Thailand's Negative Inflation: Predicting Future Monetary Policy

Table of Contents
Understanding Thailand's Negative Inflation
Causes of Deflation in Thailand
Several factors contributed to Thailand's negative inflation. Understanding these root causes is crucial for predicting future trends and formulating effective policy responses.
-
Lower Oil Prices: The global decline in oil prices significantly impacted inflation. Reduced energy costs translate directly into lower prices for transportation, manufacturing, and various consumer goods. For example, in [Insert Year], oil prices decreased by [Insert Percentage]%, directly impacting inflation rates.
-
Decreased Consumer Demand: A slowdown in consumer spending, possibly due to factors such as economic uncertainty or shifts in consumer behavior, contributed to reduced demand-pull inflation. The Consumer Confidence Index (CCI) in [Insert Period] showed a [Insert Percentage]% decrease, reflecting weakening consumer sentiment.
-
Strong Baht: The appreciation of the Thai baht against other major currencies made imports cheaper, further dampening inflationary pressures. A strong baht can make imported goods more affordable, leading to lower prices for consumers. In [Insert Period], the baht appreciated by [Insert Percentage]% against the US dollar.
-
Supply Chain Improvements: Increased efficiency and optimization within Thailand's supply chains resulted in lower production costs and subsequently, lower prices for consumers. Technological advancements and streamlined logistics played a significant role.
-
Global Economic Conditions: The global economic slowdown, particularly in major trading partners, also played a part in reducing demand for Thai exports and contributing to deflationary pressures.
Economic Implications of Negative Inflation
While some might view falling prices as positive, prolonged deflation poses significant risks to the Thai economy.
-
Decreased Consumer Spending: Consumers may postpone purchases anticipating further price drops, leading to a vicious cycle of reduced demand and further deflation. This can hinder economic growth.
-
Increased Debt Burden: Deflation increases the real value of debt, making it harder for businesses and consumers to service their loans. This can lead to increased bankruptcies and financial distress.
-
Potential for Economic Recession: Persistent deflation can trigger a deflationary spiral, leading to a decline in economic output and potentially a recession.
-
Increased Purchasing Power (Potential Benefit): On the positive side, lower prices increase the purchasing power of consumers, allowing them to buy more goods and services with the same amount of money. However, this benefit is often outweighed by the risks associated with prolonged deflation.
Analyzing the Bank of Thailand's Response
Current Monetary Policy Stance
The Bank of Thailand (BOT) has been closely monitoring the situation and has taken steps to address the negative inflation.
-
Interest Rates: The BOT's current policy interest rate is [Insert Current Interest Rate]. Recent statements suggest [Insert Summary of BOT's Stance on Interest Rates - e.g., a potential for further rate cuts or maintaining the status quo].
-
Monetary Policy Tools: Beyond interest rates, the BOT might utilize other tools such as reserve requirements or open market operations to influence liquidity and credit conditions in the market.
-
Inflation Targets: The BOT's inflation target is typically within a range of [Insert BOT's Inflation Target Range]. The current negative inflation is significantly below this target.
Potential Future Monetary Policy Adjustments
To combat deflation, the BOT might consider several policy adjustments:
-
Interest Rate Cuts: Lowering interest rates can stimulate borrowing and investment, boosting economic activity and potentially increasing inflation.
-
Quantitative Easing (QE): The BOT could inject liquidity into the financial system by purchasing government bonds or other assets, aiming to lower long-term interest rates and encourage lending.
-
Other Unconventional Measures: Depending on the severity and persistence of deflation, the BOT might explore other unconventional monetary policies, such as negative interest rates or direct lending to businesses. However, these measures carry their own set of risks and challenges.
-
Potential Scenarios:
- Scenario 1: Sustained low inflation prompts further interest rate cuts.
- Scenario 2: A slight rebound in economic activity allows the BOT to maintain current interest rates.
- Scenario 3: A sharp economic downturn necessitates more aggressive monetary easing measures.
Predicting Future Inflation Trends in Thailand
Economic Forecasts and Projections
Several reputable economic institutions offer forecasts for Thailand's inflation. [Insert Name of Institution] projects inflation to be [Insert Projected Inflation Rate] in [Insert Time Period]. This projection is based on [mention key assumptions].
Factors influencing future inflation include:
-
Global Economic Growth: Stronger global growth could increase demand for Thai exports, boosting inflation.
-
Commodity Prices: Fluctuations in global commodity prices, particularly oil, will have a direct impact on inflation.
-
Domestic Economic Activity: The strength of domestic demand and investment will play a crucial role in determining future inflation levels.
Risks and Uncertainties
Predicting future inflation is inherently challenging due to several uncertainties:
-
Geopolitical Instability: Global geopolitical events can significantly disrupt economic activity and influence inflation.
-
Unexpected Economic Shocks: Unforeseen events, such as natural disasters or major supply chain disruptions, can impact inflation unpredictably.
-
Policy Effectiveness: The effectiveness of the BOT's policy responses depends on various factors and cannot be guaranteed.
Conclusion
Thailand's negative inflation presents a complex economic challenge. The causes are multifaceted, ranging from lower oil prices and decreased consumer demand to a strong baht and global economic conditions. The Bank of Thailand's response will be crucial in steering the economy away from a potentially damaging deflationary spiral. While various policy adjustments are possible, predicting future inflation trends remains inherently uncertain due to unforeseen economic shocks and global events. Understanding the implications of Thailand's negative inflation is crucial for both businesses and consumers.
Call to Action: Stay informed about Thailand's economic developments and the evolving monetary policy landscape to better understand the impact of Thailand's negative inflation on your investments and financial planning. Follow reputable economic news sources and the Bank of Thailand's official statements for updates on Thailand's negative inflation and future monetary policy decisions. Understanding these developments will help you navigate this dynamic economic environment effectively.

Featured Posts
-
 Plany Ovechkina Vozvraschenie V Dinamo
May 07, 2025
Plany Ovechkina Vozvraschenie V Dinamo
May 07, 2025 -
 The Last Of Us Season 2 Episode 4 A Week Long Filming Process
May 07, 2025
The Last Of Us Season 2 Episode 4 A Week Long Filming Process
May 07, 2025 -
 De Bussers Leadership Go Ahead Eagles Cup Final Comeback Story
May 07, 2025
De Bussers Leadership Go Ahead Eagles Cup Final Comeback Story
May 07, 2025 -
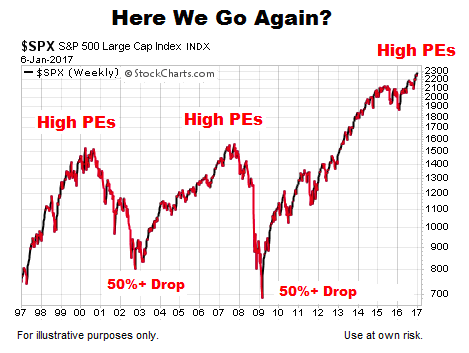 Understanding Elevated Stock Market Valuations A Bof A Viewpoint
May 07, 2025
Understanding Elevated Stock Market Valuations A Bof A Viewpoint
May 07, 2025 -
 Xrp Navigating The Etf Landscape Sec Challenges And The Path Ahead
May 07, 2025
Xrp Navigating The Etf Landscape Sec Challenges And The Path Ahead
May 07, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Istorinis Pasirodymas Nba Lyderiai Lygina Klubo Rekorda
May 07, 2025
Istorinis Pasirodymas Nba Lyderiai Lygina Klubo Rekorda
May 07, 2025 -
 Nba Lyderiai Pakartojo Klubo Rekorda Zaisdami Istoriniu Ritmu
May 07, 2025
Nba Lyderiai Pakartojo Klubo Rekorda Zaisdami Istoriniu Ritmu
May 07, 2025 -
 New Ticket Donation System From The Cleveland Cavaliers
May 07, 2025
New Ticket Donation System From The Cleveland Cavaliers
May 07, 2025 -
 Cavs New Platform Simplifies Ticket Donations For Fans
May 07, 2025
Cavs New Platform Simplifies Ticket Donations For Fans
May 07, 2025 -
 Cavs Launch New Ticket Donation Platform
May 07, 2025
Cavs Launch New Ticket Donation Platform
May 07, 2025
