Proposed Changes To Sentencing For Minors In France
Table of Contents
France is currently considering significant changes to its juvenile justice system. These proposed alterations to sentencing for minors, impacting "peines mineures France," aim to address concerns about recidivism, rehabilitation, and the overall effectiveness of the current system. This article will delve into the key proposed changes, examining their potential impact on young offenders and French society. The debate surrounding these reforms highlights a crucial shift in how France approaches juvenile delinquency, moving away from solely punitive measures towards a more rehabilitative model.
Increased Focus on Rehabilitation over Punishment (Réhabilitation plutôt que punition)
The proposed reforms emphasize rehabilitation over punishment, marking a significant departure from previous approaches to peines mineures France. This shift prioritizes reintegrating young offenders into society rather than solely focusing on retribution.
Emphasis on Educational and Social Reintegration Programs (Programmes de réinsertion scolaire et sociale)
A key component of the proposed changes involves significantly expanding educational and social reintegration programs for young offenders. This includes:
- Expansion of educational opportunities within detention facilities: Providing access to quality education, including tutoring and specialized programs, to ensure that detained minors don't fall further behind in their studies. This aims to break the cycle of poverty and lack of education often linked to juvenile delinquency.
- Increased access to vocational training and job placement services: Equipping young offenders with marketable skills to improve their employment prospects upon release. This includes apprenticeships, vocational training courses, and partnerships with businesses willing to offer employment opportunities.
- Strengthened partnerships with social workers and community organizations: Fostering collaboration between the justice system and community-based organizations to provide ongoing support and guidance to young offenders after their release. This crucial step promotes successful reintegration and reduces the likelihood of recidivism.
- Greater emphasis on restorative justice practices: Implementing programs that focus on repairing the harm caused by the offense and promoting reconciliation between the offender and the victim. This approach aims to address the underlying causes of the crime and foster a sense of responsibility in the young offender. Restorative justice offers a powerful alternative to traditional punitive measures within the context of peines mineures France.
Reduced Reliance on Incarceration (Réduction de la détention)
The proposed reforms also aim to reduce reliance on incarceration for minor offenses, exploring alternative sentencing options to address peines mineures France. This includes:
- Exploring alternative sentencing options like community service and probation: Offering non-custodial sentences that allow young offenders to remain in the community while fulfilling their sentences and receiving support. This approach is more cost-effective and often more effective in promoting rehabilitation than incarceration.
- Stricter criteria for detention, focusing on high-risk offenders: Reserving incarceration for only those young offenders deemed to pose a significant risk to public safety. This ensures that detention is used judiciously and only as a last resort.
- Increased investment in community-based support services: Providing readily accessible resources such as mentoring programs, counseling, and family support to prevent young people from entering the justice system in the first place. Early intervention is key to addressing the root causes of juvenile delinquency.
- Implementation of stricter monitoring mechanisms for probationers: Ensuring that young offenders on probation are properly supervised and receive the necessary support to successfully complete their sentences. This requires robust monitoring systems and effective communication between probation officers and other support services.
Addressing the Needs of Vulnerable Minors (Répondre aux besoins des mineurs vulnérables)
Recognizing that many young offenders come from disadvantaged backgrounds, the proposed reforms place a strong emphasis on addressing their unique needs.
Support for Children from Disadvantaged Backgrounds (Soutien aux enfants issus de milieux défavorisés)
The reforms acknowledge the link between poverty and delinquency, proposing:
- Specialized programs addressing the unique needs of children from impoverished or marginalized communities: Tailored programs that provide additional support to children facing significant social and economic challenges. This could include educational support, access to healthcare, and assistance with housing and food security.
- Increased investment in early intervention programs to prevent delinquency: Implementing preventative measures, such as after-school programs and early childhood education initiatives, to address risk factors before they escalate into criminal behavior.
- Improved access to mental health services for young offenders: Recognizing the role of mental health issues in juvenile delinquency and providing access to appropriate mental health care, including therapy and counseling.
- Consideration of mitigating factors related to poverty and social deprivation in sentencing: Taking into account the circumstances of the young offender's life when determining an appropriate sentence.
Protection of Minors with Disabilities (Protection des mineurs handicapés)
The reforms also aim to ensure that the needs of minors with disabilities are adequately addressed within the juvenile justice system:
- Specialized courts and facilities tailored to the needs of children with disabilities: Creating accessible and inclusive environments that cater to the specific needs of children with disabilities.
- Training for judicial personnel on working with children with disabilities: Equipping judges, lawyers, and other justice professionals with the knowledge and skills to effectively work with children with disabilities.
- Ensuring appropriate accommodations and support throughout the judicial process: Providing necessary support services, such as interpreters and assistive technology, to ensure that children with disabilities have equal access to justice.
- Collaboration with disability organizations to ensure effective implementation: Partnering with relevant disability organizations to develop and implement effective programs and policies for young offenders with disabilities.
Improving Transparency and Accountability (Améliorer la transparence et la responsabilisation)
Increased transparency and accountability are vital to ensuring the effectiveness of the proposed reforms to peines mineures France.
Greater Public Scrutiny of Juvenile Justice System (Contrôle public accru du système de justice pour mineurs)
The reforms aim to enhance public oversight of the juvenile justice system by:
- Increased public reporting on juvenile justice statistics and outcomes: Providing the public with access to data on sentencing practices, recidivism rates, and the effectiveness of different programs. This transparency promotes accountability and allows for informed public discourse.
- Independent oversight bodies to monitor the effectiveness of reforms: Establishing independent bodies to review the juvenile justice system and ensure that the reforms are implemented effectively and achieve their intended goals.
- Mechanisms for addressing complaints and grievances related to juvenile justice: Providing clear channels for individuals to voice their concerns and complaints about the juvenile justice system.
- Enhanced training for judicial personnel on ethical considerations: Ensuring that all personnel involved in the juvenile justice system are properly trained on ethical conduct and best practices.
Conclusion:
The proposed changes to "peines mineures France" represent a significant shift toward a more rehabilitative and child-centered approach to juvenile justice. By prioritizing education, social reintegration, and addressing the unique needs of vulnerable minors, these reforms aim to reduce recidivism and create a more just and equitable system. Staying informed about these developments and engaging in public discourse about the effectiveness of "peines mineures France" is crucial to ensure a fair and effective juvenile justice system for all. Further research and public discussion are needed to ensure the successful implementation of these vital changes to the sentencing of minors in France.
Featured Posts
-
 Escape To The Country Lifestyle Changes And Considerations
May 25, 2025
Escape To The Country Lifestyle Changes And Considerations
May 25, 2025 -
 M62 Westbound Resurfacing Manchester To Warrington Road Closure
May 25, 2025
M62 Westbound Resurfacing Manchester To Warrington Road Closure
May 25, 2025 -
 Global Healthcare Transformation Key Findings From The Philips Future Health Index 2025 On Ai
May 25, 2025
Global Healthcare Transformation Key Findings From The Philips Future Health Index 2025 On Ai
May 25, 2025 -
 Getting Tickets For Bbc Radio 1 Big Weekend A Step By Step Guide
May 25, 2025
Getting Tickets For Bbc Radio 1 Big Weekend A Step By Step Guide
May 25, 2025 -
 Heineken Revenue Surpasses Forecasts Outlook Unchanged Despite Tariff Challenges
May 25, 2025
Heineken Revenue Surpasses Forecasts Outlook Unchanged Despite Tariff Challenges
May 25, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Apple Stock Slumps 900 Million Tariff Impact
May 25, 2025
Apple Stock Slumps 900 Million Tariff Impact
May 25, 2025 -
 Is Apple Stock A Buy After Strong Q2 Earnings
May 25, 2025
Is Apple Stock A Buy After Strong Q2 Earnings
May 25, 2025 -
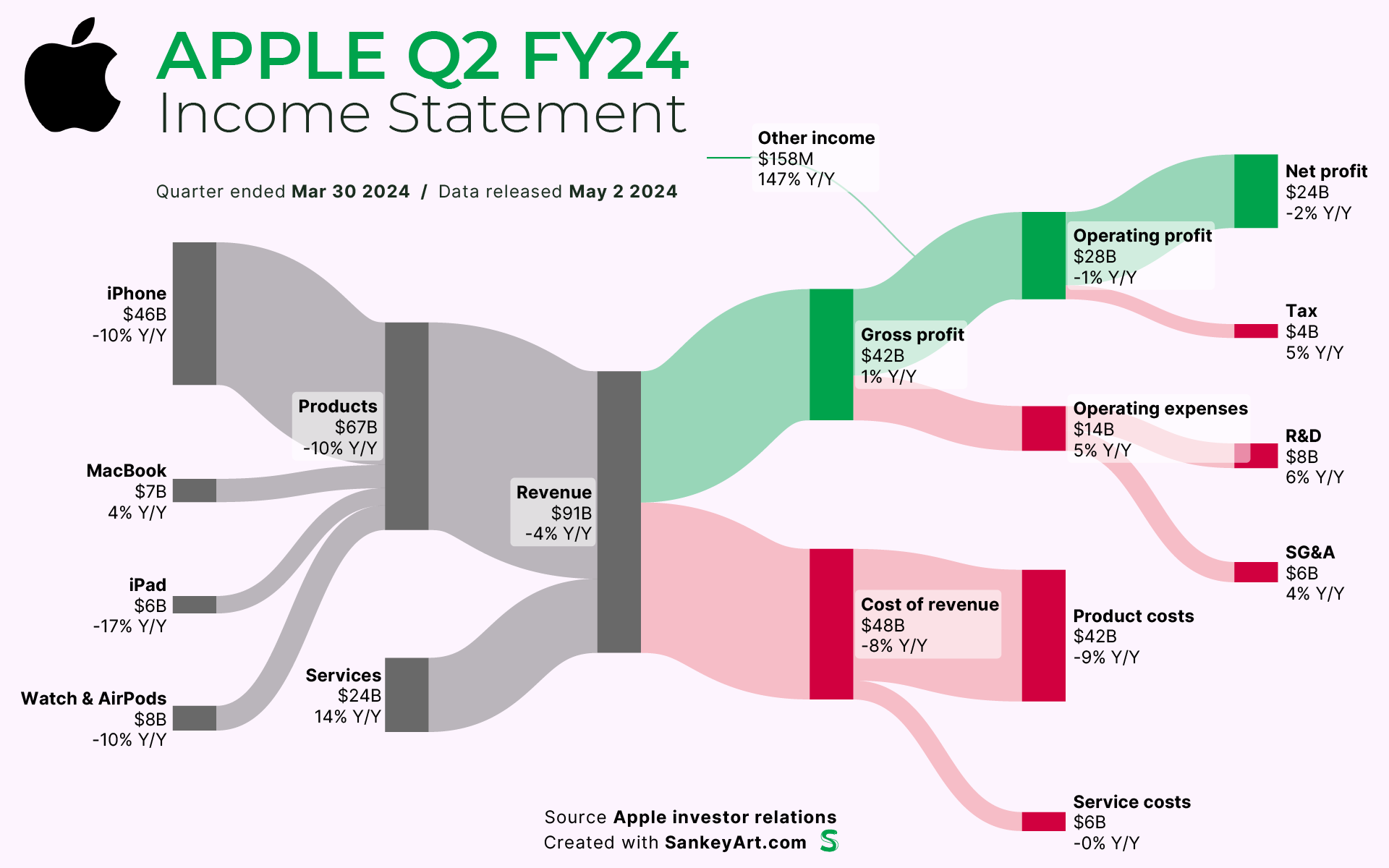 Apple Stock Analysis Of Q2 Results And Future Predictions
May 25, 2025
Apple Stock Analysis Of Q2 Results And Future Predictions
May 25, 2025 -
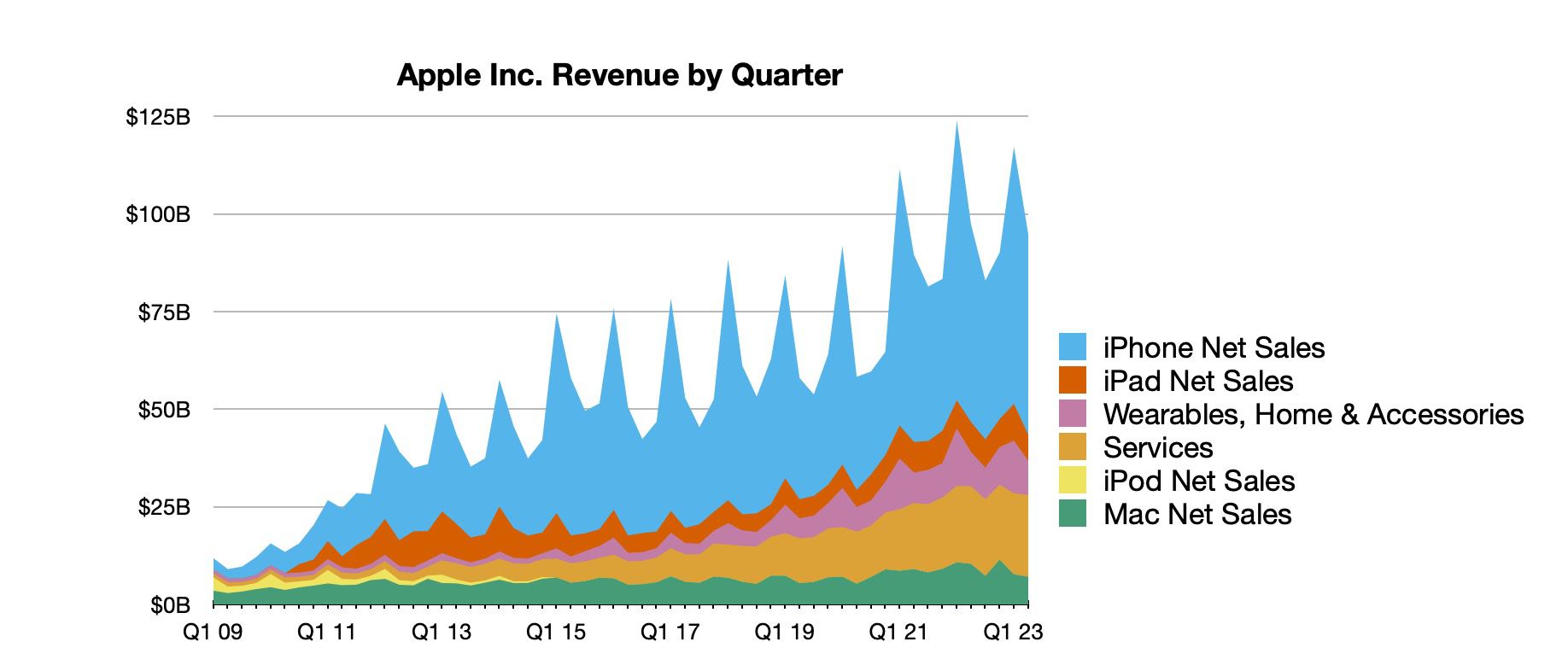 Apple Stock Q2 Earnings I Phone Sales And Investor Outlook
May 25, 2025
Apple Stock Q2 Earnings I Phone Sales And Investor Outlook
May 25, 2025 -
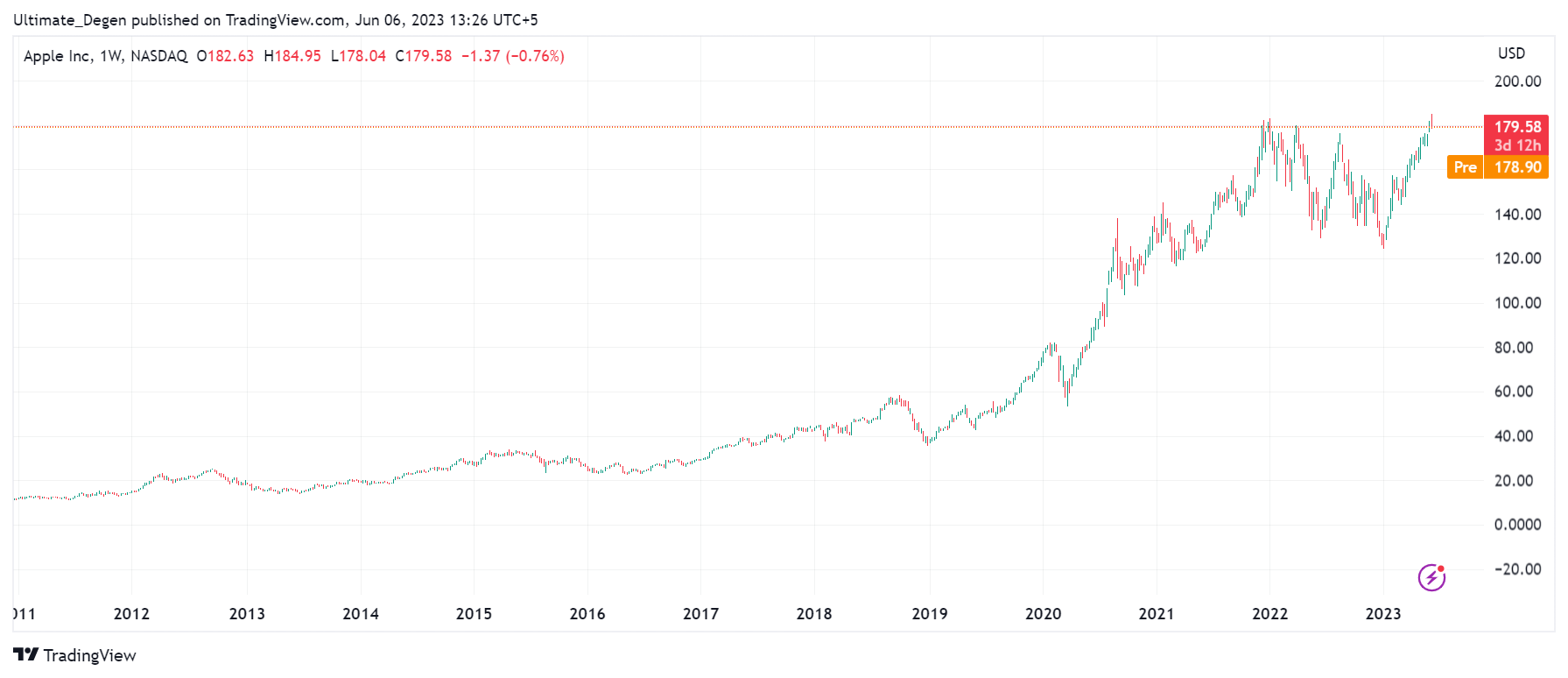 Apple Stock Performance Exceeding Q2 Expectations
May 25, 2025
Apple Stock Performance Exceeding Q2 Expectations
May 25, 2025
