The Justice Department's Decision: The Future Of School Desegregation
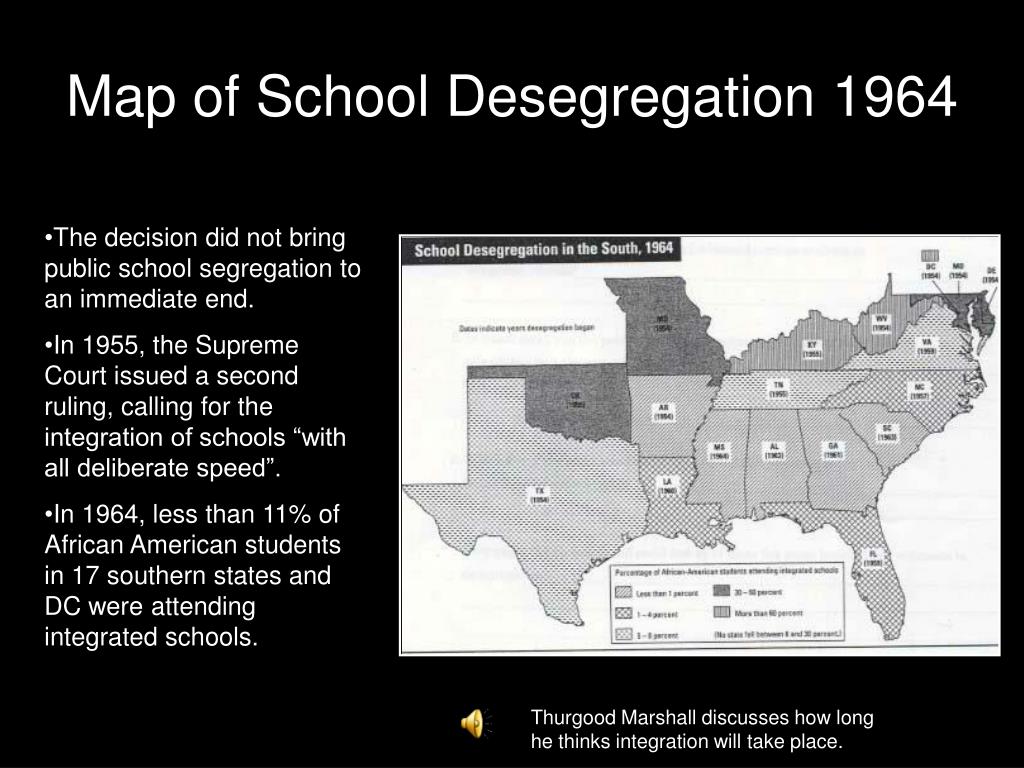
Table of Contents
The Historical Context: From Brown v. Board to the Present Day
The landmark Supreme Court case Brown v. Board of Education (1954) declared state laws establishing separate public schools for black and white students to be unconstitutional. However, the promise of Brown was slow to materialize, facing decades of resistance, legal challenges, and deeply entrenched societal biases. The Civil Rights Act of 1964 and the subsequent Voting Rights Act of 1965 were crucial legislative steps, but even these landmark achievements did not fully dismantle the system of school segregation.
Despite progress in some areas, significant racial disparities persist. The achievement gap, a stark difference in academic outcomes between students of color and their white counterparts, remains a critical issue. This gap is often linked to factors such as unequal resource allocation, discriminatory school practices, and the legacy of segregation.
- Key Supreme Court cases relevant to school desegregation: Brown v. Board of Education, Milliken v. Bradley, Parents Involved in Community Schools v. Seattle School District No. 1.
- Significant legislative acts impacting desegregation efforts: Civil Rights Act of 1964, Elementary and Secondary Education Act of 1965.
- Examples of successful and unsuccessful desegregation initiatives: Court-ordered busing programs (often met with resistance), the implementation of magnet schools (with varying degrees of success in achieving integration).
Analyzing the Justice Department's Recent Decision(s)
(Note: This section requires updating with a specific, recent Justice Department decision related to school desegregation. For the purpose of this example, we will hypothesize a decision.)
Let's assume the Justice Department recently issued a decision limiting the scope of court-ordered desegregation remedies in certain school districts. The rationale behind this hypothetical decision might be argued on the basis that previous orders are outdated, unduly burdensome on school districts, or no longer effective in addressing present-day segregation.
The legal arguments would likely center on interpretations of existing Supreme Court precedents, focusing on the balance between achieving racial integration and respecting local control of schools. The ruling’s implications would be significant, potentially impacting ongoing desegregation efforts across the nation.
- Summary of the Justice Department's key arguments (hypothetical): The department might argue that current segregation is largely a result of residential patterns rather than intentional discrimination, limiting the federal government's role in mandated desegregation.
- Potential impact on existing desegregation orders: The decision could lead to the relaxation or termination of some court orders, potentially increasing segregation in affected districts.
- Reactions from different stakeholders (hypothetical): Civil rights groups might strongly oppose the decision, while some school districts might welcome the reduction in mandated desegregation efforts.
Impact and Implications on School Districts Across the Nation
The potential effects of this hypothetical Justice Department decision would vary greatly depending on the specific context of individual school districts. Districts with existing court orders would be most directly impacted. These districts often face substantial challenges in implementing desegregation plans, including budgetary constraints, community resistance, and the complexities of redrawing attendance zones.
The decision could lead to increased segregation in some districts, particularly those with already significant racial imbalances. Conversely, some districts might see little change, as their segregation is less a result of court-ordered segregation and more a result of other factors.
- Examples of how the decision might affect specific types of school districts: Urban districts with a long history of segregation might face the most significant challenges. Suburban districts with less overt historical segregation might see fewer immediate effects.
- Potential budgetary implications for school districts: The lifting of court-ordered desegregation plans could lead to budget reallocations, potentially impacting resources for programs aimed at addressing racial disparities.
- Challenges in implementing desegregation plans: Even with court orders, achieving meaningful desegregation requires significant resources, community support, and sustained commitment.
Future Strategies for Achieving Meaningful School Integration
Despite the potential setbacks from this hypothetical Justice Department decision, there remain numerous strategies for promoting school integration. These include expanding school choice programs in a way that actively promotes integration, creating more high-quality magnet schools, and investing in early childhood education to address inequalities early on.
Addressing systemic inequalities in education is crucial. This requires a multi-pronged approach that considers factors such as funding disparities, teacher training, and curriculum development. Community engagement is essential, fostering collaboration between schools, families, and community leaders.
- Innovative strategies for promoting school integration: Implementing controlled choice plans, creating inter-district transfer programs, and fostering partnerships between schools in different neighborhoods.
- The role of community engagement in achieving desegregation goals: Building trust between schools and communities, creating platforms for dialogue, and mobilizing local support for integration initiatives.
- Potential legislative or policy changes that could support desegregation efforts: Revisiting funding formulas to address resource disparities, reforming school zoning policies to promote integration, and strengthening anti-discrimination laws in education.
Conclusion: The Justice Department's Decision and the Path Forward for School Desegregation
The hypothetical Justice Department's decision highlights the ongoing struggle for school desegregation in the US. While the ruling might present significant challenges, it also underscores the need for innovative and sustained efforts to achieve meaningful school integration. The future of school desegregation rests on a multi-faceted approach that includes addressing systemic inequalities, fostering community engagement, and enacting policies that prioritize racial equity in education. We must continue to advocate for the Justice Department's impact on school desegregation to be one that fosters equality and opportunity for all students. The future of school desegregation after the recent ruling depends on our collective commitment to dismantling the legacy of segregation and building a truly equitable education system. We urge you to stay informed, participate in advocacy efforts, and support initiatives promoting racial equality in education. The fight for truly integrated schools is far from over, and the need for action is paramount.

Featured Posts
-
 Understanding The Volatility Of Riot Platforms Stock Riot
May 02, 2025
Understanding The Volatility Of Riot Platforms Stock Riot
May 02, 2025 -
 Reform Uk Investigates Serious Bullying Allegations Against Rupert Lowe
May 02, 2025
Reform Uk Investigates Serious Bullying Allegations Against Rupert Lowe
May 02, 2025 -
 Orta Afrika Cumhuriyeti Nin Bae Ile Yeni Ticaret Anlasmasi Gelecek Icin Firsatlar
May 02, 2025
Orta Afrika Cumhuriyeti Nin Bae Ile Yeni Ticaret Anlasmasi Gelecek Icin Firsatlar
May 02, 2025 -
 South Koreas Housing Culture A New Exhibition Explores Unique Designs
May 02, 2025
South Koreas Housing Culture A New Exhibition Explores Unique Designs
May 02, 2025 -
 Exclusive Which A Lister Wants Access To Melissa Gorgas Beach House
May 02, 2025
Exclusive Which A Lister Wants Access To Melissa Gorgas Beach House
May 02, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Eneco Inaugure Le Plus Grand Parc De Batteries De Belgique A Au Roeulx
May 03, 2025
Eneco Inaugure Le Plus Grand Parc De Batteries De Belgique A Au Roeulx
May 03, 2025 -
 Huong Vi Dac Biet Cua Loai Qua Xua Gia 60 000d Kg
May 03, 2025
Huong Vi Dac Biet Cua Loai Qua Xua Gia 60 000d Kg
May 03, 2025 -
 Qua Xua It Ai Biet Den Nay Thanh Dac San 60 000d Kg
May 03, 2025
Qua Xua It Ai Biet Den Nay Thanh Dac San 60 000d Kg
May 03, 2025 -
 Largest Heat Pump In The Netherlands Operational In Utrecht
May 03, 2025
Largest Heat Pump In The Netherlands Operational In Utrecht
May 03, 2025 -
 Utrechts Wastewater Plant Home To The Netherlands Biggest Heat Pump
May 03, 2025
Utrechts Wastewater Plant Home To The Netherlands Biggest Heat Pump
May 03, 2025
