programs.
Advocacy and Future Legal Challenges
The decision to end the school desegregation order is likely to face significant opposition from civil rights organizations and community activists. Legal challenges are anticipated, arguing that the DOJ's decision violates the constitutional rights of minority students.
- Potential legal arguments against the DOJ’s decision: Arguments may center on the continuing existence of de facto segregation and the violation of the Equal Protection Clause of the Fourteenth Amendment.
- The role of community activism in advocating for school desegregation: Grassroots movements and advocacy groups will play a crucial role in pushing for continued desegregation efforts at the local level.
- Long-term implications for federal oversight of school desegregation: The long-term impact of this decision on federal involvement in school desegregation remains uncertain, with the potential for future policy shifts.
Conclusion
The Justice Department's decision to end the school desegregation order represents a significant turning point, shifting responsibility for maintaining integrated schools to local authorities. The potential consequences, including increased segregation and educational inequities, are substantial. Continued vigilance, advocacy, and potential legal challenges are crucial to safeguarding the progress made toward achieving racial equality in education.
Call to Action: Staying informed about the ongoing developments regarding school desegregation and advocating for equitable education for all students are vital steps in ensuring a fair and just future. Understanding the implications of this decision is critical for supporting effective strategies to combat the potential resurgence of school segregation and continue the fight for school desegregation.

Featured Posts
-
 Xrp Price Prediction Should You Buy Ripple Under 3
May 02, 2025
Xrp Price Prediction Should You Buy Ripple Under 3
May 02, 2025 -
 Ponants 1 500 Flight Credit Incentive For Paul Gauguin Cruise Sales
May 02, 2025
Ponants 1 500 Flight Credit Incentive For Paul Gauguin Cruise Sales
May 02, 2025 -
 Improving Election Integrity Through A Robust Poll Data System
May 02, 2025
Improving Election Integrity Through A Robust Poll Data System
May 02, 2025 -
 Rio Tinto Defends Dual Listing Against Activist Investor Pressure
May 02, 2025
Rio Tinto Defends Dual Listing Against Activist Investor Pressure
May 02, 2025 -
 Wzyr Aezm Awr Army Chyf Ka Kshmyr Pr Skht Mwqf Jng Ka Amkan
May 02, 2025
Wzyr Aezm Awr Army Chyf Ka Kshmyr Pr Skht Mwqf Jng Ka Amkan
May 02, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Backlash Against Farage Intensifies Following Zelenskyy Remarks
May 03, 2025
Backlash Against Farage Intensifies Following Zelenskyy Remarks
May 03, 2025 -
 Kivinin Kabugunu Yemek Faydalari Riskleri Ve Hazirlama Yoentemleri
May 03, 2025
Kivinin Kabugunu Yemek Faydalari Riskleri Ve Hazirlama Yoentemleri
May 03, 2025 -
 1 T
May 03, 2025
1 T
May 03, 2025 -
 Kivinin Kabugunun Faydalari Ve Zararlari Yenmeli Mi Yoksa Yenmemeli Mi
May 03, 2025
Kivinin Kabugunun Faydalari Ve Zararlari Yenmeli Mi Yoksa Yenmemeli Mi
May 03, 2025 -
 T
May 03, 2025
T
May 03, 2025
